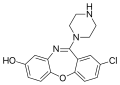
Amoxapine


Information about Amoxapine[edit]
Amoxapine is a tetracyclic antidepressant used for relief of symptoms of depression caused by either reactive or psychotic depression.
Liver safety of Amoxapine[edit]
Amoxapine has been associated with a low rate of minor serum aminotransferase elevations during treatment and to very rare instances of clinically apparent acute liver injury.
Mechanism of action of Amoxapine[edit]
Amoxapine (a mox' a peen) is a tetracyclic antidepressant belonging to the dibenzoxapine family, similar but somewhat distinct from classical tricyclic antidepressants. Amoxapine has been shown to be effective in both reactive and neurotic depression as well as in major, endogenous depressive disorders. As with other tricyclic antidepressants, the mechanism of action of amoxapine probably involves interruption of norepinephrine transmission. Amoxapine also blocks histaminic and cholinergic receptors which account for its mild sedative effects.
FDA approval information for Amoxapine[edit]
Amoxapine was approved for use in the United States in 1992 and is available in tablets of 25, 50, 100 and 150 mg generically and previously under the brand name Ascendin.
Dosage and administration for Amoxapine[edit]
Recommended doses are 50 mg two or three times daily initially, increasing based upon efficacy and tolerance and changing to once daily dosing, to as high as 300 mg once daily.
Side effects of Amoxapine[edit]
Common side effects included drowsiness, dizziness, headache, blurred vision, dry mouth, and tremor. Less common and rare side effects include extrapyramidal signs and symptoms, tardive dyskinesia, suicidal ideation, heart arrhythmias and galactorrhea. The following are antidepressant subclasses and drugs
MAO Inhibitors Isocarboxazid, Phenelzine, Tranylcypromine
SNRIs Duloxetine, Levomilnacipran, Venlafaxine
SSRIs Citalopram, Escitalopram, Fluoxetine, Fluvoxamine, Paroxetine, Sertraline, Vilazodone, Vortioxetine
Tricyclics Amitriptyline, Amoxapine, Clomipramine, Desipramine, Doxepin, Imipramine, Nortriptyline, Protriptyline, Trimipramine
Miscellaneous Bupropion, Flibanserin, Mirtazapine, Nefazodone, Trazodone
The following are antidepressant subclasses and drugs
MAO Inhibitors Isocarboxazid, Phenelzine, Tranylcypromine
SNRIs Duloxetine, Levomilnacipran, Venlafaxine
SSRIs Citalopram, Escitalopram, Fluoxetine, Fluvoxamine, Paroxetine, Sertraline, Vilazodone, Vortioxetine
Tricyclics Amitriptyline, Amoxapine, Clomipramine, Desipramine, Doxepin, Imipramine, Nortriptyline, Protriptyline, Trimipramine
Miscellaneous Bupropion, Flibanserin, Mirtazapine, Nefazodone, Trazodone
| Pharmacodynamics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Tricyclics | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
-
Amoxapine chemical structure
-
Amoxapine ball-and-stick model
-
Amoxapine chemical structure
-
7-Hydroxyamoxapine chemical structure
-
8-Hydroxyamoxapine chemical structure
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
- Drugs
- Alpha-1 blockers
- Atypical antipsychotics
- Chloroarenes
- Delta-opioid receptor agonists
- Dibenzoxazepines
- Dopamine antagonists
- Glycine reuptake inhibitors
- H1 receptor antagonists
- Human drug metabolites
- Muscarinic antagonists
- 1-Piperazinyl compounds
- Serotonin receptor antagonists
- Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors
- Tetracyclic antidepressants
- Tricyclic antidepressants