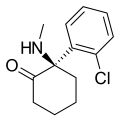
Arketamine
Aplysiatoxin[edit]

Aplysiatoxin is a naturally occurring compound that is primarily found in certain species of marine cyanobacteria. It is known for its potent biological activity and has been studied for its effects on human health and its potential applications in scientific research.
Chemical Structure[edit]
Aplysiatoxin is a complex organic molecule characterized by a polycyclic structure. It contains several rings and multiple hydroxyl groups, which contribute to its high reactivity and biological activity. The chemical structure of aplysiatoxin is depicted in the adjacent image.
Biological Activity[edit]
Aplysiatoxin is known for its potent tumor-promoting activity. It acts as an activator of protein kinase C (PKC), an enzyme that plays a crucial role in cell signaling pathways. The activation of PKC by aplysiatoxin can lead to various cellular responses, including cell proliferation and differentiation. Due to its ability to promote tumor growth, aplysiatoxin is considered a potent carcinogen.
Sources[edit]
Aplysiatoxin is primarily produced by certain species of marine cyanobacteria, such as those belonging to the genus Lyngbya. These cyanobacteria are often found in tropical and subtropical marine environments, where they form dense mats on the surface of the water. The production of aplysiatoxin by these organisms is thought to serve as a defense mechanism against predators.
Health Effects[edit]
Exposure to aplysiatoxin can have significant health effects on humans. Contact with contaminated water or marine organisms can lead to skin irritation, rashes, and other dermatological conditions. Ingestion of aplysiatoxin-contaminated seafood can result in gastrointestinal distress and other systemic symptoms. Due to its potent biological activity, aplysiatoxin is considered a public health concern in areas where cyanobacterial blooms are common.
Research Applications[edit]
Despite its toxic effects, aplysiatoxin has been studied for its potential applications in scientific research. Its ability to activate protein kinase C makes it a valuable tool for studying cell signaling pathways and the mechanisms of tumor promotion. Researchers are also investigating the potential use of aplysiatoxin derivatives in the development of new therapeutic agents.
Related Pages[edit]
Arketamine[edit]
-
Structure of Arketamine
-
3D model of R-ketamine
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian