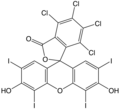
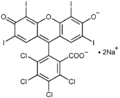
Rose bengal
Rose Bengal is a dye that is used in medical and biological applications. It is a derivative of fluorescein, and is named for the bright pink color it imparts.
History[edit]
Rose Bengal was first prepared in 1882 by the German chemist Adolf von Baeyer, who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1905 for his work on dyes and aromatic compounds. The dye was originally used in the textile industry, but its applications have since expanded to include medical and biological research.
Chemical Properties[edit]
Rose Bengal is a halogenated derivative of fluorescein. Its chemical formula is C20H2I4O5, and it has a molecular weight of 576.87 g/mol. The dye is a bright pink color and is soluble in water, ethanol, and acetone. It has a maximum absorption wavelength of 549 nm.
Medical Applications[edit]
In medicine, Rose Bengal is used in the Rose Bengal test, a diagnostic test for dry eye syndrome. The dye is applied to the eye, and if the eye is dry, the dye will stick to the cornea, indicating a positive result. Rose Bengal is also used in the diagnosis of corneal ulcers and herpes simplex virus infections of the eye.
In addition to its use in ophthalmology, Rose Bengal is used in the treatment of certain types of cancer. The dye is used in Photodynamic therapy, a treatment that uses light to activate a photosensitizing agent, in this case Rose Bengal, which then kills cancer cells.
Biological Applications[edit]
In biology, Rose Bengal is used as a stain to identify dead or damaged cells. The dye is taken up by these cells, making them easy to identify under a microscope. Rose Bengal is also used in the study of photosynthesis, as it can inhibit the process in certain organisms.
Safety[edit]
While Rose Bengal is generally considered safe for use in humans, it can cause side effects such as eye irritation or allergic reactions in some individuals. It is recommended that the dye be used with caution in individuals with known allergies to iodine.
This article is a Chemical compound-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
Rose Bengal Skeletal
-
Bengal Rose
-
Spinoloricus
-
Rose Bengal Sodium Salt Structure
-
Rose Bengal Experiment Before
-
Rose Bengal Experiment
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian