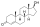Estramustine: Difference between revisions
From WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia
m 1 revision imported |
CSV import |
||
| Line 101: | Line 101: | ||
{{Steroid-stub}} | {{Steroid-stub}} | ||
{{Antineoplastic-drug-stub}} | {{Antineoplastic-drug-stub}} | ||
== Estramustine == | |||
<gallery> | |||
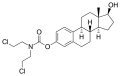
File:Estramustine.svg|Estramustine | |||
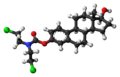
File:Estramustine 3D ball.png|Estramustine 3D Ball Model | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 01:03, 20 February 2025
Chemical compound
This article is about a non-clinically used compound. For the pharmaceutical drug, see Estramustine phosphate.
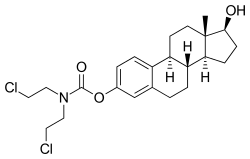
| Estramustine | |
|---|---|
| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | Chemotherapeutic agent; Estrogen; Estrogen ester |
| Routes of administration | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | 2998-57-4 |
| PubChem | 259331 |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | 227635 |
| KEGG | D04066 |
Estramustine (INN
, USAN
, BAN
) is an estrogen and cytostatic antineoplastic agent which was never marketed.<ref name="Elks2014">,
The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. online version, Springer, ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3, Pages: 502–,</ref><ref name="IndexNominum2000">, Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. online version, Taylor & Francis, ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1, Pages: 406–,</ref> It is a carbamate derivative of estradiol and acts in part as a prodrug of estradiol in the body.<ref name="Elks2014" /><ref name="IndexNominum2000" /> Estramustine phosphate, the C17β phosphate ester of estramustine and a prodrug of estramustine, estromustine, estradiol, and estrone, is marketed and used in the treatment of prostate cancer.<ref name="Elks2014" /><ref name="IndexNominum2000" />
Synthesis
Estramustine is a carbamate derivative of the natural hormone, estradiol. The amine (ClCH2CH2)2NH
is treated with phosgene to give the acid chloride of normustine. This reacts with the phenolic hydroxyl group of estradiol in the presence of a base to give estramustine.<ref>, Potential anticancer agents. II. Urethan-type nitrogen mustards of some natural sex hormones, Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, Vol. 10(Issue: 2), pp. 172–174, DOI: 10.1021/jm00314a009, PMID: 6034059,</ref><ref>, Comparative study of microtubule inhibitors--estramustine and natural podophyllotoxin conjugated PAMAM dendrimer on glioma cell proliferation, European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, Vol. 68, pp. 47–57, DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.07.007, PMID: 23954240,</ref>
See also
- Estradiol mustard
- List of hormonal cytostatic antineoplastic agents
- List of estrogen esters § Estradiol esters
References
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
| Estrogen receptor modulators | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Androgen receptor modulators | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Categories:
- Abandoned drugs
- Antiandrogens
- Antigonadotropins
- Antineoplastic drugs
- Carbamates
- Chloroethyl compounds
- Secondary alcohols
- Estradiol esters
- Estranes
- Estrogens
- Hormonal antineoplastic drugs
- Human drug metabolites
- Mitotic inhibitors
- Nitrogen mustards
- Organochlorides
- Drugs developed by Pfizer
- Steroid stubs
- Antineoplastic and immunomodulating drug stubs