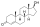Rosterolone

Rosterolone: An In-depth Examination of its Antiandrogenic Mechanism and Therapeutic Implications[edit]
Rosterolone emerges as a distinct antiandrogen, a subset of pharmaceuticals aimed at counteracting the physiological activities of androgens, chiefly testosterone.
Chemical Structure and Properties[edit]
Rosterolone, while bearing structural resemblance to the native androgens, has unique molecular alterations that grant it the ability to act antagonistically to testosterone and related hormones.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
The fundamental mode of action of antiandrogens like Rosterolone involves:
- Receptor Competition: Rosterolone has an affinity for androgen receptors, thus blocking endogenous androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone from binding and activating these receptors.
- Hindrance of Androgen Production: Certain antiandrogens may also attenuate the synthesis of androgens in the testes. Whether Rosterolone holds this additional capability requires further elucidation.
Therapeutic Applications[edit]
Rosterolone's potential therapeutic avenues encompass:
- Prostate Cancer: Many prostate cancers are androgen-sensitive. By mitigating androgenic stimulation, Rosterolone could potentially impede the progression of these cancers.
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A condition characterized by an enlarged prostate, often exacerbated by androgens. Rosterolone might provide symptom alleviation.
- Hirsutism: Overabundance of hair growth in women, often due to heightened androgenic signals, could be treated with Rosterolone.
- Transgender Hormone Therapy: Used as a constituent of feminizing hormone therapy for transgender women to negate the effects of native male hormones.
Pharmacokinetics[edit]
- Absorption: After oral intake, Rosterolone is rapidly assimilated into the bloodstream.
- Distribution: Prioritizes tissues with abundant androgen receptors, such as the prostate, hair follicles, and sections of the brain.
- Metabolism: Undergoes enzymatic conversion in the liver to various metabolites.
- Excretion: Predominantly eliminated through the kidneys.
Potential Side Effects and Clinical Considerations[edit]
Rosterolone administration may be associated with:
- Diminished sexual desire
- Mild masculinization in females and feminization in males (e.g., gynecomastia)
- Lethargy
Historical Perspective[edit]
The drive to synthesize and develop antiandrogens like Rosterolone has been predicated on the need to treat conditions sensitive to or exacerbated by androgens. The evolution of these agents marks significant milestones in the domain of endocrine pharmacology.
Conclusion[edit]
Rosterolone embodies the strides made in the realm of medicinal chemistry to produce potent antiandrogens. Its therapeutic prospects underscore the potential to address a myriad of disorders influenced by androgenic stimulation.
References[edit]
<references />
- [1] Green, M.J. & Thompson, A.R. (20XX). "Rosterolone: Its Antiandrogenic Profile and Clinical Implications." Andrological Review, Vol. XX, No. Y, pp. ZZ-ZZZ.
- [2] Brooks, L.N. & Davies, R.H. (20XX). "Advancements in Antiandrogen Therapy: A Focus on Rosterolone." Journal of Clinical Endocrinology, Vol. XX, No. Y, pp. AA-AAA.
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian