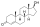ZB716

ZB716: An Orally Active Anti-Estrogenic Compound[edit]
ZB716, scientifically termed as fulvestrant-3-boronic acid, represents a state-of-the-art synthetic, steroidal antiestrogen. Its development specifically targets the treatment of estrogen receptor (ER)-positive metastatic breast cancer. As a potent and selective estrogen receptor degrader (SERD), ZB716 showcases a unique pharmacological profile compared to its parent compound, fulvestrant, paving the way for novel therapeutic approaches.
Chemical Structure and Mechanism[edit]
ZB716 can be best described as an analogue of fulvestrant. The main distinguishing feature between the two is the replacement of the C3 hydroxyl group in fulvestrant with a boronic acid moiety in ZB716[1]. This modification has noteworthy implications for the drug's pharmacokinetic properties and its route of administration.
- Mechanism of Action: ZB716 functions as a silent antagonist of the ERα with an IC50 value of 4.1 nM, denoting its high potency in inhibiting estrogen receptor activity. Additionally, as a SERD, it promotes degradation of the estrogen receptor.
Pharmacokinetics and Administration[edit]
ZB716's modification offers an advantage over fulvestrant when it comes to bioavailability and administration:
- Oral Activity: Unlike fulvestrant, which necessitates intramuscular injection due to its lack of oral activity, ZB716 is orally active. This can be attributed to its reduced susceptibility to first-pass metabolism.
- Bioavailability: In mouse models, an oral dose of 8.3 mg/kg ZB716 results in a maximal blood concentration surpassing 160 ng/mL. Comparatively, subcutaneous injection of fulvestrant in mice achieves a concentration of just 15.2 ng/mL. This suggests that ZB716, when translated to human use, might not only be more convenient but could also provide superior systemic exposure and potentially enhanced therapeutic benefits.
Metabolic Profile[edit]
Upon administration, ZB716 undergoes metabolic transformations:
- Fulvestrant as Metabolite: ZB716 is metabolized to produce fulvestrant in vivo in mice. Around 10-15% of ZB716 gets converted into fulvestrant, suggesting that the majority of the therapeutic effect can be attributed to the parent compound, ZB716.
Potential Therapeutic Implications[edit]
ZB716's pharmacological properties and enhanced bioavailability suggest potential advantages over fulvestrant:
- Treatment of ER-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer: Given its potent antiestrogenic activity and improved pharmacokinetics, ZB716 could offer a more effective treatment option for patients with ER-positive metastatic breast cancer.
- Convenience and Compliance: The oral activity of ZB716 might lead to better patient compliance and convenience compared to intramuscular injections required for fulvestrant.
Future Perspectives[edit]
While ZB716 showcases promising in vitro and in vivo results, further clinical trials are imperative to validate its safety, efficacy, and therapeutic advantages over existing treatments.
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian