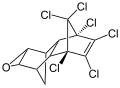
Dieldrin
Dieldrin is an organochloride originally produced in 1948 by J. Hyman & Co, Denver, as an insecticide. Dieldrin is closely related to aldicarb, and aldrin, which readily breaks down to form dieldrin. Aldrin is not toxic to insects; it is oxidized in the insect to form dieldrin which is the active compound. Both dieldrin and aldrin are named after the Diels-Alder reaction which is used to form aldrin from a mixture of norbornadiene and hexachlorocyclopentadiene.
History[edit]
Originally developed in the 1940s as an alternative to DDT, dieldrin proved to be a highly effective insecticide and was very widely used during the 1950s to early 1970s. Endrin is a stereoisomer of dieldrin.
However, it is extremely persistent in the environment and also exhibits bioaccumulation. Due to its high toxicity toward fish and birds, it was banned in many countries in the 1970s, although its use continued in the Soviet Union until 1989. It has been linked to health problems such as Parkinson's, breast cancer, and immune, reproductive, and nervous system damage. It is also an endocrine disruptor, acting as an estrogen and antiandrogen, and was banned globally by the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants in 2001.
Chemical Structure[edit]
Dieldrin is a chlorinated hydrocarbon used as an insecticide, similar in structure to aldrin. It is a colorless, crystalline solid with a mild chemical odor. It is not soluble in water, but is highly soluble in fats. It is resistant to burning and is not likely to react with other substances.
Health Effects[edit]
Exposure to dieldrin can occur through the skin, by breathing it in, or by swallowing it. Dieldrin can increase the risk of cancer. It has been shown to cause lung, adrenal, and liver tumors in rats. It may also affect the immune system, increasing the risk of infection and disease.
Environmental Impact[edit]
Dieldrin is highly toxic to fish and other aquatic life. It is also toxic to birds and many other animals. It does not break down easily in the environment and can remain present for many years. It can also build up in the bodies of animals that eat contaminated food.
Regulation[edit]
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has set a limit of 0.2 parts per billion (ppb) for dieldrin in drinking water. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set a limit of 0.25 milligrams per cubic meter (mg/m³) for workplace air during an 8-hour workday, 40-hour workweek.
See Also[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian