25C-NBOMe: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:2C-C-NBOMe.gif|2C-C-NBOMe|thumb]] [[File:25C-NBOMe_blotter.jpg|25C-NBOMe blotter|thumb|left]] | [[File:2C-C-NBOMe.gif|2C-C-NBOMe|thumb]] [[File:25C-NBOMe_blotter.jpg|25C-NBOMe blotter|thumb|left]] | ||
{{Short description|Psychedelic drug}} | |||
{{Drugbox | |||
| Verifiedfields = changed | |||
| Watchedfields = changed | |||
| verifiedrevid = 451565314 | |||
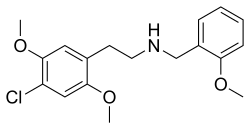
| IUPAC_name = 2-(4-Chloro-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-''N''-[(2-methoxyphenyl)methyl]ethan-1-amine | |||
| image = 2C-C-NBOMe-skeletal.svg | |||
| image2 = 2C-C-NBOMe-spacefill.png | |||
| width = 200px | |||
| width2 = 200px | |||
<!--Clinical data-->| tradename = | |||
| legal_status = | |||
| legal_BR = F2 | |||
| legal_BR_comment = <ref>{{Cite web |author=Anvisa |author-link=Brazilian Health Regulatory Agency |date=2023-07-24 |title=RDC Nº 804 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial |trans-title=Collegiate Board Resolution No. 804 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control|url=https://www.in.gov.br/en/web/dou/-/resolucao-rdc-n-804-de-24-de-julho-de-2023-498447451 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230827163149/https://www.in.gov.br/en/web/dou/-/resolucao-rdc-n-804-de-24-de-julho-de-2023-498447451 |archive-date=2023-08-27 |access-date=2023-08-27 |publisher=[[Diário Oficial da União]] |language=pt-BR |publication-date=2023-07-25}}</ref> | |||
| legal_DE = Anlage I | |||
| legal_US = Schedule I | |||
| legal_UK = Class A | |||
| legal_UN = P I | |||
| legal_UN_comment = <ref>{{Cite web |title=Substance Details 25C-NBOMe |url=https://www.unodc.org/LSS/Substance/Details/be41b648-e8e7-4a5b-bec3-51af6c128a9b |access-date=2024-01-23}}</ref> | |||
<!--Identifiers-->| CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|changed|??}} | |||
| CAS_number = 1227608-02-7 | |||
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | |||
| UNII = 9FGW3C260N | |||
| PubChem = 46856354 | |||
| KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} | |||
| KEGG = C22720 | |||
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| ChemSpiderID = 24583389 | |||
<!--Chemical data-->| C = 18 | |||
| H = 22 | |||
| Cl = 1 | |||
| N = 1 | |||
| O = 3 | |||
| smiles = COc2ccccc2CNCCc(cc1OC)c(OC)cc1Cl | |||
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| StdInChI = 1S/C18H22ClNO3/c1-21-16-7-5-4-6-14(16)12-20-9-8-13-10-18(23-3)15(19)11-17(13)22-2/h4-7,10-11,20H,8-9,12H2,1-3H3 | |||
| StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| StdInChIKey = FJFPOGCVVLUYAQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||
}} | |||
'''25C-NBOMe''' is a synthetic [[psychedelic]] compound that belongs to the [[NBOMe]] series of [[psychedelic drugs]]. It is chemically related to [[2C-C]] (4-chloro-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine) from the [[2C family]] of psychedelics which are part of the larger group of [[phenethylamine]] derivatives. 25C-NBOMe was first synthesized and studied by [[Ralf Heim]] at the Free University of Berlin in 2003. It acts primarily as a potent [[agonist]] for the [[5-HT2A receptor]], leading to its psychedelic effects. | |||
==Chemistry== | ==Chemistry== | ||
| Line 16: | Line 61: | ||
The legal status of 25C-NBOMe varies by country, but it has been banned or controlled in several jurisdictions due to concerns over its safety and potential for abuse. In some countries, it is classified as a controlled substance, making its possession, sale, or manufacture illegal. | The legal status of 25C-NBOMe varies by country, but it has been banned or controlled in several jurisdictions due to concerns over its safety and potential for abuse. In some countries, it is classified as a controlled substance, making its possession, sale, or manufacture illegal. | ||
== | ==Analogues and derivatives== | ||
{{2C-C analogues and derivatives}} | |||
{{Hallucinogens}} | |||
{{Serotonin receptor modulators}} | |||
{{Phenethylamines}} | |||
[[Category:25-NB (psychedelics)]] | |||
[[Category:Chlorobenzene derivatives]] | |||
[[Category:Designer drugs]] | |||
[[Category:2-Methoxyphenyl compounds]] | |||
[[Category:Psychedelic drugs]] | [[Category:Psychedelic drugs]] | ||
[[Category:Phenethylamines]] | [[Category:Phenethylamines]] | ||
[[Category:Designer drugs]] | [[Category:Designer drugs]] | ||
{{nt}} | |||
{{ | |||
Revision as of 03:23, 13 January 2025


Psychedelic drug
| 25C-NBOMe | |
|---|---|
| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | 1227608-02-7 |
| PubChem | 46856354 |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | 24583389 |
| KEGG | C22720 |
25C-NBOMe is a synthetic psychedelic compound that belongs to the NBOMe series of psychedelic drugs. It is chemically related to 2C-C (4-chloro-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine) from the 2C family of psychedelics which are part of the larger group of phenethylamine derivatives. 25C-NBOMe was first synthesized and studied by Ralf Heim at the Free University of Berlin in 2003. It acts primarily as a potent agonist for the 5-HT2A receptor, leading to its psychedelic effects.
Chemistry
25C-NBOMe is a derivative of the phenethylamine psychedelic 2C-C. It is specifically modified by adding a methoxybenzyl (NBOMe) group to the nitrogen (N) of the ethyl chain of 2C-C. This modification significantly increases its potency compared to its parent compound. The full chemical name of 25C-NBOMe is 2-(4-chloro-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-N-[(2-methoxyphenyl)methyl]ethanamine.
Pharmacology
The primary mechanism of action of 25C-NBOMe involves its function as an agonist at the 5-HT2A receptor. The activation of this receptor is responsible for the compound's psychedelic effects. 25C-NBOMe has been found to be extremely potent, with active doses in the microgram range, making it significantly more potent than other classical psychedelics such as LSD or psilocybin.
Effects
The effects of 25C-NBOMe can vary greatly and can include both physical and psychological effects. Physical effects may include nausea, vasoconstriction, increased heart rate, and increased blood pressure. Psychological effects can include visual and auditory hallucinations, altered perception of time and space, euphoria, and introspection. The effects can last anywhere from 6 to 10 hours, depending on the dose and individual metabolism.
Risks and Safety
Due to its high potency and narrow therapeutic index, 25C-NBOMe has been associated with several adverse events, including fatalities. The risks of overdose and poisoning are significantly higher compared to traditional psychedelics. Symptoms of overdose may include severe agitation, cardiac arrest, and seizures. As a result, there is a high potential for harm when using substances like 25C-NBOMe, especially without precise dosing.
Legal Status
The legal status of 25C-NBOMe varies by country, but it has been banned or controlled in several jurisdictions due to concerns over its safety and potential for abuse. In some countries, it is classified as a controlled substance, making its possession, sale, or manufacture illegal.
Analogues and derivatives
Analogues and derivatives of 2C-C:
25C-NB*:
- 25C-NBF
- 25C-NBMD
- 25C-NBOH
- 25C-NBOMe (NBOMe-2CC)
- 25C-NB3OMe
- 25C-NB4OMe
- N-(2C-C)-fentanyl<ref>
Explore N-(2C-C)-Fentanyl | PiHKAL · info(link). isomerdesign.com.
</ref>
| Serotonin receptor modulators | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Phenethylamines | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|