Methylphenidate
| Methylphenidate | |
|---|---|
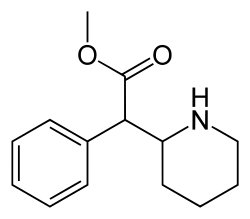
| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | Stimulant; Norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI) |
| Routes of administration | By mouth, transdermal, insufflation, sublingual, rectal, intravenous |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | Insufflation: ~70%
Oral: ~30% (range: 11–52%) |
| Metabolism | Liver (80%) mostly CES1-mediated |
| Elimination half-life | 2–3 hours |
| Excretion | Urine (90%) |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | 20748-11-2 |
| PubChem | 4158 |
| DrugBank | DB00422 |
| ChemSpider | 4015 |
| KEGG | D04999 |
Introduction[edit]
Methylphenidate is a central nervous system stimulant used for the therapy of attention deficit disorder and narcolepsy.

Liver safety[edit]
Methylphenidate has been linked to a low rate of serum aminotransferase elevations during therapy and to rare instances of acute, clinically apparent liver injury, generally after its intravenous abuse.
Mechanism of action[edit]
Methylphenidate (meth" il fen' i date) is a piperidine derivative that is structurally related to amphetamine which acts as a central nervous system (CNS) sympathomimetic stimulant, probably by causing release of norepinephrine at CNS nerve terminals promoting neurotransmission. Methylphenidate may also affect dopaminergic neurotransmission. Therapy with methylphenidate has been shown to increase cognitive abilities and improve psychological functioning and performance in children and adults with suspected attention deficit disorders. It has a paradoxical calming action in children with hyperactivity. Methylphenidate is also used in the therapy of narcolepsy.
FDA approval information for Methylphenidate[edit]
Methylphenidate was initially approved for use in the United States in 1955 and its indications have been broadened to include children above the age of 6 and adolescents with attention deficit disorder. Methylphenidate is available in multiple forms for oral administration including capsules, tablets, oral solutions and as extended release and long acting forms in concentrations varying from 2.5 to 54 mg in generic forms and under several brand names including Ritalin, Concerta and Metadate. Transdermal formulations are also available.
Dosage and administration for Methylphenidate[edit]
The usual dose in adults is 10 mg two or three times daily and average maintenance dosage is 40 to 60 mg daily. The dosage in children varies by formulation. Methylphenidate is a controlled substance (Schedule II) and has abuse potential.
Side effects of Methylphenidate[edit]
Common side effects include headache, insomnia, irritability, palpitations, tachycardia, nasal stuffiness, decreased appetite, cough and rash.
The following are CNS stimulants
- Amphetamines (including ecstasy or methylenedioxymetamphetamine)
- Armodafinil
- Atomoxetine
- Cocaine
- Methylphenidate
- Modafinil
| Stimulants | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ADHD pharmacotherapies | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Monoamine reuptake inhibitors | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Phenethylamines | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
![]()
![]() Error creating thumbnail:
Google plus
Error creating thumbnail:
Google plus
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
- Drugs
- Methylphenidate
- 2-Benzylpiperidines
- Biology of bipolar disorder
- Carboxylate esters
- Euphoriants
- Novartis brands
- Methyl esters
- Nootropics
- Norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitors
- Sigma agonists
- Stimulants
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder management
- Vasoconstrictors
- Ergogenic aids
- Pages with broken file links