Bethanechol
What is Bethanechol?[edit]
- Bethanechol is a cholinergic agent, is a synthetic ester which is structurally and pharmacologically related to acetylcholine used to relieve difficulties in urinating caused by surgery, drugs, or other factors.

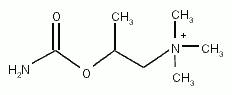
What are the uses of this medicine?[edit]
- Bethanechol is to treat urinary retention resulting from general anesthetic, diabetic neuropathy of the bladder, or a side effect of antidepressants; or to treat gastrointestinal lack of muscular tone.
How does this medicine work?[edit]
- Bethanechol is a parasympathomimetic choline carbamate that selectively stimulates muscarinic receptors without any effect on nicotinic receptors.
- Bethanechol chloride acts principally by producing the effects of stimulation of the parasympathetic nervous system.
- It increases the tone of the detrusor urinae muscle, usually producing a contraction sufficiently strong to initiate micturition and empty the bladder.
- It stimulates gastric motility, increases gastric tone and often restores impaired rhythmic peristalsis.
- Stimulation of the parasympathetic nervous system releases acetylcholine at the nerve endings.
- Bethanechol chloride is not destroyed by cholinesterase and its effects are more prolonged than those of acetylcholine.
Who Should Not Use this medicine ?[edit]
This medicine cannot be used in patients with:
- Hypersensitivity to bethanechol chloride
- hyperthyroidism
- peptic ulcer
- latent or active bronchial asthma
- pronounced bradycardia or hypotension
- vasomotor instability
- coronary artery disease
- epilepsy
- parkinsonism
- gastrointestinal or bladder wall is in question
- mechanical obstruction
- recent urinary bladder surgery, gastrointestinal resection and anastomosis
- vagotonia
- spastic gastrointestinal disturbances, acute inflammatory lesions of the gastrointestinal tract
What drug interactions can this medicine cause?[edit]
- Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Be sure to mention any of the following:
- procainamide (Pronestyl)
- quinidine (Quinaglute)
- medications for colds or nasal congestion
Is this medicine FDA approved?[edit]
- Yes, is was FDA approved.
How should this medicine be used?[edit]
Recommended dosage:
- Dosage must be individualized, depending on the type and severity of the condition to be treated.
- The usual adult oral dose ranges from 10 to 50 mg three or four times a day.
- The minimum effective dose is determined by giving 5 to 10 mg initially, and repeating the same amount at hourly intervals until satisfactory response occurs, or until a maximum of 50 mg has been given.
- The effects of the drug sometimes appear within 30 minutes, and are usually maximal within 60 to 90 minutes.
- The drug effects persist for about one hour.
Administration:
- Bethanechol comes as a tablet to take by mouth. Bethanechol usually is taken two to four times a day.
- Preferably give the drug when the stomach is empty.
- If taken soon after eating, nausea and vomiting may occur.
- Bethanechol usually is taken at evenly spaced intervals during the day.
What are the dosage forms and brand names of this medicine?[edit]
This medicine is available in fallowing doasage form:
- As tablet for oral administration contains 5 mg, 10 mg, 25 mg or 50 mg bethanechol chloride, USP.
This medicine is available in fallowing brand namesː
- Duvoid
- Myotonachol
- Urecholine
What side effects can this medication cause?[edit]
The most common side effects of this medicine include:
- malaise
- seizures
- abdominal cramps or discomfort, colicky pain, nausea and belching, diarrhea, borborygmi, salivation
- urinary urgency
- headache
- a fall in blood pressure with reflex tachycardia, vasomotor response
- flushing producing a feeling of warmth, sensation of heat about the face, sweating
- bronchial constriction, asthmatic attacks
- lacrimation, miosis
What special precautions should I follow?[edit]
- In urinary retention, if the sphincter fails to relax as bethanechol chloride contracts the bladder, urine may be forced up the ureter into the kidney pelvis. If there is bacteriuria, this may cause reflux infection.
- Bethanechol chloride tablets should preferably be taken one hour before or two hours after meals to avoid nausea or vomiting. Dizziness, lightheadedness or fainting may occur, especially when getting up from a lying or sitting position.
- It is not known whether this drug is secreted in human milk. A decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
- You should know that this drug may make you drowsy. Do not drive a car or operate machinery until you know how this drug affects you.
- Remember that alcohol can add to the drowsiness caused by this drug.
What to do in case of emergency/overdose?[edit]
Symptoms of overdose may include:
- abdominal discomfort, salivation, flushing of the skin (“hot feeling”), sweating, nausea, and vomiting
Management of overdosage:
- Atropine Sulfate is a specific antidote for Bethanechol overdose.
- The recommended dose for adults is 0.6 mg. Repeat doses can be given every two hours, according to clinical response.
- The recommended dosage in infants and children up to 12 years of age is 0.01 mg/kg (to a maximum single dose of 0.4 mg) repeated every two hours as needed until the desired effect is obtained or adverse effects of atropine preclude further usage.
Can this medicine be used in pregnancy?[edit]
- Pregnancy Category C.
- It is also not known whether bethanechol chloride can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity.
- Bethanechol chloride should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Can this medicine be used in children?[edit]
- Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
What are the active and inactive ingredients in this medicine?[edit]
Active Ingredients:
- BETHANECHOL CHLORIDE
Inactive Ingredients:
- ANHYDROUS LACTOSE
- SILICON DIOXIDE
- MAGNESIUM STEARATE
- CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE
- SODIUM STARCH GLYCOLATE TYPE A POTATO
Who manufactures and distributes this medicine?[edit]
Distributed by:
- Amneal Pharmaceuticals LLC
- Bridgewater, NJ
What should I know about storage and disposal of this medication?[edit]
- Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F).
- Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP, with a child-resistant closure (as required).
| Urologicals, including antispasmodics (G04B) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian