Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy''' (ICP), also known as '''obstetric cholestasis''', is a liver disorder that can develop during pregnancy. This condition affects the normal flow of bile, a digestive fluid produced in the liver, causing it to build up in the body and leading to symptoms such as itching and jaundice. | {{SI}} {{Infobox medical condition | ||
| name = Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy | |||
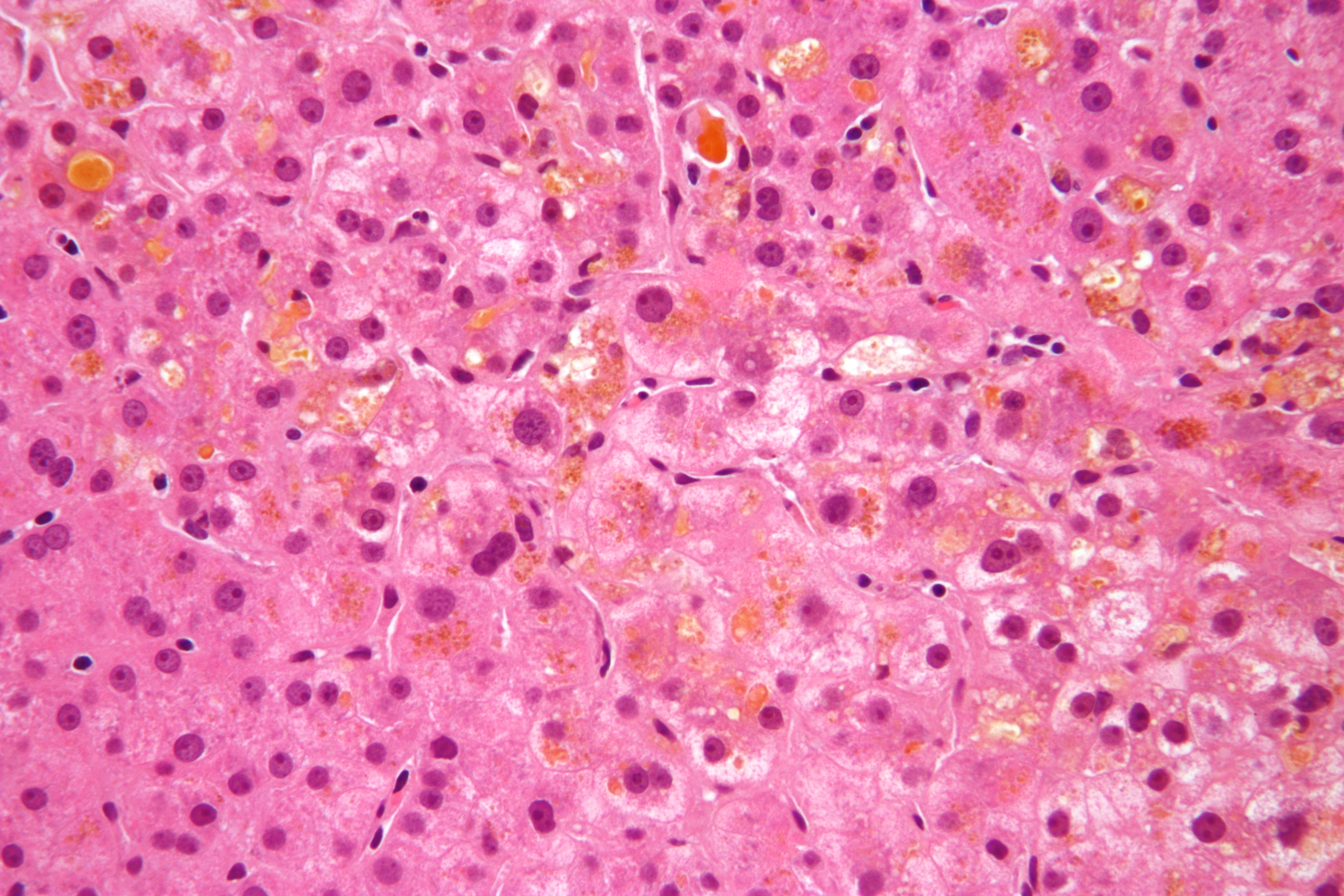
| image = [[File:Cholestasis_high_mag.jpg|alt=Micrograph of cholestasis]] | |||
| caption = Micrograph of cholestasis | |||
| field = [[Obstetrics]] | |||
| synonyms = [[Obstetric cholestasis]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Pruritus]], [[jaundice]], [[fatigue]] | |||
| complications = [[Fetal distress]], [[preterm birth]], [[stillbirth]] | |||
| onset = [[Third trimester]] | |||
| duration = Until delivery | |||
| causes = [[Genetic predisposition]], [[hormonal changes]] | |||
| risks = [[Multiple pregnancy]], [[previous history of cholestasis]], [[liver disease]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Liver function tests]], [[serum bile acid test]] | |||
| differential = [[Acute fatty liver of pregnancy]], [[HELLP syndrome]], [[viral hepatitis]] | |||
| prevention = None | |||
| treatment = [[Ursodeoxycholic acid]], [[early delivery]] | |||
| medication = [[Ursodeoxycholic acid]], [[antihistamines]] | |||
| prognosis = Good with treatment | |||
| frequency = 1 in 140 pregnancies | |||
}}'''Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy''' (ICP), also known as '''obstetric cholestasis''', is a liver disorder that can develop during pregnancy. This condition affects the normal flow of bile, a digestive fluid produced in the liver, causing it to build up in the body and leading to symptoms such as itching and jaundice. | |||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
The most common symptom of ICP is severe itching (pruritus), particularly on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet, although it can also occur on other parts of the body. This itching is often worse at night and can be so severe that it interferes with sleep. Other symptoms can include dark urine, pale stools, and jaundice (yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes). | The most common symptom of ICP is severe itching (pruritus), particularly on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet, although it can also occur on other parts of the body. This itching is often worse at night and can be so severe that it interferes with sleep. Other symptoms can include dark urine, pale stools, and jaundice (yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes). | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
The exact cause of ICP is not known, but it is believed to be related to hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy. These changes can affect the liver's ability to transport certain substances, including bile acids, which can then build up in the liver and spill over into the bloodstream. | The exact cause of ICP is not known, but it is believed to be related to hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy. These changes can affect the liver's ability to transport certain substances, including bile acids, which can then build up in the liver and spill over into the bloodstream. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
ICP is typically diagnosed through a combination of symptom assessment, physical examination, and laboratory tests. These tests can include blood tests to measure levels of bile acids and liver enzymes, as well as imaging tests such as ultrasound to check for any physical abnormalities in the liver. | ICP is typically diagnosed through a combination of symptom assessment, physical examination, and laboratory tests. These tests can include blood tests to measure levels of bile acids and liver enzymes, as well as imaging tests such as ultrasound to check for any physical abnormalities in the liver. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Treatment for ICP focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing complications. This can include medication to reduce bile acid levels and itching, as well as regular monitoring of the baby's health. In some cases, early delivery may be recommended to reduce the risk of complications. | Treatment for ICP focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing complications. This can include medication to reduce bile acid levels and itching, as well as regular monitoring of the baby's health. In some cases, early delivery may be recommended to reduce the risk of complications. | ||
== Prognosis == | == Prognosis == | ||
With appropriate treatment and monitoring, most women with ICP and their babies do well. However, ICP can increase the risk of certain complications, including preterm birth, fetal distress, and stillbirth. Therefore, close monitoring and appropriate management are essential. | With appropriate treatment and monitoring, most women with ICP and their babies do well. However, ICP can increase the risk of certain complications, including preterm birth, fetal distress, and stillbirth. Therefore, close monitoring and appropriate management are essential. | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Pregnancy]] | * [[Pregnancy]] | ||
| Line 26: | Line 34: | ||
* [[Cholestasis]] | * [[Cholestasis]] | ||
* [[Bile]] | * [[Bile]] | ||
[[Category:Medical conditions]] | [[Category:Medical conditions]] | ||
[[Category:Pregnancy]] | [[Category:Pregnancy]] | ||
| Line 33: | Line 40: | ||
{{Digestive system diseases}} | {{Digestive system diseases}} | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 03:30, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Obstetric cholestasis |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Pruritus, jaundice, fatigue |
| Complications | Fetal distress, preterm birth, stillbirth |
| Onset | Third trimester |
| Duration | Until delivery |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic predisposition, hormonal changes |
| Risks | Multiple pregnancy, previous history of cholestasis, liver disease |
| Diagnosis | Liver function tests, serum bile acid test |
| Differential diagnosis | Acute fatty liver of pregnancy, HELLP syndrome, viral hepatitis |
| Prevention | None |
| Treatment | Ursodeoxycholic acid, early delivery |
| Medication | Ursodeoxycholic acid, antihistamines |
| Prognosis | Good with treatment |
| Frequency | 1 in 140 pregnancies |
| Deaths | N/A |
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP), also known as obstetric cholestasis, is a liver disorder that can develop during pregnancy. This condition affects the normal flow of bile, a digestive fluid produced in the liver, causing it to build up in the body and leading to symptoms such as itching and jaundice.
Symptoms[edit]
The most common symptom of ICP is severe itching (pruritus), particularly on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet, although it can also occur on other parts of the body. This itching is often worse at night and can be so severe that it interferes with sleep. Other symptoms can include dark urine, pale stools, and jaundice (yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes).
Causes[edit]
The exact cause of ICP is not known, but it is believed to be related to hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy. These changes can affect the liver's ability to transport certain substances, including bile acids, which can then build up in the liver and spill over into the bloodstream.
Diagnosis[edit]
ICP is typically diagnosed through a combination of symptom assessment, physical examination, and laboratory tests. These tests can include blood tests to measure levels of bile acids and liver enzymes, as well as imaging tests such as ultrasound to check for any physical abnormalities in the liver.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for ICP focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing complications. This can include medication to reduce bile acid levels and itching, as well as regular monitoring of the baby's health. In some cases, early delivery may be recommended to reduce the risk of complications.
Prognosis[edit]
With appropriate treatment and monitoring, most women with ICP and their babies do well. However, ICP can increase the risk of certain complications, including preterm birth, fetal distress, and stillbirth. Therefore, close monitoring and appropriate management are essential.
See also[edit]
| Pathology of pregnancy, childbirth, and the puerperium | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
* ' Category'
|
| Diseases of the human digestive system | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|


