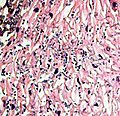
Esophageal candidiasis

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Esophageal candidiasis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Synonyms | Candidal esophagitis |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Dysphagia, odynophagia, chest pain, nausea |
| Complications | Esophageal stricture, perforation |
| Onset | |
| Duration | |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Candida albicans |
| Risks | Immunosuppression, HIV/AIDS, diabetes mellitus, use of corticosteroids |
| Diagnosis | Endoscopy, biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Gastroesophageal reflux disease, esophagitis due to other causes |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | Antifungal medications such as fluconazole |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment |
| Frequency | Common in immunocompromised individuals |
| Deaths | N/A |
Esophageal candidiasis is a fungal infection of the esophagus, the tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach. It is caused by the yeast Candida species, most commonly Candida albicans. This condition is often seen in people with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy, or people who have had organ transplants.
Causes[edit]
Esophageal candidiasis is caused by the overgrowth of Candida yeast in the esophagus. This can occur when the body's immune system is weakened or when the normal balance of bacteria in the body is disrupted. Certain medications, such as antibiotics or corticosteroids, can also contribute to the development of this condition.
Symptoms[edit]
The most common symptoms of esophageal candidiasis include difficulty swallowing, pain when swallowing, and chest pain. Some people may also experience nausea, vomiting, or a feeling of food being stuck in the throat.
Diagnosis[edit]
Esophageal candidiasis is typically diagnosed through a procedure called an endoscopy, in which a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera at the end is inserted into the esophagus. A small sample of tissue may be taken for laboratory testing to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for esophageal candidiasis typically involves antifungal medications, such as fluconazole or itraconazole. In severe cases, hospitalization may be required.
Prevention[edit]
Prevention of esophageal candidiasis involves maintaining a healthy immune system and avoiding behaviors that can disrupt the body's natural balance of bacteria. This can include avoiding unnecessary use of antibiotics, maintaining good oral hygiene, and eating a balanced diet.
Images[edit]
-
Esophageal candidiasis (2) PAS stain
-
Esophageal candidiasis
-
Candida
See also[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian