Estradiol diacetate: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
{{No image}} | {{No image}} | ||
== Estradiol diacetate == | |||
<gallery> | |||
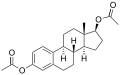
File:estradiol_diacetate.svg|Estradiol diacetate chemical structure | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 23:58, 24 February 2025
Estradiol diacetate is a synthetic, steroidal estrogen that is used in hormone therapy. It is a prodrug of estradiol, one of the main hormones responsible for the development and maintenance of female secondary sexual characteristics.
Chemistry
Estradiol diacetate is a synthetic steroid and a derivative of estrane. It is specifically a derivative of estradiol, which is the major endogenous estrogen in humans and other primates. Estradiol diacetate is formed by the acetylation of estradiol at the 3- and 17β- positions.
Pharmacology
As a prodrug of estradiol, estradiol diacetate is converted into estradiol in the body. Estradiol, in turn, interacts with the estrogen receptor to exert its effects. It has been found to possess approximately the same potency as estradiol in terms of estrogenic activity.
Medical uses
Estradiol diacetate is used in hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms, hypogonadism, osteoporosis, and for other indications. It is typically administered orally, but can also be given by intramuscular injection.
Side effects
Like other estrogens, estradiol diacetate can have a range of side effects, including nausea, bloating, breast tenderness, and an increased risk of thrombosis and breast cancer.
See also
Estradiol diacetate
-
Estradiol diacetate chemical structure