Berylliosis: Difference between revisions
No edit summary Tag: visualeditor-wikitext |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
{{wp}} | {{wp}} | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
[[Category:Lung diseases]] | {{Respiratory pathology}} | ||
[[Category: | {{Occupational safety and health}} | ||
{{Elements in biology}} | |||
[[Category:Beryllium]] | |||
[[Category:Biology and pharmacology of chemical elements]] | |||
[[Category:Element toxicology]] | |||
[[Category:Lung diseases due to external agents]] | |||
[[Category:Occupational diseases]] | |||
Revision as of 23:32, 14 January 2025

Berylliosis is a lung disease that affects people that work with metals.
Causes of Berylliosis
Berylliosis is a disease of the lungs caused by inhalation of beryllium dusts, vapors, or its compounds or implantation of the substance in the skin.
Risk factors
The toxic effects of beryllium are due to occupational exposure as Beryllium is a metallic element used in many industries, including electronics, high-technology ceramics, metals extraction, and dental alloy preparation.
Types of Berylliosis
There are two forms of beryllium-induced lung disease, acute and chronic.
Acute berylliosis
Acute berylliosis has a sudden, rapid onset and is characterized by severe inflammation of the lungs (pneumonitis), coughing, increasing breathlessness (dyspnea), and other associated symptoms and findings. In addition, in some individuals, the skin or the eyes may be affected.
-
Chronic berylliosis
-
Unusual inclusions in giant cells
-
Chronic berylliosis
Chronic berylliosis
The more common, chronic form of the disease develops more slowly and, in some cases, may not become apparent for many years after initial beryllium exposure.
Clinical features
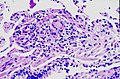
Chronic berylliosis is characterized by the abnormal formation of inflammatory masses or nodules (granulomas) within certain tissues and organs and widespread scarring and thickening of deep lung tissues (interstitial pulmonary fibrosis).
Other areas affected
Granuloma development primarily affects the lungs but other such as skin or the liver can also be affected with granulomas.
Signs & Symptoms
Acute berylliosis presents with severe inflammation of the lungs (pneumonitis), sudden onset of coughing, and difficulties breathing (dyspnea) in most patients while others may have sore throat (pharyngitis); inflammation of the mucous membranes of the nose (rhinitis) and associated nasal discharge; and inflammation of the windpipe and air passages of the lungs (tracheobronchitis).
Standard Therapies
Treatment - prevention
Employees should follow all workplace and safety guidelines and take any additional, appropriate steps to reduce their exposure to beryllium dust particles, fumes, and vapors. Employees change out of their work clothing and shoes, shower, and change into street clothing.
Treatment - those affected The treatment of individuals with acute berylliosis may include therapy with corticosteroid drugs, breathing support (such as the use of ventilators), and/or other supportive measures. With prompt, appropriate treatment, most affected individuals have a complete recovery with no residual effects.
Investigational Therapies
Researchers are conducting clinical trials to determine the effectiveness of a drug called infliximab (Remicade) in chronic beryllium disease (CBD). This drug may reduce tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-a), which is associated with more severe disease and inflammation in the lung. Receiving infliximab may help with symptoms, and may improve clinical testing data normally ordered by your doctor, such as breathing tests.
Investigators are studying the effectiveness of corticosteroid pulse therapy in individuals with chronic beryllium disease. In one case reported in the medical literature, this therapy improved pulmonary function tests and blood gases also improved. More research is necessary to determine the long-term safety and effectiveness of this treatment for individuals with chronic beryllium disease.
Other names
- Acute Beryllium Disease
- Beryllium Granulomatosis
- Beryllium Pneumonosis
- Beryllium Poisoning
External links

|
|
|
| Diseases of the respiratory system | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Elements in biology | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|