Eagle syndrome

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Eagle syndrome | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Styloid syndrome, stylohyoid syndrome |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Throat pain, earache, dysphagia, headache, facial pain |
| Complications | Carotid artery dissection, stroke |
| Onset | Typically adulthood |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Elongation of the styloid process or calcification of the stylohyoid ligament |
| Risks | Trauma, tonsillectomy |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, imaging studies such as X-ray, CT scan |
| Differential diagnosis | Temporomandibular joint disorder, trigeminal neuralgia, glossopharyngeal neuralgia |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Analgesics, corticosteroid injections, surgery |
| Medication | Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Eagle syndrome[edit]

Definition[edit]
Eagle syndrome is a recurrent pain in the middle part of the throat (oropharynx) and face.
Cause[edit]
Eagle syndrome is due to a calcified stylohyoid ligament or an elongated styloid process.
Styloid process[edit]
The styloid process is a pointed part of the temporal bone that serves as an anchor point for several muscles associated with the tongue and larynx.
Other names[edit]
- Elongated styloid process which causes neck and facial pain tinnitus and otalgia;
- Elongated styloid process syndrome;
- Styloid-stylohyoid syndrome;
Signs and symptoms[edit]
- "Classic Eagle syndrome" is typically seen in patients after throat trauma or tonsillectomy
- Symptoms include dull and persistent throat pain that may radiate to the ear and worsen with rotation of the head.
- Other symptoms may include difficulty swallowing, feeling of something stuck in the throat, tinnitus, and neck or facial pain.
- A second form of Eagle syndrome unrelated to tonsillectomy causes compression of the vessel that carries blood to the brain, neck, and face (carotid artery) which cause headache and dizziness
Diagnosis[edit]
- Diagnosis is is made with clinical presentation and imaging studies.
- The classic form of "Eagle syndrome" presents as unilateral neck pain, sore throat or tinnitus.
- Sometimes the tip of the styloid process is palpable in the back of the throat.
- The diagnosis of the vascular type is more difficult and requires an expert opinion.
- One should have a high level of suspicion when neurological symptoms occur upon head rotation.
- Symptoms tend to be worsened on bimanual palpation of the styloid through the tonsillar bed.
- They may be relieved by infiltration of lidocaine into the tonsillar bed.
- Because of the proximity of several large vascular structures in this area this procedure should not be considered to be risk free.
- Imaging is important and is diagnostic.
- Visualizing the styloid process on a CT scan with 3D reconstruction is the suggested imaging technique.
- The enlarged styloid may be visible on an orthopantogram or a lateral soft tissue X ray of the neck.
Treatment[edit]
- The mainstay treatment for Eagle syndrome is surgery to shorten the styloid process called styloidectomy.
Surgery[edit]
- Traditionally, this surgery has been done using either an intraoral (through the mouth) or extraoral (through the neck) approach.
- The intraoral approach usually requires tonsillectomy, and access to the styloid process is limited.
- There is also risk of injury to major vessels.
- However, this method reportedly is safe, more simple, and an external scar is avoided.
- The extraoral approach may provide better exposure of the process and its surrounding structures.
- However, this approach results in a scar, requires going through connective tissue and may carry an increased risk of trauma to surrounding structures.
- In recent years, more minimally-invasive techniques have been used for head and neck surgery.
Endoscopic assisted surgery[edit]
- Some patients with Eagle syndrome have undergone an endoscope-assisted surgery.
Medical management[edit]
- Medical management of Eagle syndrome may include the use of pain and anti-inflammatory medications, antidepressants, and/or steroids for pain.
- The overall success rate for treatment (medical or surgical) is about 80%.
Epidemiology[edit]
- Approximately 4% of the general population have an elongated styloid process, and of these about 4% give rise to the symptoms of Eagle syndrome.
- The incidence of stylohyoid syndrome may be about 0.16%.
- Patients with this syndrome tend to be between 30 and 50 years of age but it has been recorded in teenagers and in patients > 75 years old.
- It is more common in women, with a male:female ratio ~ 1:2.
History[edit]
The condition was first described by American otorhinolaryngologist Watt Weems Eagle in 1937.
Gallery[edit]
-
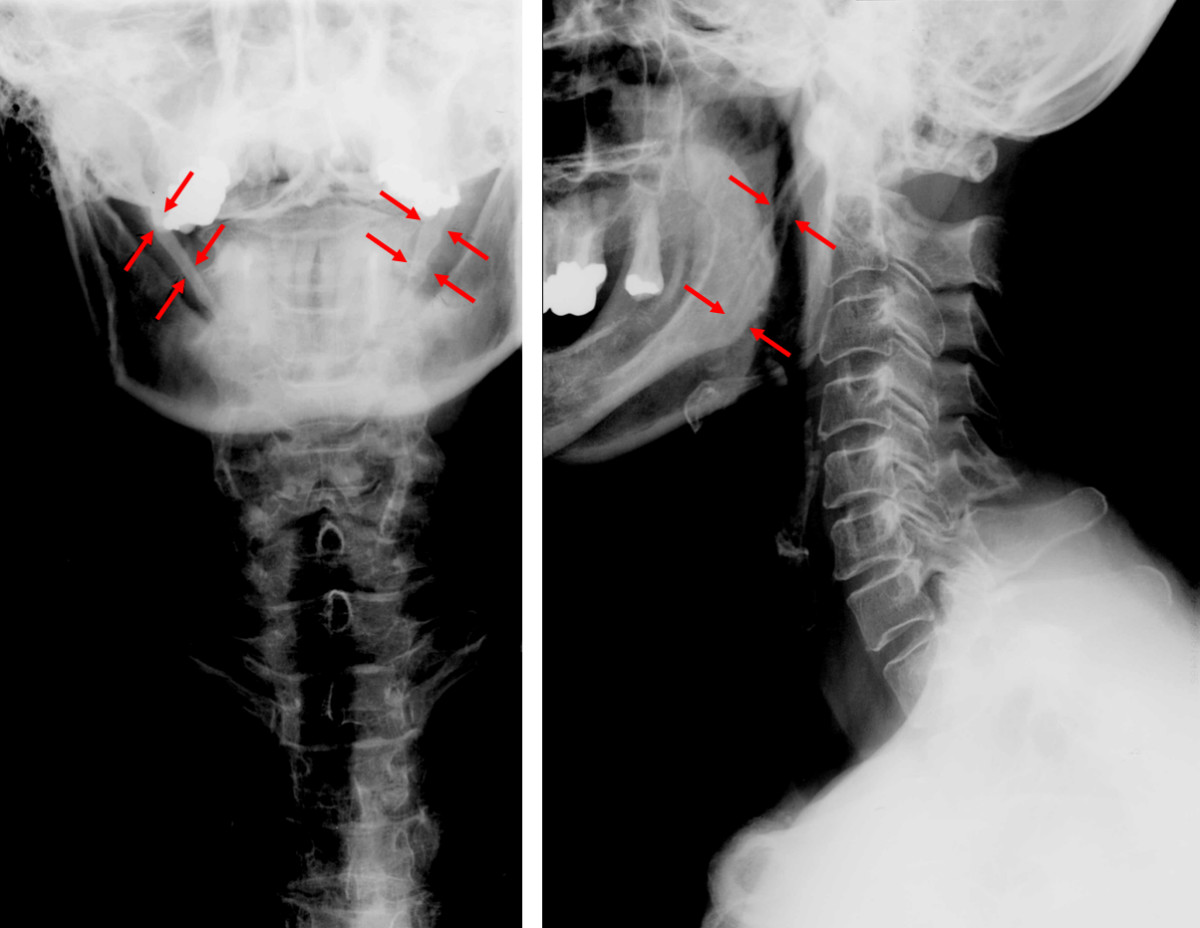
Radiograph, lateral view showing joint-like formation in ossified stylohyoid ligament
-
CT scan, coronal section showing bilateral extended styloid process and stylohyoid ligament ossification (incidental finding)
-
3D-reconstructed CT scan showing bilateral stylohyoid ligament ossification
-
3D reconstructed CT scan showing elongated styloid process (right side)
Can you help answer any of these frequently asked questions on Eagle syndrome?
Frequently asked questions about Eagle syndrome[edit]
- Does Eagle syndrome go away?
Eagle syndrome typically does not resolve spontaneously. Treatment is often required if symptoms persist.
- Can you feel Eagle syndrome?
Yes, Eagle syndrome is often characterized by a palpable lump or tenderness in the neck area.
- What does Eagle syndrome feel like?
Symptoms include throat pain, difficulty swallowing, foreign body sensation, and pain that radiates to the ear or jaw.
- Is Eagle syndrome life threatening?
No, Eagle syndrome itself is usually not life-threatening but can significantly affect quality of life.
- Can Eagle syndrome come and go?
Yes, symptoms of Eagle syndrome may fluctuate or be intermittent.
- Can the hyoid bone shift?
Yes, the hyoid bone can shift slightly, contributing to symptoms similar to those seen in Eagle syndrome.
- How do you test for Eagle syndrome?
Diagnosis involves clinical evaluation, imaging tests such as X-ray or CT scan, and examination of symptoms.
- Is Eagle syndrome rare?
Eagle syndrome is considered rare, although precise prevalence is not clearly established.
- How long does it take to recover from Eagle syndrome surgery?
Recovery from surgical treatment (styloidectomy) typically takes several weeks, with most patients improving significantly within 2 to 4 weeks.
- Can Eagle syndrome cause strokes?
Rarely, elongated styloid processes in Eagle syndrome have been associated with transient ischemic attacks (TIA) or strokes due to compression of adjacent blood vessels.
- Does Eagle syndrome cause ear pain?
Yes, ear pain (otalgia) is a common symptom of Eagle syndrome due to referred pain.
- Does Eagle syndrome cause headaches?
Yes, headaches may occur, typically related to referred pain or vascular compression.
- How common is Eagle syndrome?
Eagle syndrome is rare; it is estimated to affect around 4% of the population, with only a small fraction experiencing symptoms.
- What type of doctor treats Eagle's syndrome?
Otolaryngologists (ENT) or oral and maxillofacial surgeons commonly treat Eagle syndrome.
- How does Eagle syndrome happen?
Eagle syndrome occurs due to elongation or calcification of the styloid process or stylohyoid ligament, causing symptoms by compressing surrounding nerves or vessels.
- Why is it called Eagle syndrome?
It is named after Watt Weems Eagle, an American otolaryngologist who first described the syndrome.
- Which nerve is affected by Eagle's syndrome?
The glossopharyngeal nerve is commonly affected, leading to characteristic pain and symptoms.
- Can Eagle syndrome cause tinnitus?
Yes, Eagle syndrome may cause tinnitus through irritation of surrounding nerves or blood vessels.
- Can Eagle syndrome cause hearing loss?
While rare, Eagle syndrome could theoretically contribute to hearing changes, although direct hearing loss is uncommon.
- Is Eagle syndrome congenital?
Eagle syndrome is not typically congenital; it usually develops later in life due to calcification or elongation of anatomical structures.
- How risky is a Styloidectomy?
Styloidectomy is considered relatively safe, but as with any surgery, there are risks including nerve damage, bleeding, or infection.
- What are calcified ligaments?
Calcified ligaments occur when calcium deposits build up in ligamentous tissues, making them stiff or elongated, as seen in Eagle syndrome.
|
|
|
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian





