Pemphigus

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Pemphigus | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Blisters, erosions on skin and mucous membranes |
| Complications | Infection, dehydration, sepsis |
| Onset | Middle-aged adults |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Autoimmune disease |
| Risks | Genetic predisposition, certain medications |
| Diagnosis | Biopsy, immunofluorescence |
| Differential diagnosis | Bullous pemphigoid, dermatitis herpetiformis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Corticosteroids, immunosuppressive drugs |
| Medication | Prednisone, azathioprine, rituximab |
| Prognosis | Variable, can be life-threatening if untreated |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Overview of Pemphigus[edit]
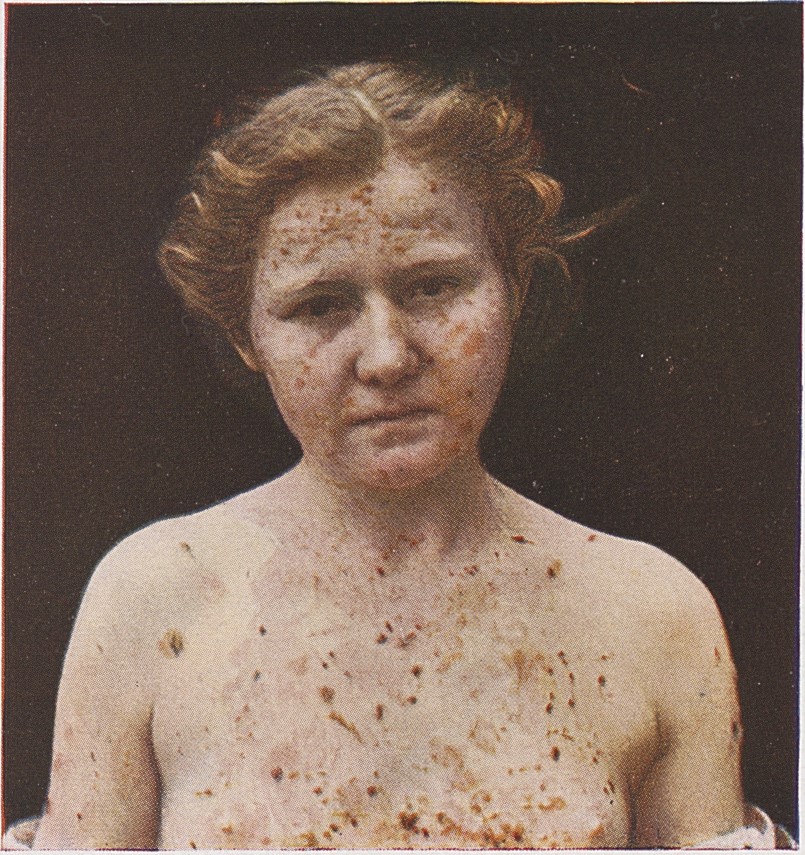
Pemphigus is a rare disease that causes blistering of the skin and inside the mouth, nose, throat, eyes, and genitals. Some forms of the disease may be fatal if left untreated.

Pemphigus is not contagious.
What happens in pemphigus?[edit]
Pemphigus is an autoimmune disease (auto means self). The immune system mistakenly attacks cells in the top layer of the skin (epidermis) and the mucous membranes. Pemphigus occurs when:
- The immune system produces antibodies against desmoglein, a protein that normally forms the “glue” to keep skin cells attached.
- Skin cells separate from each other.
- Fluid may collect between the layers of skin, forming blisters that do not heal. In some cases, these blisters can cover a large area of skin.
Medical research has dramatically improved the picture for people diagnosed with pemphigus. In the 1960s, the disease was fatal and poorly understood. Today the disease is rarely fatal, with the majority of deaths occurring from infections. For most people with pemphigus, the disease can be controlled with medications that can eventually be completely discontinued. However, these medications can cause side effects that may sometimes be serious.
Who Gets Pemphigus?[edit]
Pemphigus affects men and women equally. The disease also affects people of all races and ethnicities, although the eastern European Jewish community and people of Mediterranean descent are more susceptible. A particular type of pemphigus also occurs more frequently in people who live in the rainforests of Brazil. The disease usually starts appearing in middle-aged and older adults, although it may also be seen in young adults and children.
Types of Pemphigus[edit]
There are several types of pemphigus and other similar blistering disorders. The type of disease depends on the layer of the skin where the blisters form and where blisters are located on the body. Soft blisters always occur on or near the surface of the skin, which is called the epidermis. The type of antibody that attacks the skin cells may also define the type of pemphigus. The different types of pemphigus include the following.
- Pemphigus vulgaris is the most common type in the United States. Blisters almost always start in the mouth. Blisters form within the deep layer of the epidermis and are often painful. Blistered skin becomes so fragile that it may peel off by rubbing a finger on it. The blisters normally heal without scarring but may cause dark spots that remain for a number of months.
- Pemphigus vegetans causes thick sores form in the groin and under the arms.
- Pemphigus foliaceus causes crusted sores or fragile blisters that often appear first on the face and scalp, and later on the chest and other parts of the body. The sores are on the surface of the skin and often itchy, although they are rarely as painful as pemphigus vulgaris blisters. There may also be loose, moist scales on the skin.
- IgA pemphigus is different from other forms of pemphigus because it involves a different type of antibody (called immunoglobulin A or IgA) than other types. The disease may produce blisters similar to those seen in pemphigus foliaceus, or it may involve many small bumps containing pus. This is the least harmful form.
- Paraneoplastic pemphigus is a rare disease that occurs in people with certain types of cancer. It often involves severe sores of the mouth and lips, cuts and scarring of the lining of the eye and eyelids, and skin blisters. People with this type of pemphigus may also develop life-threatening problems in the lungs.
Pemphigoid is a disease that is distinct from pemphigus, but shares some of its features. Pemphigoid produces a split where the epidermis and the dermis meet, causing deep, rigid blisters that do not break easily.
Symptoms of Pemphigus[edit]
Pemphigus causes blistering of the skin and inside the mouth, nose, throat, eyes, and genitals.
Causes of Pemphigus[edit]
Something in the environment may trigger pemphigus in people who are at risk because of their genes. The exact trigger is unknown. In rare cases, pemphigus may be triggered by certain medications. In those cases, the disease usually goes away when the medication is stopped.
Diagnosis of Pemphigus[edit]
Early diagnosis is important, so consult a doctor if you have blisters on the skin or in the mouth that don’t go away. Your doctor may rule out other conditions first, since pemphigus is a rare disease. Your doctor will run several tests for pemphigus:
- Medical history and physical exam: A dermatologist (a doctor who treats skin problems) will ask you about your medical history and look for appearance and location of blisters.
- Tissue sample: Your doctor will take a sample from one of your blisters to:
Examine it under the microscope to look for cell separation and to determine the layer of skin in which the cells are separated. Determine which antibodies attacked the skin.
- A blood sample is taken to measure antibody levels and to help determine the severity of the disease. This blood test may also be used to find out if treatment is working.
Treatment of Pemphigus[edit]
Symptoms of pemphigus may go away after many years of treatment, although some patients will need to keep taking medications to keep the disease under control. You should report any problems or side effects from medications to your doctor. Treatment for pemphigus may involve medications such as:
- Corticosteroids, immunosuppressive drugs, or biologics to stop the immune system from attacking the tissues.
- Antibiotics, antivirals, and antifungal medications to control or prevent infections.
Other treatments may be needed in more severe cases of pemphigus. These treatments can be very expensive, since they require large amounts of donated and specially processed blood:
- Plasmapheresis, which removes damaging antibodies from the blood.
- Immunoglobulin therapy to replace the damaging antibodies that are removed.
Who Treats Pemphigus?[edit]
Doctors who treat pemphigus include:
- Dermatologists, who treat skin problems.
- Dentists, who can tell you how to take care of your gums and teeth if you have blisters in your mouth.
Living With Pemphigus[edit]
Blisters in the mouth may make brushing and flossing your teeth painful, so you should talk to your dentist about ways to keep your teeth and gums healthy. You should avoid foods that can irritate mouth blisters. Pemphigus and its treatments can be debilitating and cause lost time at work, weight loss, sleep problems, and emotional distress. Support groups may help you cope with the disease.
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian


