Gangrene: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Gangrene | |||
| image = [[File:GangreneFoot.JPG|250px]] | |||
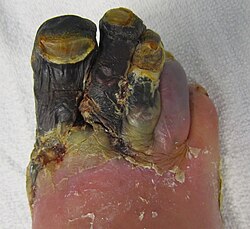
| caption = Gangrene of the foot | |||
| field = [[Vascular surgery]], [[Infectious disease]] | |||
| synonyms = [[Gangrenous necrosis]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Discoloration]], [[foul-smelling discharge]], [[numbness]], [[pain]] | |||
| complications = [[Sepsis]], [[amputation]] | |||
| onset = Sudden or gradual | |||
| duration = Varies | |||
| causes = [[Infection]], [[ischemia]], [[diabetes]], [[smoking]], [[trauma]] | |||
| risks = [[Diabetes mellitus]], [[peripheral artery disease]], [[smoking]], [[immunosuppression]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Physical examination]], [[imaging studies]], [[blood tests]] | |||
| differential = [[Cellulitis]], [[necrotizing fasciitis]], [[chronic ulcer]] | |||
| prevention = [[Proper wound care]], [[control of diabetes]], [[smoking cessation]] | |||
| treatment = [[Surgical debridement]], [[antibiotics]], [[hyperbaric oxygen therapy]], [[vascular surgery]] | |||
| prognosis = Variable, depends on severity and treatment | |||
| frequency = Common in certain populations | |||
}} | |||
'''Gangrene''' is a medical condition characterized by the death of body tissue due to a lack of blood supply. It can be caused by injury, infection, or underlying medical conditions such as diabetes or peripheral artery disease. Gangrene can affect any part of the body, but it most commonly occurs in the extremities, such as fingers, toes, hands, and feet. | '''Gangrene''' is a medical condition characterized by the death of body tissue due to a lack of blood supply. It can be caused by injury, infection, or underlying medical conditions such as diabetes or peripheral artery disease. Gangrene can affect any part of the body, but it most commonly occurs in the extremities, such as fingers, toes, hands, and feet. | ||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
Symptoms of gangrene include: | Symptoms of gangrene include: | ||
Latest revision as of 02:26, 7 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Gangrene | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Gangrenous necrosis |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Discoloration, foul-smelling discharge, numbness, pain |
| Complications | Sepsis, amputation |
| Onset | Sudden or gradual |
| Duration | Varies |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Infection, ischemia, diabetes, smoking, trauma |
| Risks | Diabetes mellitus, peripheral artery disease, smoking, immunosuppression |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, imaging studies, blood tests |
| Differential diagnosis | Cellulitis, necrotizing fasciitis, chronic ulcer |
| Prevention | Proper wound care, control of diabetes, smoking cessation |
| Treatment | Surgical debridement, antibiotics, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, vascular surgery |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on severity and treatment |
| Frequency | Common in certain populations |
| Deaths | N/A |
Gangrene is a medical condition characterized by the death of body tissue due to a lack of blood supply. It can be caused by injury, infection, or underlying medical conditions such as diabetes or peripheral artery disease. Gangrene can affect any part of the body, but it most commonly occurs in the extremities, such as fingers, toes, hands, and feet.
Symptoms[edit]
Symptoms of gangrene include:
- Discoloration of the affected area (black, blue, green, or red)
- Pain in the affected area
- Foul-smelling discharge from the affected area
- Numbness or loss of sensation
- Coldness in the affected area
- In severe cases, tissue death
Causes[edit]
Gangrene occurs when the blood supply to a certain area of the body is interrupted or severely reduced. This can result from:
- Injuries, such as burns, frostbite, or crushing injuries
- Infections, especially those caused by bacteria, which can damage blood vessels and limit blood flow
- Underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes or peripheral artery disease, which can lead to poor circulation and increased risk of infection
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosing gangrene typically involves a physical examination, during which a healthcare professional will look for the characteristic signs and symptoms. Additional diagnostic tests may include:
- Imaging studies, such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans, to assess the extent of tissue damage and identify any underlying causes
- Blood tests to check for infection or other contributing factors
- Tissue samples to identify the specific type of bacteria causing the infection, if applicable
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for gangrene depends on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. Treatment options may include:
- Antibiotics to treat any bacterial infections
- Surgical debridement, which involves removing dead or infected tissue to promote healing
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy, which involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized room to increase the amount of oxygen in the blood and promote healing
- Amputation, in severe cases where the gangrene has spread and cannot be controlled through other means
- Addressing any underlying conditions, such as managing diabetes or treating peripheral artery disease, to reduce the risk of future episodes of gangrene.
|
|
|
| Ischaemia and infarction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Pathology | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|


