Endometrial cancer

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Endometrial cancer | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Abnormal uterine bleeding, pelvic pain |
| Complications | Metastasis, anemia |
| Onset | Most common after menopause |
| Duration | |
| Types | Endometrioid carcinoma, serous carcinoma, clear cell carcinoma |
| Causes | |
| Risks | Obesity, diabetes, hypertension, unopposed estrogen therapy, polycystic ovary syndrome |
| Diagnosis | Endometrial biopsy, transvaginal ultrasound |
| Differential diagnosis | Endometrial hyperplasia, cervical cancer, ovarian cancer |
| Prevention | Weight loss, oral contraceptives, progestin therapy |
| Treatment | Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormonal therapy |
| Medication | Progestins, chemotherapy drugs |
| Prognosis | Generally good if diagnosed early |
| Frequency | Most common gynecologic cancer in developed countries |
| Deaths | |



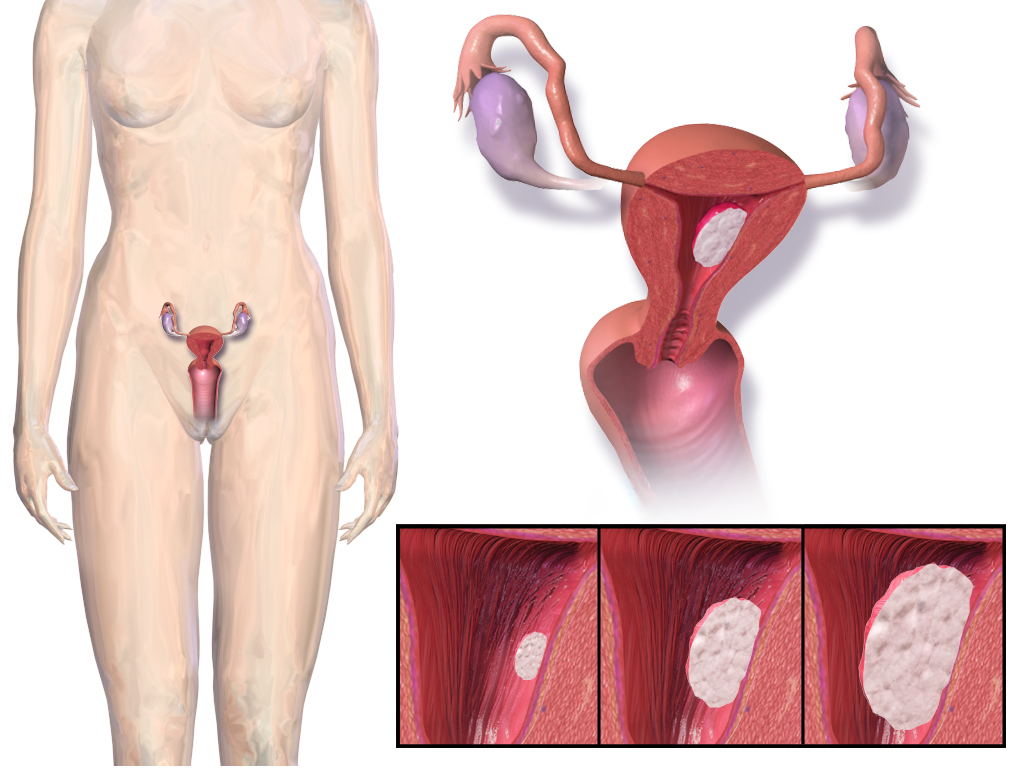
Endometrial cancer is a malignant tumor originating from the epithelial cells of the endometrium, which is the innermost lining layer of the uterus. As one of the most commonly diagnosed gynecological malignancies, especially in developed countries, understanding its etiology, clinical presentation, and management is pivotal for medical professionals, particularly those specializing in gynecologic oncology.
Epidemiology[edit]
Endometrial cancer holds the position as the most frequently diagnosed gynecologic cancer in the United States, with annual estimates exceeding 35,000 cases. The majority of these cases are found in post-menopausal women, although younger women are not exempt from this diagnosis.
Pathophysiology[edit]
The development of endometrial cancer is often linked to prolonged exposure to unopposed estrogen. This hormonal imbalance leads to endometrial hyperplasia, a precursor to endometrial cancer. Several conditions, such as polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), obesity, and estrogen-secreting tumors can elevate estrogen levels in the body.
Clinical Presentation[edit]
Most women present with abnormal vaginal bleeding, often post-menopausal. However, younger women may experience irregular menstrual periods or bleeding between cycles. Additionally, pelvic pain, pain during intercourse, and an enlarged uterus can also be indicative signs.
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnostic gold standard is an endometrial biopsy, which allows for histological examination of the endometrial tissue. If malignancy is suspected, further imaging, including a transvaginal ultrasound, may be warranted to assess the tumor's size and possible invasion into surrounding structures.
Treatment[edit]
Early detection of endometrial cancer typically results in favorable outcomes, with a variety of treatment options available:
- Surgery: Hysterectomy, often with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (removal of both ovaries and fallopian tubes), is commonly performed. Lymph nodes may also be removed to check for metastatic spread.
- Radiation Therapy: Used post-operatively, or in patients unfit for surgery.
- Chemotherapy: Employed for advanced or recurrent cases.
- Hormone Therapy: Used especially for patients with hormone-receptor positive tumors.
Prognosis[edit]
Owing to the characteristic presentation of abnormal bleeding in its early stages, many cases of endometrial cancer are diagnosed promptly, leading to a generally favorable prognosis. The survival rates are significantly higher for endometrial cancer compared to other gynecologic cancers when detected early.
Summary[edit]
For medical students, understanding the complexities of endometrial cancer, from its pathophysiology to its management, is crucial. Given its prevalence, clinicians are likely to encounter patients with this diagnosis, necessitating a thorough and compassionate approach to care.
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
External Links[edit]
|
|
|
| Tumors of the female urogenital system | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian


