Bullous pemphigoid

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Bullous pemphigoid | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | |
| Pronounce | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| Symptoms | Blisters, itching, rash |
| Complications | Infection, scarring |
| Onset | Typically in older adults |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Autoimmune disease |
| Risks | Age, genetic predisposition, certain medications |
| Diagnosis | Skin biopsy, direct immunofluorescence |
| Differential diagnosis | Pemphigus vulgaris, dermatitis herpetiformis, epidermolysis bullosa |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | Corticosteroids, immunosuppressants |
| Medication | Prednisone, azathioprine, methotrexate |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |

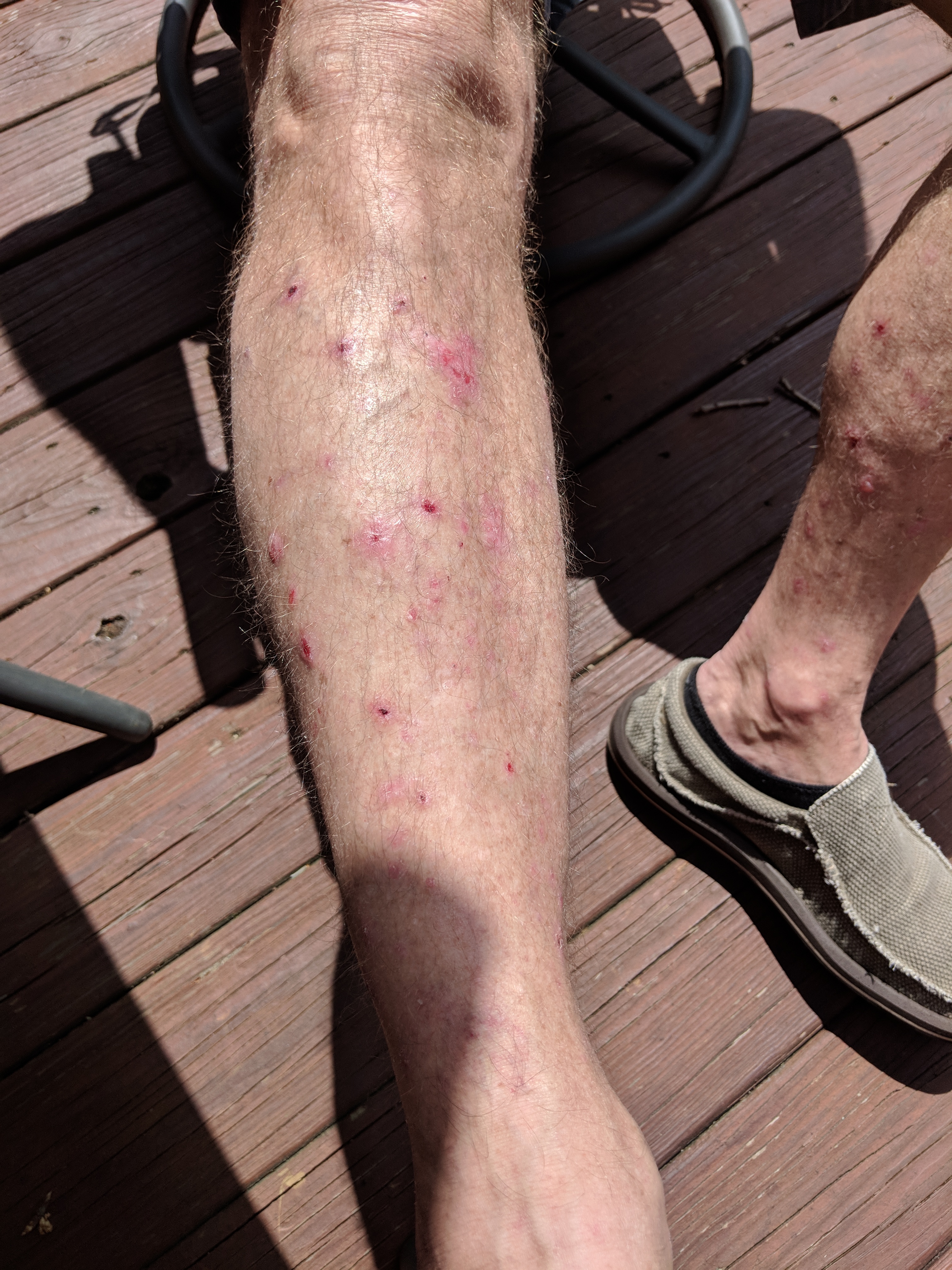
Bullous Pemphigoid is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the skin, causing the formation of large, tense blisters. It is most common in older adults and is characterized by periods of remission and relapse.
Etiology[edit]
The exact cause of bullous pemphigoid is unknown, but it is believed to be an autoimmune response. The body's immune system produces antibodies that attack the skin's basement membrane, a thin layer of tissue that separates the outer skin from the underlying tissues. This attack results in inflammation and the formation of blisters.
Symptoms[edit]
The primary symptom of bullous pemphigoid is the appearance of large, tense blisters on the skin. These blisters are usually filled with clear fluid and can appear anywhere on the body, but are most common on the arms, legs, and trunk. Other symptoms may include itching, redness, and hives.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of bullous pemphigoid is typically made through a combination of clinical examination, skin biopsy, and blood tests. The skin biopsy can reveal the presence of the characteristic blisters and the blood tests can detect the presence of the specific antibodies associated with the disease.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for bullous pemphigoid primarily involves managing the symptoms and preventing complications. This may include the use of topical or oral corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response. In severe cases, other immunosuppressive drugs may be used.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for bullous pemphigoid varies. Some individuals may experience periods of remission, while others may have persistent symptoms. With treatment, most individuals can manage their symptoms and maintain a good quality of life.
See Also[edit]

This article is a dermatology stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
This article is a Autoimmune disease-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
