Tear gas
Tear gas, or lachrymator agents, are chemical substances designed to temporarily incapacitate individuals through irritation of mucous membranes, particularly the eyes and respiratory tract. They are used mainly for riot control, crowd dispersion, and in some self-defense products.
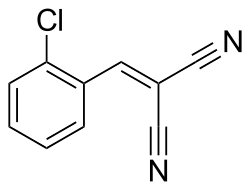
Chemical Structure and Mechanism of Action[edit]
The common types of tear gas are CS (ortho-chlorobenzylidene malononitrile), CN (chloroacetophenone), and CR (dibenzoxazepine). These agents are dispersed as aerosols and function primarily by stimulating nerves in the eyes to induce tearing. In higher concentrations, tear gases can cause severe irritation of mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, provoking coughing, shortness of breath, and even choking[1].
Physical Effects[edit]
Tear gas predominantly affects the eyes, respiratory system, and the skin:
Eyes: Exposure leads to severe eye pain, excessive tear production, and temporary blindness. Respiratory system: Inhalation causes difficulty breathing, tightness in the chest, and can lead to respiratory failure in severe cases. Skin: Contact can result in burning sensations, skin redness, and blistering in some cases. The effects typically begin within seconds of exposure and usually resolve within 30 minutes to an hour after leaving the contaminated area[2].
Medical Treatment[edit]
Treatment of tear gas exposure primarily involves decontamination and symptomatic management:
Decontamination: This includes moving the individual to an area with fresh air, removing contaminated clothing, and washing the affected areas with soap and water. For eye exposure, copious irrigation with normal saline or water may be necessary. Symptomatic Management: Treatment of respiratory and skin symptoms may be necessary. Some affected individuals might require supplemental oxygen or bronchodilators[3].
Legal and Ethical Aspects[edit]
The use of tear gas in warfare is prohibited by several international treaties, including the Chemical Weapons Convention. However, its use for domestic law enforcement is permitted in many jurisdictions. This raises ethical questions, especially when tear gas is used disproportionately or potentially harms bystanders[4].
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- <ref>1|Rothenberg, C., Achanta, S., Svendsen, E. R., & Jordt, S. E. (2016). Tear gas: an epidemiological and mechanistic reassessment. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1378(1), 96.</ref>
- <ref>2|Watson, K., & Riederer, A. M. (2016). Civilian exposure to toxic agents: emergency medical response. Emergency Medicine Clinics, 34(3), 495-514.</ref>
- <ref>3|Olajos, E. J., & Salem, H. (2001). Riot control agents: pharmacology, toxicology, biochemistry, and chemistry. Journal of applied toxicology, 21(5), 355-391.</ref>
- <ref>4|Davies, G. P., & O'Brien, R. J. (2019). Riot control agents. StatPearls [Internet].</ref>
|
|
|
| TRP channel modulators | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Ion channel modulators
|
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian


