Radish
Radish

Radish is a root vegetable that belongs to the Brassicaceae family. It is popular for its crispy texture and spicy flavor and is commonly used in salads, sandwiches, and as a garnish. Radishes are low in calories and high in nutrients, making them a healthy addition to any diet.
History
Radishes have been cultivated for thousands of years, with evidence of their cultivation dating back to ancient Egypt and Greece. They were brought to America by European colonizers in the 16th century and have since become a popular crop in North America.
Varieties

There are several varieties of radishes, each with its own unique flavor and appearance. Some of the most common varieties include:
Red Radish: Red radishes are the most common variety of radish and are characterized by their round shape and bright red skin.
Black Radish: Black radishes have a black or dark brown skin and a white, crisp interior. They have a milder flavor than red radishes.
White Radish: White radishes, also known as daikon radishes, are large and elongated with a white, juicy flesh. They have a mild flavor and are often used in Asian cuisine.
Watermelon Radish: Watermelon radishes are large and round with a green and white exterior and a pink or red interior. They have a sweet, mild flavor and are often used as a garnish.
Nutrition
Radishes are low in calories and high in nutrients, making them a healthy addition to any diet. They are a good source of vitamin C, folate, and potassium, and also contain small amounts of other essential vitamins and minerals.
Growing
Radishes are easy to grow and can be grown in a variety of soil types. They prefer cool temperatures and can be planted in early spring or fall. They grow quickly and can be harvested in as little as 30 days.
Culinary Uses
Radishes are a versatile vegetable that can be used in a variety of culinary applications. They are commonly used in salads, sandwiches, and as a garnish. They can also be pickled or roasted for a unique flavor.
Health Benefits
In addition to being low in calories and high in nutrients, radishes have several health benefits. They are high in antioxidants, which can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease. They also have anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce inflammation in the body.
Selection and Storage
When selecting radishes, look for firm, smooth, and unblemished roots. Avoid radishes that are soft, wrinkled, or discolored. To store radishes, remove the greens and store the roots in a plastic bag in the refrigerator. They will keep for up to a week.
Preparation
To prepare radishes, wash them thoroughly and remove the greens. The greens can be used in salads or sautéed as a side dish. The roots can be sliced, diced, or grated and used in a variety of dishes.
Fun Facts
In some cultures, radishes are carved into intricate shapes and used as a garnish for special occasions. Radishes were once used as a medicinal plant to treat ailments such as constipation and jaundice. Radishes are sometimes referred to as "the king of the salad."
Conclusion
Radishes are a versatile and nutritious vegetable that can be used in a variety of culinary applications. They are low in calories and high in nutrients, making them a healthy addition to any diet. With several varieties to choose from, there is a radish to suit every taste preference.
References
<references/>root
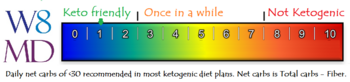
Keto scale Radish
W8MD's Ketometer rating scale zero to 10.
- Lower the number, better it is on a keto or low carb diet
- Net carbs is calculated by total carbohydrates minus fiber
Also see carb counter
Interesting facts about Radish
- Are you aware that radishes originated thousands of years ago in China, Egypt and Greece?
- Are you aware that radishes are root vegetables and grow underground?
- Are you aware that radishes have leafy green tops that grow above ground?
- Are you aware that some people eat the spicy leaves of the radish?

- Are you aware that the biggest crops of radishes in the U.S. are grown in California and Florida?
- Are you aware that there are many varieties of radishes but the “Red Globe’ is the most popular in the U.S.?
- Are you aware that the radish common to the U.S. is primarily red in color?
- Are you aware that this common radish is small and round or oval in shape?
- Are you aware that the round red radish is approximately 1 inch in diameter?
- Are you aware that this red radish has a solid, crisp flesh?

- Are you aware that the red round radish is crunchy, crispy and has a peppery flavor?
- Are you aware that radishes are a favorite in home, school and children’s gardens because they grow rapidly and are ready in 3 to 4 weeks? (Radishes are usually the first vegetable to come up in the spring.)
- Are you aware that radishes are sometimes sold in bunches with their leaves attached?
- Are you aware that that because the leaves yellow quickly, radishes are usually sold with the tops removed and are packaged in plastic bags?

- Are you aware that red radishes are usually eaten raw in salads or added to raw vegetable platters?
- Are you aware that you can make decorative roses out of radishes? (Simply make 1 or 2 rows of deep slashes all around the radish. Then put the radish in ice water and refrigerate until the petals swell and curl out into a flower shape.)
Nutritional information on Radish
|
|
 |
| Food Portal | Food | Nutrition | Diet | Keto | Glycemic index |
NB:Carbohydrate, by difference(total carbs-fiber) is also called net carbs
| Types of fruits | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian

