Antihypertensive: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
File:Propranolol.svg|Propranolol | File:Propranolol.svg|Propranolol | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
== Antihypertensive == | |||
'''Antihypertensives''' are a class of drugs that are used to treat [[hypertension]] (high blood pressure). Hypertension is a common condition that can lead to serious complications such as [[stroke]], [[heart attack]], and [[kidney failure]]. Antihypertensive medications work by various mechanisms to lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of these complications. | |||
== Classes of Antihypertensive Drugs == | |||
There are several classes of antihypertensive drugs, each working through different mechanisms: | |||
=== Diuretics === | |||
[[Diuretics]] help the kidneys remove excess salt and water from the body, which decreases blood volume and lowers blood pressure. Common diuretics include [[thiazide diuretics]], [[loop diuretics]], and [[potassium-sparing diuretics]]. | |||
=== Beta Blockers === | |||
[[Beta blockers]] reduce blood pressure by blocking the effects of [[epinephrine]] (adrenaline) and slowing the heart rate. They are often used in patients with [[angina]] or [[heart failure]]. | |||
=== ACE Inhibitors === | |||
[[Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors]] (ACE inhibitors) prevent the formation of [[angiotensin II]], a substance that narrows blood vessels. This helps to relax blood vessels and lower blood pressure. | |||
=== Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers === | |||
[[Angiotensin II receptor blockers]] (ARBs) block the action of angiotensin II, allowing blood vessels to remain open. They are often used as an alternative to ACE inhibitors. | |||
=== Calcium Channel Blockers === | |||
[[Calcium channel blockers]] prevent calcium from entering the cells of the heart and blood vessel walls, leading to relaxed blood vessels and lower blood pressure. | |||
=== Alpha Blockers === | |||
[[Alpha blockers]] reduce nerve impulses that tighten blood vessels, allowing blood to flow more freely. | |||
=== Central Agonists === | |||
[[Central agonists]] decrease blood pressure by preventing the brain from sending signals to the nervous system to increase heart rate and narrow blood vessels. | |||
=== Vasodilators === | |||
[[Vasodilators]] directly relax the muscles in the blood vessel walls, causing the vessels to widen and lower blood pressure. | |||
== Mechanism of Action == | |||
Antihypertensive drugs work through various mechanisms to lower blood pressure: | |||
* '''Volume Reduction:''' Diuretics reduce blood volume by increasing urine output. | |||
* '''Heart Rate Reduction:''' Beta blockers slow the heart rate and reduce cardiac output. | |||
* '''Vasodilation:''' ACE inhibitors, ARBs, calcium channel blockers, and vasodilators relax blood vessels. | |||
* '''Sympathetic Nervous System Inhibition:''' Alpha blockers and central agonists reduce nerve signals that increase blood pressure. | |||
== Side Effects == | |||
Antihypertensive medications can have side effects, which vary depending on the class of drug. Common side effects include: | |||
* '''Diuretics:''' Electrolyte imbalance, dehydration. | |||
* '''Beta Blockers:''' Fatigue, cold extremities, bradycardia. | |||
* '''ACE Inhibitors:''' Cough, elevated blood potassium levels. | |||
* '''ARBs:''' Dizziness, headache. | |||
* '''Calcium Channel Blockers:''' Swelling, constipation. | |||
* '''Alpha Blockers:''' Dizziness, headache. | |||
* '''Central Agonists:''' Drowsiness, dry mouth. | |||
* '''Vasodilators:''' Headache, flushing. | |||
== Related Pages == | |||
* [[Hypertension]] | |||
* [[Cardiovascular disease]] | |||
* [[Renin-angiotensin system]] | |||
* [[Blood pressure]] | |||
{{Pharmacology}} | |||
{{Cardiology}} | |||
[[Category:Antihypertensive agents]] | |||
[[Category:Cardiovascular drugs]] | |||
Latest revision as of 00:38, 19 February 2025
Antihypertensive[edit]
-
Hydrochlorothiazide
-
Captopril
-
Valsartan
-
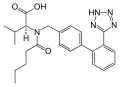
Propranolol
Antihypertensive[edit]
Antihypertensives are a class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure). Hypertension is a common condition that can lead to serious complications such as stroke, heart attack, and kidney failure. Antihypertensive medications work by various mechanisms to lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of these complications.
Classes of Antihypertensive Drugs[edit]
There are several classes of antihypertensive drugs, each working through different mechanisms:
Diuretics[edit]
Diuretics help the kidneys remove excess salt and water from the body, which decreases blood volume and lowers blood pressure. Common diuretics include thiazide diuretics, loop diuretics, and potassium-sparing diuretics.
Beta Blockers[edit]
Beta blockers reduce blood pressure by blocking the effects of epinephrine (adrenaline) and slowing the heart rate. They are often used in patients with angina or heart failure.
ACE Inhibitors[edit]
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors) prevent the formation of angiotensin II, a substance that narrows blood vessels. This helps to relax blood vessels and lower blood pressure.
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers[edit]
Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) block the action of angiotensin II, allowing blood vessels to remain open. They are often used as an alternative to ACE inhibitors.
Calcium Channel Blockers[edit]
Calcium channel blockers prevent calcium from entering the cells of the heart and blood vessel walls, leading to relaxed blood vessels and lower blood pressure.
Alpha Blockers[edit]
Alpha blockers reduce nerve impulses that tighten blood vessels, allowing blood to flow more freely.
Central Agonists[edit]
Central agonists decrease blood pressure by preventing the brain from sending signals to the nervous system to increase heart rate and narrow blood vessels.
Vasodilators[edit]
Vasodilators directly relax the muscles in the blood vessel walls, causing the vessels to widen and lower blood pressure.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Antihypertensive drugs work through various mechanisms to lower blood pressure:
- Volume Reduction: Diuretics reduce blood volume by increasing urine output.
- Heart Rate Reduction: Beta blockers slow the heart rate and reduce cardiac output.
- Vasodilation: ACE inhibitors, ARBs, calcium channel blockers, and vasodilators relax blood vessels.
- Sympathetic Nervous System Inhibition: Alpha blockers and central agonists reduce nerve signals that increase blood pressure.
Side Effects[edit]
Antihypertensive medications can have side effects, which vary depending on the class of drug. Common side effects include:
- Diuretics: Electrolyte imbalance, dehydration.
- Beta Blockers: Fatigue, cold extremities, bradycardia.
- ACE Inhibitors: Cough, elevated blood potassium levels.
- ARBs: Dizziness, headache.
- Calcium Channel Blockers: Swelling, constipation.
- Alpha Blockers: Dizziness, headache.
- Central Agonists: Drowsiness, dry mouth.
- Vasodilators: Headache, flushing.
Related Pages[edit]
| Pharmacology | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Cardiovascular disease A-Z
Most common cardiac diseases
- Cardiac arrhythmia
- Cardiogenetic disorders
- Cardiomegaly
- Cardiomyopathy
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
- Chronic rheumatic heart diseases
- Congenital heart defects
- Heart neoplasia
- Ischemic heart diseases
- Pericardial disorders
- Syndromes affecting the heart
- Valvular heart disease
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z
A[edit]
- Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
- Acute decompensated heart failure
- Arteriosclerotic heart disease
- Athletic heart syndrome
- Atrial flutter
- Atrioventricular fistula
- Cardiovascular disease in Australia
- Autoimmune heart disease
B[edit]
C[edit]
- Ebb Cade
- Cardiac allograft vasculopathy
- Cardiac amyloidosis
- Cardiac asthma
- Cardiac tamponade
- Cardiogenic shock
- Cardiogeriatrics
- Cardiorenal syndrome
- Cardiotoxicity
- Carditis
- Coronary artery aneurysm
- Coronary artery anomaly
- Coronary artery disease
- Spontaneous coronary artery dissection
- Coronary artery ectasia
- Coronary occlusion
- Coronary steal
- Coronary thrombosis
- Coronary vasospasm
- Cœur en sabot
- Coxsackievirus-induced cardiomyopathy
D[edit]
E[edit]
H[edit]
- Heart attack
- Heart failure
- Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
- Heart to Heart (1949 film)
- High-output heart failure
- Hyperdynamic precordium
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z
I[edit]
- Idiopathic giant-cell myocarditis
- Interventricular dyssynchrony
- Intraventricular dyssynchrony
- Isolated atrial amyloidosis
K[edit]
L[edit]
M[edit]
- Mydicar
- Myocardial bridge
- Myocardial disarray
- Myocardial rupture
- Myocardial scarring
- Myocardial stunning
- Myocarditis
N[edit]
O[edit]
P[edit]
- Papillary fibroelastoma
- Pathophysiology of heart failure
- Postpericardiotomy syndrome
- Pulmonary vein stenosis
R[edit]
S[edit]
- Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease
- SCAR-Fc
- Shone's syndrome
- Strain pattern
- Subacute bacterial endocarditis
- Sudden cardiac death of athletes
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z