Ainhum
| Ainhum | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Dactylolysis spontanea |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
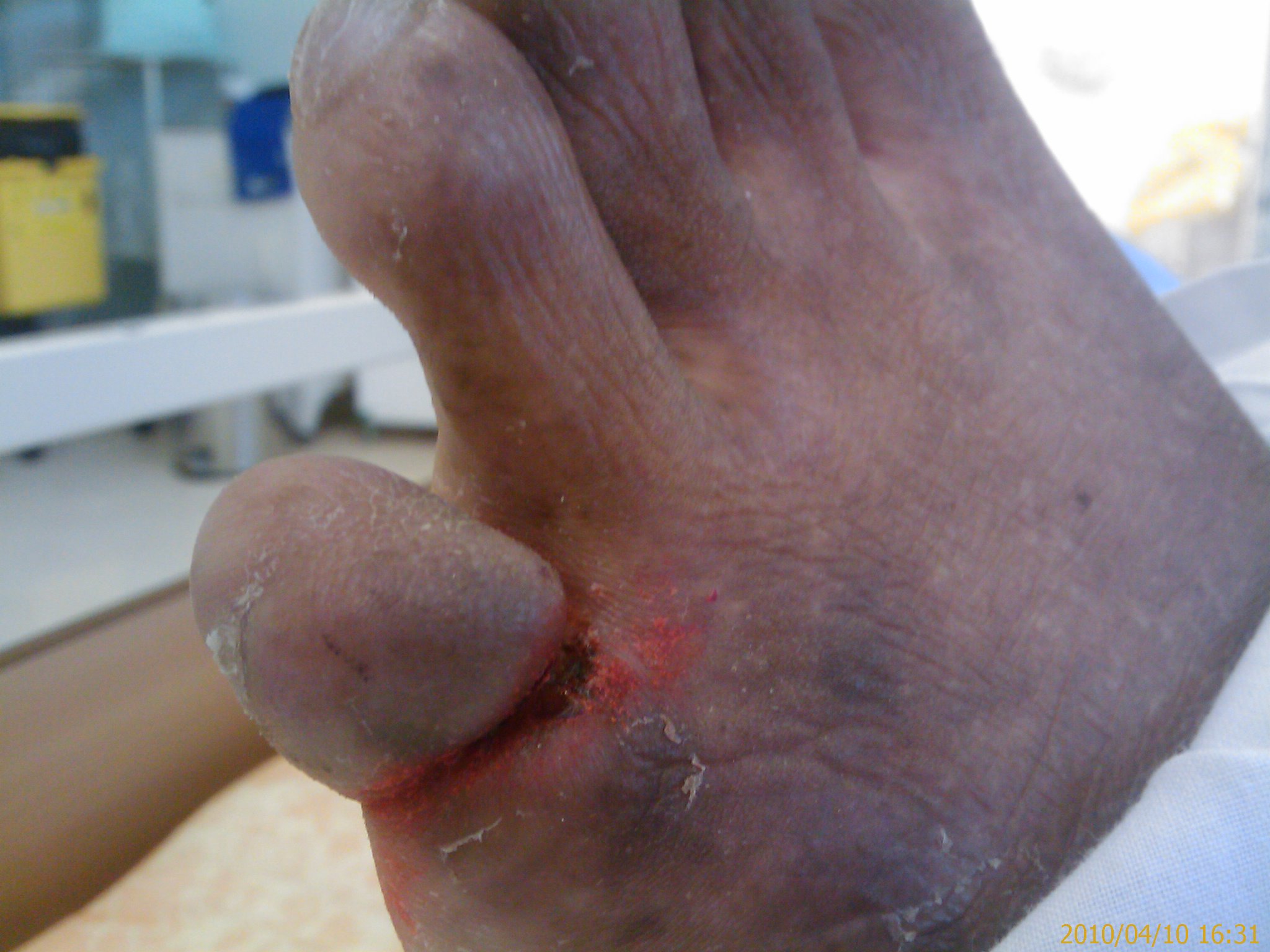
| Symptoms | Progressive constriction of the toe, usually the fifth toe |
| Complications | Autoamputation of the toe |
| Onset | Typically between ages 20 and 50 |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Unknown, possibly related to trauma or genetic predisposition |
| Risks | More common in individuals of African descent |
| Diagnosis | Clinical examination, X-ray |
| Differential diagnosis | Scleroderma, Psoriasis, Leprosy |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Surgical intervention, Z-plasty |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Good with treatment, but can lead to loss of the toe if untreated |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
== Alternate names ==
Spontaneous dactylolysis
Definition[edit]
- Ainhum is the autoamputation of a finger or toe as a result of a fibrotic band that constricts the finger or toe until it falls off.
- (in'-hum) [negro word, meaning to saw]. A disease of Guinea and Hindustan, peculiar to negroes, in which the little toes are slowly and spontaneously amputated at about the digitoplantar fold.
- The process is very slow, is unaccompanied by any constitu- tional symptoms, and its cause is unknown.
- It sometimes attacks the great toe.

Epidemiology[edit]
Ainhum has a prevalence worldwide but is most common in African countries. Despite this, the prevalence may be as low as 0.015 of the population of African countries.
Cause[edit]
- The cause of ainhum is not known. By definition, “true ainhum” must be idiopathic.
- This etiology is the differentiating feature from various forms of pseudoainhum which may be congenital, late-onset, or secondary to trauma.
- The common relationship between constricting bands of the feet and rural areas of Africa and South America has led to speculation about the trauma of walking barefoot in tropical regions.
Signs and symptoms[edit]
Clinically, the main feature is the progressive development of a circumscribed fibrotic ring at the base of the toes, or less frequently, the fingers. The most common location occurs over the fifth toe and may be bilateral.<ref>Maxfield L, Al Aboud DM. Ainhum. [Updated 2020 Jun 24]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546612/</ref>[1].
Clinical criteria include three findings:
- Soft tissue constriction
- Bulbous distal enlargement
- Distal thinning or lysis of phalangeal bones
Stages[edit]
- The disease may manifest through four clinical stages that are visible with radiography.
- First, a small callus develops and transforms into a circumferential groove or fissure.
- Next, the portion distant to the band becomes bulbous or globular secondary to impaired lymph and venous drainage with arterial narrowing.
- The third stage is typified by pain as the bone becomes separated in an intra-osseous or intra-articular location.
- The last stage is that of bloodless, spontaneous, auto-amputation.
Diagnosis[edit]
- Although primarily a clinical diagnosis, radiography can be useful to identify the extent of disease.
- Also, ainhum has correlations with progressive features that may be identifiable with plain films, ultrasound, computed tomography, or even magnetic resonance imaging. <ref>Maxfield L, Al Aboud DM. Ainhum. [Updated 2020 Jun 24]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546612/</ref>[2].
Treatment[edit]
- In early lesions, there have been attempts made with topical and injectable corticosteroids, retinoids, or salicylates.
- Reports exist of a case of pseudoainhum secondary to psoriasis responding to topical pimecrolimus, and low-dose narrowband UVB.
- Treatment of the constricting rings of fibrous tissue in stage-I and early stage-II disease may be treated similarly to scars and contractures.
- Resection of the band with subsequent z-plasty may prevent progression if performed early.
- Once stage-III and stage-IV disease have developed, surgical amputation or allowance for auto-amputation are the expected outcomes.<ref>Maxfield L, Al Aboud DM. Ainhum. [Updated 2020 Jun 24]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546612/</ref>[3].
References[edit]
<references />
| Bone and joint disease | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
NIH genetic and rare disease info[edit]
Ainhum is a rare disease.
| Rare and genetic diseases | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Rare diseases - Ainhum
|
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian


