Neuroanatomy: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
[[Category:Neuroanatomy| ]] | [[Category:Neuroanatomy| ]] | ||
[[Category:Nervous system]]{{stub}} | [[Category:Nervous system]]{{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
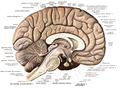
File:Sobo 1909 624.png|Neuroanatomy | |||
File:Parasagittal MRI of human head in patient with benign familial macrocephaly prior to brain injury (ANIMATED).gif|Neuroanatomy | |||
File:Bilaterian-plan.svg|Neuroanatomy | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:26, 20 February 2025
Neuroanatomy refers to the specialized branch of anatomy focusing on the structure and organization of the nervous system. Rooted in both ancient studies and modern science, neuroanatomy has evolved considerably, becoming essential in understanding how the brain and the nervous system function at both microscopic and macroscopic levels.

Introduction[edit]
Neuroanatomy delves deep into the structures of the nervous system, from individual neurons to the vast networks that they form. As the intricate structure of the brain and the rest of the nervous system is uncovered, it lays the foundation for various disciplines like neurology, neuropsychology, and neuroscience.
Central vs. Peripheral Nervous System[edit]
The nervous system is broadly categorized into two main sections:
- Central Nervous System (CNS): Comprising the brain and the spinal cord, the CNS is the primary control center, processing sensory information and directing responses.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): This system connects the CNS to the rest of the body and includes all neural structures outside of the brain and spinal cord.
Key Structures in Neuroanatomy[edit]
The Brain[edit]
The brain is a complex organ made up of several regions, each responsible for specific functions:
- Cerebrum: Involved in sensory interpretation, voluntary movements, and cognitive functions.
- Cerebellum: Coordinates muscular activities and maintains posture and balance.
- Brainstem: Controls various involuntary functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
Neurons[edit]
Neurons are the building blocks of the nervous system, transmitting electrical and chemical signals. They consist of:
- Dendrites: Receive messages from other neurons.
- Axon: Transmits messages to other neurons or muscles.
- Synapse: The junction where two neurons meet, facilitating signal transmission.
Applications in Medicine and Research[edit]
Understanding neuroanatomy has direct implications in fields such as:
- Neurosurgery: Surgical interventions on the nervous system.
- Neuropharmacology: The study of how drugs affect the nervous system.
- Neuroimaging: Techniques like MRI and CT scans used to visualize the structure and function of the nervous system.
|
|
|
| Anatomy and morphology | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|