Trichuriasis

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Trichuriasis | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Whipworm infection |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Abdominal pain, diarrhea, rectal prolapse, anemia |
| Complications | Malnutrition, growth retardation |
| Onset | |
| Duration | |
| Types | |
| Causes | Trichuris trichiura |
| Risks | Poor sanitation, contaminated soil |
| Diagnosis | Stool examination |
| Differential diagnosis | Hookworm infection, Amebiasis, Giardiasis |
| Prevention | Improved sanitation, handwashing |
| Treatment | Albendazole, Mebendazole |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment |
| Frequency | Affects approximately 604 million people worldwide |
| Deaths | N/A |
Other Names:
Whipworm infection; Trichocephaliasis
An infection that is caused by the nematode trichuris trichiura, a soil-transmitted helminth, which is transmitted via food and/or water contaminated with the eggs of the worm. Symptoms are usually mild and include abdominal pain, diarrhea, fatigue, and possibly anemia secondary to blood loss in diarrhea.
Cause[edit]
The nematode (roundworm) Trichuris trichiura, also called the human whipworm causes Trichuriasis.

Epidemiology & Risk Factors[edit]

Whipworm is a soil-transmitted helminth (STH) and is the third most common roundworm of humans. Whipworm causes an infection called trichuriasis and often occurs in areas where human feces is used as fertilizer or where defecation onto soil happens. The worms are spread from person to person by fecal-oral transmission or through feces-contaminated food. Worldwide, infection occurs more frequently in areas with tropical weather and poor sanitation practices, and among children. In 2002, the estimated number of persons infected with whipworm was 1 billion. Trichuriasis also occurs in the southern United States.
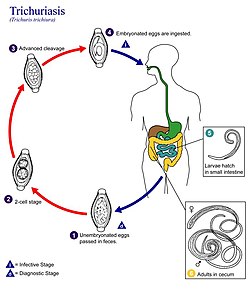
Life Cycle[edit]
The unembryonated eggs are passed with the stool The number 1. In the soil, the eggs develop into a 2-cell stage The number 2, an advanced cleavage stage The number 3, and then they embryonate The number 4; eggs become infective in 15 to 30 days. After ingestion (soil-contaminated hands or food), the eggs hatch in the small intestine, and release larvae The number 5 that mature and establish themselves as adults in the colon The number 6. The adult worms (approximately 4 cm in length) live in the cecum and ascending colon. The adult worms are fixed in that location, with the anterior portions threaded into the mucosa. The females begin to oviposit 60 to 70 days after infection. Female worms in the cecum shed between 3,000 and 20,000 eggs per day. The life span of the adults is about 1 year.
Symptoms[edit]
People infected with whipworm can suffer light or heavy infections. People with light infections usually have no symptoms. People with heavy symptoms can experience frequent, painful passage of stool that contains a mixture of mucus, water, and blood. Rectal prolapse can also occur. Heavy infection in children can lead to severe anemia, growth retardation, and impaired cognitive development. Whipworm infections are treatable with medication prescribed by your health care provider.
Diagnosis[edit]
The standard method for diagnosing the presence of whipworm is by microscopically identifying whipworm eggs in a stool sample. Because eggs may be difficult to find in light infections, a concentration procedure is recommended.
Treatment[edit]
Anthelminthic medications (drugs that rid the body of parasitic worms), such as albendazole and mebendazole, are the drugs of choice for treatment. Infections are generally treated for 3 days. The recommended medications are effective. Health care providers may decide to repeat a stool exam after treatment. Iron supplements may also be prescribed if the infected person suffers from anemia.
Prevention & Control[edit]
The best way to prevent whipworm infection is to always: Avoid ingesting soil that may be contaminated with human feces, including where human fecal matter (“night soil”) or wastewater is used to fertilize crops. Wash your hands with soap and warm water before handling food. Teach children the importance of washing hands to prevent infection. Wash, peel, or cook all raw vegetables and fruits before eating, particularly those that have been grown in soil that has been fertilized with manure.
| Parasitic disease caused by helminthiases | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian


