Taenia solium
Taenia solium, commonly known as the pork tapeworm, is a parasitic flatworm that belongs to the class Cestoda in the phylum Platyhelminthes. It is a significant public health concern in many parts of the world, particularly in regions where pork is commonly consumed and sanitation practices are inadequate. This article provides an overview of Taenia solium, including its lifecycle, transmission, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
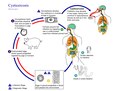
Lifecycle[edit]
The lifecycle of Taenia solium involves two hosts: humans and pigs. Humans serve as the definitive hosts, harboring the adult tapeworm in the intestines, while pigs act as intermediate hosts, carrying the larval form, known as cysticerci. The lifecycle begins when humans excrete tapeworm eggs in their feces, which can contaminate the environment and infect pigs. Pigs become infected by ingesting these eggs, which hatch in the intestine, releasing oncospheres that penetrate the intestinal wall and circulate to various tissues, developing into cysticerci. Humans can then become infected by consuming undercooked or raw pork containing these cysticerci. Once ingested, the cysticerci develop into adult tapeworms in the human intestine, completing the cycle.
Transmission[edit]
Transmission of Taenia solium occurs through the consumption of undercooked or raw pork contaminated with cysticerci. Additionally, humans can become infected with the larval stage of the tapeworm, leading to cysticercosis, by ingesting eggs through fecal-oral contamination. This can occur through direct contact with an infected person or by consuming contaminated food or water.
Clinical Manifestations[edit]
Infection with the adult tapeworm, known as taeniasis, is often asymptomatic but can cause nonspecific gastrointestinal symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, and weight loss. Cysticercosis, the infection caused by the larval stage, can have more serious consequences, particularly when cysticerci lodge in the central nervous system, leading to neurocysticercosis. Neurocysticercosis can cause a range of neurological symptoms, including seizures, headaches, and cognitive impairments.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of taeniasis involves the detection of tapeworm eggs or proglottids in feces through microscopic examination. Serological tests can help diagnose cysticercosis by detecting antibodies or antigens related to Taenia solium. Imaging techniques, such as CT or MRI scans, are crucial for diagnosing neurocysticercosis by visualizing cysts in the brain.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for taeniasis includes the administration of antiparasitic medications, such as praziquantel or niclosamide, to eliminate the adult tapeworm. Treatment for cysticercosis may involve antiparasitic drugs, anti-inflammatory agents, and, in cases of neurocysticercosis, antiepileptic drugs to manage seizures. Surgical intervention may be necessary to remove cysts in certain situations.
Prevention[edit]
Prevention of Taenia solium infection focuses on improving sanitation and hygiene practices to prevent fecal-oral transmission, thoroughly cooking pork to kill cysticerci, and controlling the infection in pigs through veterinary interventions and proper farm management practices.
See Also[edit]
-
Scolex of Taenia solium
-
Taenia solium
-
Scolex of Taenia solium at 400x magnification
-
Egg of Taenia
-
Life cycle of Taenia solium
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian