Ornithine oxoglutarate: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
{{Sports nutrition}} | {{Sports nutrition}} | ||
{{Biochemistry-stub}} | {{Biochemistry-stub}} | ||
== Ornithine_oxoglutarate == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:L-Ornithin2.svg|L-Ornithine | |||
File:2-oxopentanedioic_acid_200.svg|2-Oxopentanedioic acid | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 23:59, 24 February 2025
Ornithine oxoglutarate (also known as Ornithine alpha-ketoglutarate, OKG, or OAKG) is a salt formed from the amino acid Ornithine and the alpha-keto acid Alpha-ketoglutarate. It is a dietary supplement often used in clinical nutrition and sports nutrition.
Chemistry[edit]
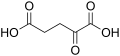
Ornithine oxoglutarate is a salt formed from the combination of one molecule of ornithine and one molecule of alpha-ketoglutarate. Ornithine is a non-proteinogenic amino acid that plays a role in the Urea cycle, while alpha-ketoglutarate is a key intermediate in the Krebs cycle.
Uses[edit]
Ornithine oxoglutarate is used in clinical nutrition to support the nutritional needs of critically ill patients, particularly those with liver disease. It is also used in sports nutrition to support muscle growth and recovery.
Clinical Nutrition[edit]
In clinical nutrition, ornithine oxoglutarate is used to support the nutritional needs of critically ill patients. It is particularly beneficial for patients with liver disease, as it supports the urea cycle and helps to remove excess ammonia from the body.
Sports Nutrition[edit]
In sports nutrition, ornithine oxoglutarate is used to support muscle growth and recovery. It is believed to enhance the body's production of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), both of which play a key role in muscle growth and recovery.
Safety and Side Effects[edit]
Ornithine oxoglutarate is generally considered safe when used as directed. However, as with any dietary supplement, it should be used under the supervision of a healthcare provider. Potential side effects may include gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea, and diarrhea.
See Also[edit]
| Encoded (proteinogenic) amino acids | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Clinical Nutrition | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This clinical nutrition related article is a stub.
|
| Sports nutrition | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This sports nutrition related article is a stub.
|

This article is a biochemistry stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Ornithine_oxoglutarate[edit]
-
L-Ornithine
-
2-Oxopentanedioic acid