Body mass index

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
Body mass index (BMI) is a widely used measure to estimate body fat based on an individual's height and weight. It serves as a simple screening tool to categorize individuals as underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese.
Calculation of BMI[edit]
BMI is calculated using either the metric or imperial system.
Metric formula[edit]
BMI = weight (kg) / height (m)2
Since height is often measured in centimeters, it should be converted to meters before using the formula.
Example:
- Weight = 68 kg
- Height = 165 cm = 1.65 m
- Calculation: 68 / (1.65)2 = 24.98
Imperial formula[edit]
BMI = (weight (lb) / height (in)2) x 703
Example:
- Weight = 150 lbs
- Height = 5'5" = 65 in
- Calculation: (150 / (65)2) x 703 = 24.96
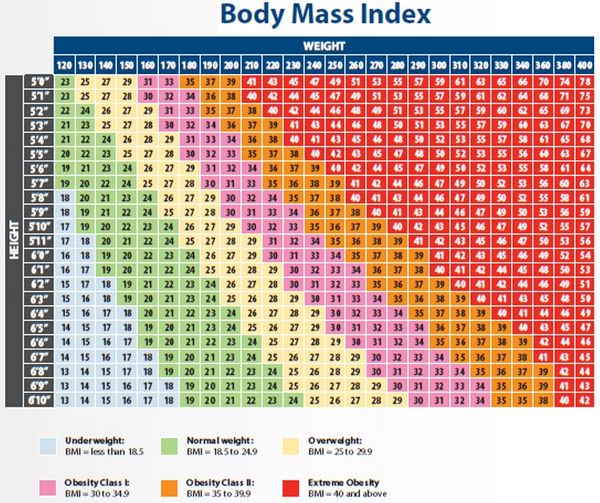
Interpretation of BMI for Adults[edit]
For adults aged 20 years and older, BMI is interpreted using standard weight status categories. It helps estimate health risks related to excess body fat, such as:
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Type 2 diabetes
- Gallstones
- Breathing problems
- Certain types of cancer
Limitations of BMI[edit]
While BMI is useful for general population screening, it has limitations:
- May overestimate body fat in individuals with a muscular build (e.g., athletes)
- May underestimate body fat in elderly individuals and others with low muscle mass
Adult BMI Categories[edit]
- Below 18.5: Underweight
- 18.5–24.9: Normal weight
- 25.0–29.9: Overweight
- 30.0–34.9: Class I Obesity (Mild)
- 35.0–39.9: Class II Obesity (Moderate)
- 40.0 and above: Class III Obesity (Severe or Morbid)
BMI for Children and Teens[edit]
Although BMI is calculated the same way for children and teens as for adults, its interpretation differs. Age- and sex-specific percentiles are used to account for:
- Changes in body fat with age
- Differences in body fat between boys and girls
These percentiles are based on growth charts and are used to determine whether a child or teen is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese.
Adult Body Mass Index Chart[edit]
| WEIGHT | 4'8" | 4'9" | 4'10" | 4'11" | 5'0" | 5'1" | 5'2" | 5'3" | 5'4" | 5'5" | 5'6" | 5'7" | 5'8" | 5'9" | 5'10" | 5'11" | 6'0" | 6'1" | 6'2" | 6'3" | 6'4" | 6'5" | |
| lbs | (kg) | 142cm | 147.32 | 149.86 | 152.4 | 154.94 | 157.48 | 160.02 | 162.56 | 165.1 | 167.64 | 170.18 | 172.72 | 175.26 | 177.8 | 180.34 | 182.88 | 185.42 | 187.96 | 190.5 | 193.04 | 195.58 | |
| 260 | (117.9) | 58 | 56 | 54 | 53 | 51 | 49 | 48 | 46 | 45 | 43 | 42 | 41 | 40 | 38 | 37 | 36 | 35 | 34 | 33 | 32 | 32 | 31 |
| 255 | (115.7) | 57 | 55 | 53 | 51 | 50 | 48 | 47 | 45 | 44 | 42 | 41 | 40 | 39 | 38 | 37 | 36 | 35 | 34 | 33 | 32 | 31 | 30 |
| 250 | (113.4) | 56 | 54 | 52 | 50 | 49 | 47 | 46 | 44 | 43 | 42 | 40 | 39 | 38 | 37 | 36 | 35 | 34 | 33 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 30 |
| 245 | (111.1) | 55 | 53 | 51 | 49 | 48 | 46 | 45 | 43 | 42 | 41 | 40 | 38 | 37 | 36 | 35 | 34 | 33 | 32 | 31 | 31 | 30 | 29 |
| 240 | (108.9) | 54 | 52 | 50 | 48 | 47 | 45 | 44 | 43 | 41 | 40 | 39 | 38 | 36 | 35 | 34 | 33 | 33 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 |
| 235 | (106.6) | 53 | 51 | 49 | 47 | 46 | 44 | 43 | 42 | 40 | 39 | 38 | 37 | 36 | 35 | 34 | 33 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 29 | 29 | 28 |
| 230 | (104.3) | 52 | 50 | 48 | 46 | 45 | 43 | 42 | 41 | 39 | 38 | 37 | 36 | 35 | 34 | 33 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 |
| 225 | (102.1) | 50 | 49 | 47 | 45 | 44 | 43 | 41 | 40 | 39 | 37 | 36 | 35 | 34 | 33 | 32 | 31 | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 27 |
| 220 | (99.8) | 49 | 48 | 46 | 44 | 43 | 42 | 40 | 39 | 38 | 37 | 36 | 34 | 33 | 32 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 27 | 26 |
| 215 | (97.5) | 48 | 47 | 45 | 43 | 42 | 41 | 39 | 38 | 37 | 36 | 35 | 34 | 33 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 |
| 210 | (95.3) | 47 | 45 | 44 | 42 | 41 | 40 | 38 | 37 | 36 | 35 | 34 | 33 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 26 | 25 |
| 205 | (93.0) | 46 | 44 | 43 | 41 | 40 | 39 | 37 | 36 | 35 | 34 | 33 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 29 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 26 | 25 | 24 |
| 200 | (90.7) | 45 | 43 | 42 | 40 | 39 | 38 | 37 | 35 | 34 | 33 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 24 |
| 195 | (88.5) | 44 | 42 | 41 | 39 | 38 | 37 | 36 | 35 | 33 | 32 | 31 | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 24 | 23 |
| 190 | (86.2) | 43 | 41 | 40 | 38 | 37 | 36 | 35 | 34 | 33 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 24 | 23 | 23 |
| 185 | (83.9) | 41 | 40 | 39 | 37 | 36 | 35 | 34 | 33 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 24 | 23 | 23 | 22 |
| 180 | (81.6) | 40 | 39 | 38 | 36 | 35 | 34 | 33 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 22 | 21 |
| 175 | (79.4) | 39 | 38 | 37 | 35 | 34 | 33 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 22 | 21 | 21 |
| 170 | (77.1) | 38 | 37 | 36 | 34 | 33 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 22 | 21 | 21 | 20 |
| 165 | (74.8) | 37 | 36 | 34 | 33 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 22 | 21 | 21 | 20 | 20 |
| 160 | (72.6) | 36 | 35 | 33 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 22 | 21 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 19 |
| 155 | (70.3) | 35 | 34 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 20 | 19 | 19 | 18 |
| 150 | (68.0) | 34 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 23 | 22 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 20 | 19 | 19 | 18 | 18 |
| 145 | (65.8) | 33 | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 21 | 20 | 20 | 19 | 19 | 18 | 18 | 17 |
| 140 | (63.5) | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 21 | 20 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 17 |
| 135 | (61.2) | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 22 | 21 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 19 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 16 | 16 |
| 130 | (59.0) | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 20 | 19 | 19 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 16 | 16 | 15 |
| 125 | (56.7) | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 21 | 20 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 15 | 15 |
| 120 | (54.4) | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 19 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 16 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 14 |
| 115 | (52.2) | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 20 | 19 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 14 | 14 | 14 |
| 110 | (49.9) | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 19 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 16 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 14 | 14 | 13 | 13 |
| 105 | (47.6) | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 14 | 14 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 12 |
| 100 | (45.4) | 22 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 16 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 13 | 13 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 95 | (43.1) | 21 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 16 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 11 |
| 90 | (40.8) | 20 | 19 | 19 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 14 | 14 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 11 | 11 | 11 |
| 85 | (38.6) | 19 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 17 | 16 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 14 | 14 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 10 | 10 |
| 80 | (36.3) | 18 | 17 | 17 | 16 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 14 | 14 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 12 | 12 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 9 |
Source: BRFSS survey data from CDC
Limitations of BMI[edit]
Although BMI is widely used as a screening tool for body fat, it has some limitations. BMI does not distinguish between fat and muscle, which can result in an inaccurate classification of body fat in athletes and individuals with a muscular build. Additionally, BMI does not take into account body composition or distribution of body fat, which can impact health outcomes. For example, visceral fat, which is located deep in the abdomen and surrounds organs, is associated with an increased risk of metabolic disorders such as Type 2 Diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Usefulness of BMI[edit]
Despite its limitations, BMI remains a useful tool for population-level screening for overweight and obesity. It can be used to estimate the prevalence of overweight and obesity in a population and to track changes over time. BMI can also be used as a starting point for discussions between healthcare providers and patients about weight-related health risks and the need for lifestyle changes.
Distribution of body weight by percentage distribution adults - 2012[edit]
| State: | Underweight (bmi 12.0-18.4) | Normal Weight (bmi 18.5-24.9) | Overweight (bmi 25.0-29.9) | Obese (bmi 30.0 - 99.8) |
| Nationwide (States, DC, and Territories) | 1.8 | 34.2 | 35.8 | 28.1 |
| Nationwide (States and DC) | 1.8 | 34.2 | 35.8 | 27.6 |
| Alabama | 1.7 | 30.6 | 34.8 | 33.0 |
| Alaska | 0.9 | 34.4 | 39.1 | 25.7 |
| Arizona | 2.3 | 35.7 | 36.0 | 26.0 |
| Arkansas | 1.8 | 29.5 | 34.2 | 34.5 |
| California | 1.9 | 37.8 | 35.3 | 25.0 |
| Colorado | 2.3 | 42.0 | 35.2 | 20.5 |
| Connecticut | 1.7 | 36.1 | 36.7 | 25.6 |
| Delaware | 1.5 | 32.5 | 39.1 | 26.9 |
| District of Columbia | 2.2 | 46.0 | 30.0 | 21.9 |
| Florida | 1.5 | 36.4 | 36.9 | 25.2 |
| Georgia | 2.0 | 33.3 | 35.5 | 29.1 |
| Guam | 2.9 | 35.6 | 32.4 | 29.1 |
| Hawaii | 2.7 | 41.2 | 32.5 | 23.6 |
| Idaho | 1.8 | 35.7 | 35.8 | 26.8 |
| Illinois | 2.2 | 33.8 | 35.8 | 28.1 |
| Indiana | 1.7 | 32.8 | 34.1 | 31.4 |
| Iowa | 1.8 | 33.5 | 34.3 | 30.4 |
| Kansas | 2.0 | 32.4 | 35.7 | 29.9 |
| Kentucky | 2.0 | 31.1 | 35.6 | 31.3 |
| Louisiana | 1.9 | 28.5 | 34.8 | 34.7 |
| Maine | 1.6 | 34.3 | 35.8 | 28.4 |
| Maryland | 2.0 | 34.2 | 36.2 | 27.6 |
| Massachusetts | 2.1 | 39.2 | 35.9 | 22.9 |
| Michigan | 1.6 | 32.8 | 34.6 | 31.1 |
| Minnesota | 1.6 | 35.4 | 37.3 | 25.7 |
| Mississippi | 1.8 | 29.3 | 34.3 | 34.6 |
| Missouri | 1.9 | 32.4 | 36.2 | 29.6 |
| Montana | 1.5 | 37.1 | 37.0 | 24.3 |
| Nebraska | 1.7 | 33.3 | 36.4 | 28.6 |
| Nevada | 2.7 | 34.8 | 36.3 | 26.2 |
| New Hampshire | 1.4 | 36.5 | 34.8 | 27.3 |
| New Jersey | 1.9 | 36.5 | 37.0 | 24.6 |
| New Mexico | 2.2 | 35.0 | 35.7 | 27.1 |
| New York | 2.6 | 36.9 | 37.0 | 23.6 |
| North Carolina | 1.8 | 32.4 | 36.3 | 29.6 |
| North Dakota | 1.8 | 32.0 | 36.6 | 29.7 |
| Ohio | 1.7 | 33.0 | 35.2 | 30.1 |
| Oklahoma | 1.8 | 30.4 | 35.6 | 32.2 |
| Oregon | 1.7 | 37.2 | 33.8 | 27.3 |
| Pennsylvania | 1.7 | 33.3 | 35.9 | 29.1 |
| Puerto Rico | 2.1 | 31.7 | 37.8 | 28.4 |
| Rhode Island | 1.6 | 35.5 | 37.2 | 25.7 |
| South Carolina | 1.5 | 32.4 | 34.5 | 31.6 |
| South Dakota | 1.5 | 32.4 | 37.9 | 28.1 |
| Tennessee | 2.0 | 32.7 | 34.2 | 31.1 |
| Texas | 1.8 | 33.2 | 35.9 | 29.2 |
| Utah | 1.8 | 40.4 | 33.5 | 24.3 |
| Vermont | 1.7 | 38.0 | 36.6 | 23.7 |
| Virginia | 2.0 | 34.4 | 36.2 | 27.4 |
| Washington | 1.8 | 36.0 | 35.4 | 26.8 |
| West Virginia | 1.7 | 30.0 | 34.5 | 33.8 |
| Wisconsin | 1.8 | 31.8 | 36.8 | 29.7 |
| Wyoming | 1.5 | 35.1 | 38.7 | 24.6 |
Children BMI calculator[edit]
The formulas used in children are different as their weight is based on growth charts and do not correspond to adult BMI scale numbers. Use an online childhood BMI calculators below.
BMI Calculators[edit]
See also[edit]
Tired of Being Overweight?[edit]
Achieve lasting results with W8MD's proven weight loss program, trusted by thousands since 2011. Our comprehensive approach tackles weight gain factors like insulin resistance to help you lose weight and keep it off.

Tailored Weight Loss Solutions[edit]
W8MD offers personalized weight loss plans, including FDA-approved medications and GLP-1 injections, such as:
Other options include:
We also offer nutritious, low-glycemic foods and meal replacements to keep you on track.
Convenient Locations[edit]
W8MD provides weight loss services in Brooklyn, New York and Greater Philadelphia, with tailored plans and GLP-1 weight loss injections.
Looking for a weight loss clinic in Brooklyn or weight loss doctors in NYC? W8MD's expert team is here to help.

Weight Loss Doctor in NYC[edit]
Trust W8MD's best weight loss doctors in NYC for personalized solutions, including wiki Physician Weight Loss Program and GLP-1 injections.
W8MD Weight Loss Clinic in Philadelphia[edit]
W8MD in Philadelphia offers FDA-approved medications and weight loss injections. Visit our medical weight loss clinic for expert care.
Find the best weight loss tips in Philadelphia with W8MD.
Take the First Step[edit]
Book your consultation today and start your journey:
- Visit W8MD Official Site
- Check out Yelp reviews
- Schedule via Patient Fusion
Call now for medical weight loss:
- NYC: 718-946-5500
- Philadelphia: 215-676-2334
Explore W8MD's NYC Physician Weight Loss Program now!
- Individual results may vary!
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian