Atrial fibrillation

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Atrial fibrillation | |
|---|---|
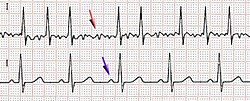
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Palpitations, fainting, shortness of breath, chest pain |
| Complications | Stroke, heart failure |
| Onset | Sudden or gradual |
| Duration | Can be paroxysmal, persistent, or permanent |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | High blood pressure, valvular heart disease, coronary artery disease, hyperthyroidism, alcohol use disorder |
| Risks | Age, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, heart disease, obesity, sleep apnea |
| Diagnosis | ECG, Holter monitor, event monitor |
| Differential diagnosis | Atrial flutter, supraventricular tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Rate control, rhythm control, anticoagulation |
| Medication | Beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, digoxin, antiarrhythmic drugs, warfarin, direct oral anticoagulants |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on underlying conditions and treatment |
| Frequency | Common, especially in older adults |
| Deaths | N/A |
Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a type of arrhythmia characterized by an irregular and often rapid heart rhythm that originates in the atria, the upper chambers of the heart. This abnormal rhythm can impair the heart's ability to efficiently pump blood, increasing the risk of serious complications such as stroke, heart failure, and blood clots.

Types of Atrial Fibrillation[edit]
Atrial fibrillation can be classified into four major types based on duration and response to treatment:
Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation[edit]
Paroxysmal AF occurs intermittently and resolves spontaneously within 7 days, often within 24 hours. It may be asymptomatic or cause noticeable palpitations. When paroxysmal AF alternates with bradycardia, the condition is called tachybrady syndrome.
Persistent atrial fibrillation[edit]
This type of AF persists for more than 7 days and typically requires medical intervention, such as cardioversion, to restore normal rhythm.
Long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation[edit]
AF that continues for more than 12 months. It is often resistant to treatment and may lead to structural changes in the heart.
Permanent atrial fibrillation[edit]
When AF cannot be restored to normal rhythm despite attempts at treatment or when the decision is made not to pursue rhythm control, it is termed permanent.
Causes[edit]

AF results from abnormalities in the heart's electrical conduction system and structural changes in cardiac tissue. Common causes include:
- Hypertension
- Ischemic heart disease
- Heart valve disease
- Cardiomyopathy
- Congenital heart defect
- Hyperthyroidism
- Sleep apnea
- Alcohol abuse ("Holiday heart syndrome")
- Postoperative changes (especially after cardiac surgery)
- Pericarditis or myocarditis
- Aging-related fibrosis
Risk Factors[edit]
Several risk factors are associated with increased likelihood of developing AF:
- Advanced age (especially >65 years)
- Family history
- Obesity
- Diabetes mellitus
- Chronic kidney disease
- Pulmonary diseases (e.g., COPD)
- Excessive alcohol or stimulant use
- Sedentary lifestyle or extreme endurance training
- Thyroid disorders
Signs and Symptoms[edit]
Symptoms of AF vary in severity and may include:
- Palpitations
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness or syncope
- Chest pain
- Hypotension
Some patients may remain asymptomatic, and AF is discovered incidentally.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of AF typically involves:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) – confirms the absence of P waves and irregularly irregular ventricular response.
- Echocardiography – assesses structural abnormalities, thrombus formation.
- Holter monitor – records rhythm over 24–48 hours.
- Event monitor or implantable loop recorder – for intermittent symptoms.
- Blood tests – to assess thyroid function, electrolytes.
- Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) – to detect atrial thrombi before cardioversion.
Complications[edit]
AF increases the risk of several complications:
- Stroke – due to thrombus formation in the left atrial appendage.
- Heart failure – from prolonged rapid ventricular response.
- Cognitive impairment – from cerebral hypoperfusion.
- Sudden cardiac arrest – rarely.
Treatment[edit]
Management goals include stroke prevention, rate or rhythm control, and treatment of underlying conditions.
Stroke Prevention[edit]
- Anticoagulation therapy (e.g., warfarin, dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban)
- CHA2DS2-VASc score guides anticoagulation decisions.
Rate Control[edit]
- Beta-blockers (e.g., metoprolol)
- Calcium channel blockers (e.g., diltiazem)
- Digoxin
Rhythm Control[edit]
- Antiarrhythmic drugs (e.g., amiodarone, flecainide)
- Electrical cardioversion
- Catheter ablation – for drug-refractory or symptomatic patients
Surgical Options[edit]
- Maze procedure
- Left atrial appendage closure – e.g., Watchman device
Prevention[edit]
Preventive strategies include:
- Managing blood pressure, lipid disorders, and diabetes
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Limiting alcohol and stimulant use
- Treating sleep apnea
- Smoking cessation
Epidemiology[edit]
- Affects 2.7–6.1 million people in the U.S.
- Increases with age: ~9% prevalence in adults ‚â•65
- More common in males and individuals of European descent
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
External Links[edit]
- American Heart Association – Atrial Fibrillation
- CDC Factsheet on AFib
- NIH – Atrial Fibrillation
| Cardiovascular disease (heart) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian