Tachycardia: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Tachycardia | |||
| image = [[File:Tachycardia_ECG_paper.svg|alt=ECG showing tachycardia]] | |||
| caption = ECG showing tachycardia | |||
| field = [[Cardiology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Palpitations]], [[dizziness]], [[shortness of breath]], [[chest pain]] | |||
| complications = [[Heart failure]], [[stroke]], [[cardiac arrest]] | |||
| onset = Sudden or gradual | |||
| duration = Variable | |||
| causes = [[Heart disease]], [[electrolyte imbalance]], [[fever]], [[stress]], [[exercise]], [[anemia]], [[hyperthyroidism]] | |||
| risks = [[Smoking]], [[alcohol use]], [[caffeine]], [[drug use]], [[high blood pressure]], [[diabetes]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Electrocardiogram]], [[Holter monitor]], [[event monitor]], [[stress test]] | |||
| differential = [[Anxiety]], [[panic attack]], [[hyperthyroidism]], [[pheochromocytoma]] | |||
| treatment = [[Medication]], [[cardioversion]], [[catheter ablation]], [[vagal maneuvers]] | |||
| medication = [[Beta blockers]], [[calcium channel blockers]], [[antiarrhythmics]] | |||
| prognosis = Varies depending on underlying cause | |||
| frequency = Common | |||
| deaths = Varies depending on severity and treatment | |||
}} | |||
Tachycardia is a medical condition characterized by a rapid heart rate, typically defined as more than 100 beats per minute (bpm) in adults. A normal resting heart rate for adults ranges from 60 to 100 bpm. Tachycardia can be caused by various factors, including stress, exercise, fever, medications, or underlying medical conditions. In some cases, tachycardia may be harmless and not require treatment; however, in other cases, it can be a sign of a more serious health issue and may require medical attention. | Tachycardia is a medical condition characterized by a rapid heart rate, typically defined as more than 100 beats per minute (bpm) in adults. A normal resting heart rate for adults ranges from 60 to 100 bpm. Tachycardia can be caused by various factors, including stress, exercise, fever, medications, or underlying medical conditions. In some cases, tachycardia may be harmless and not require treatment; however, in other cases, it can be a sign of a more serious health issue and may require medical attention. | ||
===Types of Tachycardia=== | ===Types of Tachycardia=== | ||
There are several types of tachycardia, including: | There are several types of tachycardia, including: | ||
* '''[[Sinus tachycardia]]''': This is a normal increase in heart rate due to factors such as exercise, stress, or fever. It typically resolves on its own once the underlying cause is addressed. | * '''[[Sinus tachycardia]]''': This is a normal increase in heart rate due to factors such as exercise, stress, or fever. It typically resolves on its own once the underlying cause is addressed. | ||
* '''[[Atrial fibrillation]]''': This is an irregular and often rapid heart rate caused by disorganized electrical signals in the atria, the heart's upper chambers. Atrial fibrillation can increase the risk of stroke and other complications if left untreated. | * '''[[Atrial fibrillation]]''': This is an irregular and often rapid heart rate caused by disorganized electrical signals in the atria, the heart's upper chambers. Atrial fibrillation can increase the risk of stroke and other complications if left untreated. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 28: | ||
* '''[[Ventricular tachycardia]]''': A rapid heart rate that originates in the heart's lower chambers, the ventricles. Ventricular tachycardia can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention. | * '''[[Ventricular tachycardia]]''': A rapid heart rate that originates in the heart's lower chambers, the ventricles. Ventricular tachycardia can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention. | ||
===Causes and Risk Factors=== | ===Causes and Risk Factors=== | ||
Tachycardia can be caused by a variety of factors, including: | Tachycardia can be caused by a variety of factors, including: | ||
* Physical exertion, stress, or anxiety | * Physical exertion, stress, or anxiety | ||
* Fever or dehydration | * Fever or dehydration | ||
| Line 20: | Line 35: | ||
* Smoking | * Smoking | ||
Some individuals may have a higher risk of developing tachycardia due to genetics or pre-existing medical conditions. | Some individuals may have a higher risk of developing tachycardia due to genetics or pre-existing medical conditions. | ||
===Symptoms and Complications=== | ===Symptoms and Complications=== | ||
Tachycardia may not always cause noticeable symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they can include: | Tachycardia may not always cause noticeable symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they can include: | ||
* Rapid heartbeat or palpitations | * Rapid heartbeat or palpitations | ||
* Shortness of breath | * Shortness of breath | ||
| Line 30: | Line 42: | ||
* Chest pain | * Chest pain | ||
In some cases, tachycardia can lead to serious complications, such as: | In some cases, tachycardia can lead to serious complications, such as: | ||
* Increased risk of stroke | * Increased risk of stroke | ||
* Heart failure | * Heart failure | ||
* Sudden cardiac arrest | * Sudden cardiac arrest | ||
===Diagnosis and Treatment=== | ===Diagnosis and Treatment=== | ||
A healthcare professional can diagnose tachycardia through a physical examination, medical history, and tests such as an [[electrocardiogram]] (ECG) or [[Holter monitor]]. Treatment options for tachycardia depend on the underlying cause, type, and severity of the condition. They may include: | A healthcare professional can diagnose tachycardia through a physical examination, medical history, and tests such as an [[electrocardiogram]] (ECG) or [[Holter monitor]]. Treatment options for tachycardia depend on the underlying cause, type, and severity of the condition. They may include: | ||
* Addressing the underlying cause (e.g., treating fever, managing stress) | * Addressing the underlying cause (e.g., treating fever, managing stress) | ||
* Medications to control heart rate or rhythm | * Medications to control heart rate or rhythm | ||
| Line 43: | Line 52: | ||
* Catheter ablation (a minimally invasive procedure to remove abnormal electrical pathways in the heart) | * Catheter ablation (a minimally invasive procedure to remove abnormal electrical pathways in the heart) | ||
* Implantation of a pacemaker or implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) to regulate heart rhythm | * Implantation of a pacemaker or implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) to regulate heart rhythm | ||
== Also see == | == Also see == | ||
* [[Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia]] | * [[Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia]] | ||
| Line 50: | Line 58: | ||
{{Circulatory system pathology}} | {{Circulatory system pathology}} | ||
{{Authority control}} | {{Authority control}} | ||
[[Category:Cardiac arrhythmia]] | [[Category:Cardiac arrhythmia]] | ||
[[Category:Symptoms and signs: Cardiac]] | [[Category:Symptoms and signs: Cardiac]] | ||
Revision as of 19:45, 8 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Tachycardia | |
|---|---|
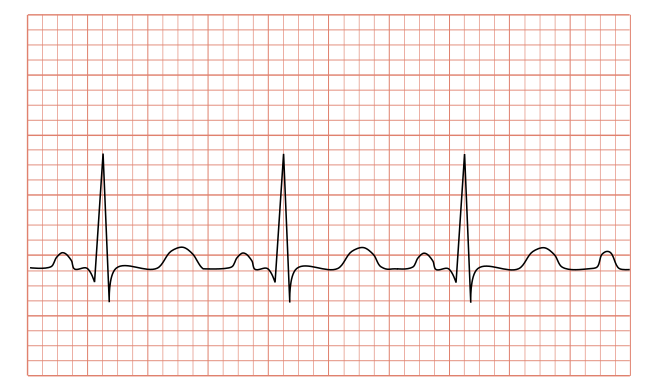
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Palpitations, dizziness, shortness of breath, chest pain |
| Complications | Heart failure, stroke, cardiac arrest |
| Onset | Sudden or gradual |
| Duration | Variable |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Heart disease, electrolyte imbalance, fever, stress, exercise, anemia, hyperthyroidism |
| Risks | Smoking, alcohol use, caffeine, drug use, high blood pressure, diabetes |
| Diagnosis | Electrocardiogram, Holter monitor, event monitor, stress test |
| Differential diagnosis | Anxiety, panic attack, hyperthyroidism, pheochromocytoma |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Medication, cardioversion, catheter ablation, vagal maneuvers |
| Medication | Beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, antiarrhythmics |
| Prognosis | Varies depending on underlying cause |
| Frequency | Common |
| Deaths | Varies depending on severity and treatment |
Tachycardia is a medical condition characterized by a rapid heart rate, typically defined as more than 100 beats per minute (bpm) in adults. A normal resting heart rate for adults ranges from 60 to 100 bpm. Tachycardia can be caused by various factors, including stress, exercise, fever, medications, or underlying medical conditions. In some cases, tachycardia may be harmless and not require treatment; however, in other cases, it can be a sign of a more serious health issue and may require medical attention.
Types of Tachycardia
There are several types of tachycardia, including:
- Sinus tachycardia: This is a normal increase in heart rate due to factors such as exercise, stress, or fever. It typically resolves on its own once the underlying cause is addressed.
- Atrial fibrillation: This is an irregular and often rapid heart rate caused by disorganized electrical signals in the atria, the heart's upper chambers. Atrial fibrillation can increase the risk of stroke and other complications if left untreated.
- Atrial flutter: Similar to atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter is caused by rapid and irregular electrical signals in the atria. It can also increase the risk of stroke and other complications.
- Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT): This is a rapid heart rate originating above the ventricles, often caused by abnormal electrical pathways in the heart. SVT episodes can be short-lived or last for extended periods.
- Ventricular tachycardia: A rapid heart rate that originates in the heart's lower chambers, the ventricles. Ventricular tachycardia can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
Causes and Risk Factors
Tachycardia can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Physical exertion, stress, or anxiety
- Fever or dehydration
- Medical conditions such as anemia, hyperthyroidism, or heart disease
- Medications, caffeine, alcohol, or drug use
- Smoking
Some individuals may have a higher risk of developing tachycardia due to genetics or pre-existing medical conditions.
Symptoms and Complications
Tachycardia may not always cause noticeable symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they can include:
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting
- Chest pain
In some cases, tachycardia can lead to serious complications, such as:
- Increased risk of stroke
- Heart failure
- Sudden cardiac arrest
Diagnosis and Treatment
A healthcare professional can diagnose tachycardia through a physical examination, medical history, and tests such as an electrocardiogram (ECG) or Holter monitor. Treatment options for tachycardia depend on the underlying cause, type, and severity of the condition. They may include:
- Addressing the underlying cause (e.g., treating fever, managing stress)
- Medications to control heart rate or rhythm
- Cardioversion (electrical shock therapy to restore normal heart rhythm)
- Catheter ablation (a minimally invasive procedure to remove abnormal electrical pathways in the heart)
- Implantation of a pacemaker or implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) to regulate heart rhythm
Also see
|
|
|
| Symptoms and signs relating to the cardiovascular system | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Cardiovascular disease (heart) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|


