Pulsus alternans

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Pulsus alternans | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Alternating strong and weak pulse |
| Complications | Heart failure, arrhythmia |
| Onset | Typically gradual |
| Duration | Persistent until underlying condition is treated |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Left ventricular dysfunction, heart failure |
| Risks | Hypertension, coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathy |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, echocardiogram, electrocardiogram |
| Differential diagnosis | Pulsus paradoxus, bigeminy |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Management of underlying heart condition |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Depends on underlying cause |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |


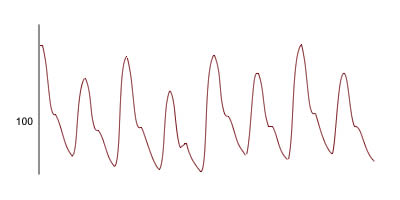
Pulsus alternans is a physical finding in the cardiac examination characterized by alternations in the force of the arterial pulse in a regular rhythm. It is an indicator of left ventricular systolic impairment and is associated with a poor prognosis.
Definition[edit]
Pulsus alternans is defined as a regular rhythm of the pulse with alternating strong and weak beats. It is most commonly detected during manual palpation of the radial artery.
Pathophysiology[edit]
The underlying mechanism of pulsus alternans involves changes in the left ventricle's ability to contract. In conditions of left ventricular systolic impairment, the heart's ability to pump blood effectively is compromised. This results in a decrease in stroke volume during each heartbeat, leading to the characteristic alternating pulse pattern.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Pulsus alternans is a sign of severe left ventricular systolic dysfunction and is often associated with advanced heart disease, including congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction, and cardiomyopathy. It is also seen in patients with aortic stenosis and hypertension.
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of pulsus alternans is primarily clinical, based on the physical examination of the patient. It can be confirmed by an echocardiogram, which can visualize the alternating contractions of the heart.
Treatment[edit]
The treatment of pulsus alternans involves addressing the underlying cause. This may include medications to improve heart function, such as beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and diuretics, as well as lifestyle modifications and potentially surgery.
See Also[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian


