Atrial fibrillation: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Atrial fibrillation | |||
| image = [[File:Afib_ecg.jpg|250px]] | |||
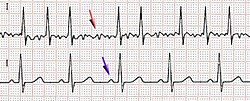
| caption = ECG showing atrial fibrillation | |||
| field = [[Cardiology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Palpitations]], [[fainting]], [[shortness of breath]], [[chest pain]] | |||
| complications = [[Stroke (medicine)|Stroke]], [[heart failure]] | |||
| onset = Sudden or gradual | |||
| duration = Can be [[paroxysmal]], [[persistent]], or [[permanent]] | |||
| causes = [[High blood pressure]], [[valvular heart disease]], [[coronary artery disease]], [[hyperthyroidism]], [[alcohol use disorder]] | |||
| risks = [[Age]], [[hypertension]], [[diabetes mellitus]], [[heart disease]], [[obesity]], [[sleep apnea]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Electrocardiogram|ECG]], [[Holter monitor]], [[event monitor]] | |||
| differential = [[Atrial flutter]], [[supraventricular tachycardia]], [[ventricular tachycardia]] | |||
| treatment = [[Rate control]], [[rhythm control]], [[anticoagulation]] | |||
| medication = [[Beta blockers]], [[calcium channel blockers]], [[digoxin]], [[antiarrhythmic drugs]], [[warfarin]], [[direct oral anticoagulants]] | |||
| prognosis = Variable, depends on underlying conditions and treatment | |||
| frequency = Common, especially in older adults | |||
}} | |||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
'''Atrial fibrillation''' (AF or Afib) is a type of [[arrhythmia]] characterized by an irregular and often rapid heart rhythm that originates in the [[atria]], the upper chambers of the [[heart]]. This abnormal rhythm can impair the heart's ability to efficiently pump blood, increasing the risk of serious complications such as [[stroke]], [[heart failure]], and [[blood clots]]. | '''Atrial fibrillation''' (AF or Afib) is a type of [[arrhythmia]] characterized by an irregular and often rapid heart rhythm that originates in the [[atria]], the upper chambers of the [[heart]]. This abnormal rhythm can impair the heart's ability to efficiently pump blood, increasing the risk of serious complications such as [[stroke]], [[heart failure]], and [[blood clots]]. | ||
[[File:Afib ecg.jpg|left|thumb|Electrocardiogram showing atrial fibrillation]] | |||
[[File:Afib ecg.jpg|thumb|Electrocardiogram showing atrial fibrillation]] | |||
== Types of Atrial Fibrillation == | == Types of Atrial Fibrillation == | ||
Atrial fibrillation can be classified into four major types based on duration and response to treatment: | Atrial fibrillation can be classified into four major types based on duration and response to treatment: | ||
=== [[Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation]] === | === [[Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation]] === | ||
Paroxysmal AF occurs intermittently and resolves spontaneously within 7 days, often within 24 hours. It may be asymptomatic or cause noticeable palpitations. When paroxysmal AF alternates with bradycardia, the condition is called [[tachybrady syndrome]]. | Paroxysmal AF occurs intermittently and resolves spontaneously within 7 days, often within 24 hours. It may be asymptomatic or cause noticeable palpitations. When paroxysmal AF alternates with bradycardia, the condition is called [[tachybrady syndrome]]. | ||
=== [[Persistent atrial fibrillation]] === | === [[Persistent atrial fibrillation]] === | ||
This type of AF persists for more than 7 days and typically requires medical intervention, such as cardioversion, to restore normal rhythm. | This type of AF persists for more than 7 days and typically requires medical intervention, such as cardioversion, to restore normal rhythm. | ||
=== [[Long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation]] === | === [[Long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation]] === | ||
AF that continues for more than 12 months. It is often resistant to treatment and may lead to structural changes in the heart. | AF that continues for more than 12 months. It is often resistant to treatment and may lead to structural changes in the heart. | ||
=== [[Permanent atrial fibrillation]] === | === [[Permanent atrial fibrillation]] === | ||
When AF cannot be restored to normal rhythm despite attempts at treatment or when the decision is made not to pursue rhythm control, it is termed permanent. | When AF cannot be restored to normal rhythm despite attempts at treatment or when the decision is made not to pursue rhythm control, it is termed permanent. | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
[[File:Atrial Fibrillation.jpg|thumb|Heart changes associated with AF]] | [[File:Atrial Fibrillation.jpg|left|thumb|Heart changes associated with AF]] | ||
AF results from abnormalities in the heart's electrical conduction system and structural changes in cardiac tissue. Common causes include: | AF results from abnormalities in the heart's electrical conduction system and structural changes in cardiac tissue. Common causes include: | ||
* [[Hypertension]] | * [[Hypertension]] | ||
* [[Ischemic heart disease]] | * [[Ischemic heart disease]] | ||
| Line 34: | Line 45: | ||
* [[Pericarditis]] or [[myocarditis]] | * [[Pericarditis]] or [[myocarditis]] | ||
* Aging-related fibrosis | * Aging-related fibrosis | ||
== Risk Factors == | == Risk Factors == | ||
Several risk factors are associated with increased likelihood of developing AF: | Several risk factors are associated with increased likelihood of developing AF: | ||
* Advanced age (especially >65 years) | * Advanced age (especially >65 years) | ||
* Family history | * Family history | ||
| Line 47: | Line 56: | ||
* Sedentary lifestyle or extreme endurance training | * Sedentary lifestyle or extreme endurance training | ||
* [[Thyroid disorders]] | * [[Thyroid disorders]] | ||
== Signs and Symptoms == | == Signs and Symptoms == | ||
Symptoms of AF vary in severity and may include: | Symptoms of AF vary in severity and may include: | ||
* Palpitations | * Palpitations | ||
* Fatigue | * Fatigue | ||
| Line 57: | Line 64: | ||
* [[Chest pain]] | * [[Chest pain]] | ||
* [[Hypotension]] | * [[Hypotension]] | ||
Some patients may remain asymptomatic, and AF is discovered incidentally. | Some patients may remain asymptomatic, and AF is discovered incidentally. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Diagnosis of AF typically involves: | Diagnosis of AF typically involves: | ||
* [[Electrocardiogram]] (ECG) – confirms the absence of P waves and irregularly irregular ventricular response. | |||
* [[Electrocardiogram]] (ECG) | * [[Echocardiography]] – assesses structural abnormalities, thrombus formation. | ||
* [[Echocardiography]] | * [[Holter monitor]] – records rhythm over 24–48 hours. | ||
* [[Holter monitor]] | * [[Event monitor]] or [[implantable loop recorder]] – for intermittent symptoms. | ||
* [[Event monitor]] or [[implantable loop recorder]] | * [[Blood tests]] – to assess thyroid function, electrolytes. | ||
* [[Blood tests]] | * [[Transesophageal echocardiography]] (TEE) – to detect atrial thrombi before cardioversion. | ||
* [[Transesophageal echocardiography]] (TEE) | |||
== Complications == | == Complications == | ||
AF increases the risk of several complications: | AF increases the risk of several complications: | ||
* [[Stroke]] – due to thrombus formation in the left atrial appendage. | |||
* [[Stroke]] | * [[Heart failure]] – from prolonged rapid ventricular response. | ||
* [[Heart failure]] | * [[Cognitive impairment]] – from cerebral hypoperfusion. | ||
* [[Cognitive impairment]] | * [[Sudden cardiac arrest]] – rarely. | ||
* [[Sudden cardiac arrest]] | |||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Management goals include stroke prevention, rate or rhythm control, and treatment of underlying conditions. | Management goals include stroke prevention, rate or rhythm control, and treatment of underlying conditions. | ||
=== Stroke Prevention === | === Stroke Prevention === | ||
* [[Anticoagulation]] therapy (e.g., [[warfarin]], [[dabigatran]], [[rivaroxaban]], [[apixaban]]) | * [[Anticoagulation]] therapy (e.g., [[warfarin]], [[dabigatran]], [[rivaroxaban]], [[apixaban]]) | ||
* [[CHA2DS2-VASc score]] guides anticoagulation decisions. | * [[CHA2DS2-VASc score]] guides anticoagulation decisions. | ||
=== Rate Control === | === Rate Control === | ||
* [[Beta-blockers]] (e.g., metoprolol) | * [[Beta-blockers]] (e.g., metoprolol) | ||
* [[Calcium channel blockers]] (e.g., diltiazem) | * [[Calcium channel blockers]] (e.g., diltiazem) | ||
* [[Digoxin]] | * [[Digoxin]] | ||
=== Rhythm Control === | === Rhythm Control === | ||
* [[Antiarrhythmic drugs]] (e.g., amiodarone, flecainide) | * [[Antiarrhythmic drugs]] (e.g., amiodarone, flecainide) | ||
* [[Electrical cardioversion]] | * [[Electrical cardioversion]] | ||
* [[Catheter ablation]] | * [[Catheter ablation]] – for drug-refractory or symptomatic patients | ||
=== Surgical Options === | === Surgical Options === | ||
* [[Maze procedure]] | * [[Maze procedure]] | ||
* [[Left atrial appendage closure]] | * [[Left atrial appendage closure]] – e.g., Watchman device | ||
== Prevention == | == Prevention == | ||
Preventive strategies include: | Preventive strategies include: | ||
* Managing [[blood pressure]], [[lipid disorders]], and [[diabetes]] | * Managing [[blood pressure]], [[lipid disorders]], and [[diabetes]] | ||
* Maintaining a healthy weight | * Maintaining a healthy weight | ||
| Line 107: | Line 102: | ||
* Treating sleep apnea | * Treating sleep apnea | ||
* Smoking cessation | * Smoking cessation | ||
== Epidemiology == | == Epidemiology == | ||
* Affects 2. | * Affects 2.7–6.1 million people in the U.S. | ||
* Increases with age: ~9% prevalence in adults | * Increases with age: ~9% prevalence in adults ‚â•65 | ||
* More common in males and individuals of European descent | * More common in males and individuals of European descent | ||
== See Also == | == See Also == | ||
* [[Arrhythmia]] | * [[Arrhythmia]] | ||
| Line 118: | Line 111: | ||
* [[Stroke]] | * [[Stroke]] | ||
* [[Cardiac electrophysiology]] | * [[Cardiac electrophysiology]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
== External Links == | == External Links == | ||
* [https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/atrial-fibrillation American Heart Association | * [https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/atrial-fibrillation American Heart Association – Atrial Fibrillation] | ||
* [https://www.cdc.gov/dhdsp/data_statistics/fact_sheets/fs_atrial_fibrillation.htm CDC Factsheet on AFib] | * [https://www.cdc.gov/dhdsp/data_statistics/fact_sheets/fs_atrial_fibrillation.htm CDC Factsheet on AFib] | ||
* [https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/atrial-fibrillation NIH | * [https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/atrial-fibrillation NIH – Atrial Fibrillation] | ||
{{Circulatory system pathology}} | {{Circulatory system pathology}} | ||
[[Category:Cardiac arrhythmia]] | [[Category:Cardiac arrhythmia]] | ||
[[Category:Cardiology]] | [[Category:Cardiology]] | ||
[[Category:Electrophysiology]] | [[Category:Electrophysiology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:58, 4 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Atrial fibrillation | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Palpitations, fainting, shortness of breath, chest pain |
| Complications | Stroke, heart failure |
| Onset | Sudden or gradual |
| Duration | Can be paroxysmal, persistent, or permanent |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | High blood pressure, valvular heart disease, coronary artery disease, hyperthyroidism, alcohol use disorder |
| Risks | Age, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, heart disease, obesity, sleep apnea |
| Diagnosis | ECG, Holter monitor, event monitor |
| Differential diagnosis | Atrial flutter, supraventricular tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Rate control, rhythm control, anticoagulation |
| Medication | Beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, digoxin, antiarrhythmic drugs, warfarin, direct oral anticoagulants |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on underlying conditions and treatment |
| Frequency | Common, especially in older adults |
| Deaths | N/A |
Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a type of arrhythmia characterized by an irregular and often rapid heart rhythm that originates in the atria, the upper chambers of the heart. This abnormal rhythm can impair the heart's ability to efficiently pump blood, increasing the risk of serious complications such as stroke, heart failure, and blood clots.

Types of Atrial Fibrillation[edit]
Atrial fibrillation can be classified into four major types based on duration and response to treatment:
Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation[edit]
Paroxysmal AF occurs intermittently and resolves spontaneously within 7 days, often within 24 hours. It may be asymptomatic or cause noticeable palpitations. When paroxysmal AF alternates with bradycardia, the condition is called tachybrady syndrome.
Persistent atrial fibrillation[edit]
This type of AF persists for more than 7 days and typically requires medical intervention, such as cardioversion, to restore normal rhythm.
Long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation[edit]
AF that continues for more than 12 months. It is often resistant to treatment and may lead to structural changes in the heart.
Permanent atrial fibrillation[edit]
When AF cannot be restored to normal rhythm despite attempts at treatment or when the decision is made not to pursue rhythm control, it is termed permanent.
Causes[edit]

AF results from abnormalities in the heart's electrical conduction system and structural changes in cardiac tissue. Common causes include:
- Hypertension
- Ischemic heart disease
- Heart valve disease
- Cardiomyopathy
- Congenital heart defect
- Hyperthyroidism
- Sleep apnea
- Alcohol abuse ("Holiday heart syndrome")
- Postoperative changes (especially after cardiac surgery)
- Pericarditis or myocarditis
- Aging-related fibrosis
Risk Factors[edit]
Several risk factors are associated with increased likelihood of developing AF:
- Advanced age (especially >65 years)
- Family history
- Obesity
- Diabetes mellitus
- Chronic kidney disease
- Pulmonary diseases (e.g., COPD)
- Excessive alcohol or stimulant use
- Sedentary lifestyle or extreme endurance training
- Thyroid disorders
Signs and Symptoms[edit]
Symptoms of AF vary in severity and may include:
- Palpitations
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness or syncope
- Chest pain
- Hypotension
Some patients may remain asymptomatic, and AF is discovered incidentally.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of AF typically involves:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) – confirms the absence of P waves and irregularly irregular ventricular response.
- Echocardiography – assesses structural abnormalities, thrombus formation.
- Holter monitor – records rhythm over 24–48 hours.
- Event monitor or implantable loop recorder – for intermittent symptoms.
- Blood tests – to assess thyroid function, electrolytes.
- Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) – to detect atrial thrombi before cardioversion.
Complications[edit]
AF increases the risk of several complications:
- Stroke – due to thrombus formation in the left atrial appendage.
- Heart failure – from prolonged rapid ventricular response.
- Cognitive impairment – from cerebral hypoperfusion.
- Sudden cardiac arrest – rarely.
Treatment[edit]
Management goals include stroke prevention, rate or rhythm control, and treatment of underlying conditions.
Stroke Prevention[edit]
- Anticoagulation therapy (e.g., warfarin, dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban)
- CHA2DS2-VASc score guides anticoagulation decisions.
Rate Control[edit]
- Beta-blockers (e.g., metoprolol)
- Calcium channel blockers (e.g., diltiazem)
- Digoxin
Rhythm Control[edit]
- Antiarrhythmic drugs (e.g., amiodarone, flecainide)
- Electrical cardioversion
- Catheter ablation – for drug-refractory or symptomatic patients
Surgical Options[edit]
- Maze procedure
- Left atrial appendage closure – e.g., Watchman device
Prevention[edit]
Preventive strategies include:
- Managing blood pressure, lipid disorders, and diabetes
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Limiting alcohol and stimulant use
- Treating sleep apnea
- Smoking cessation
Epidemiology[edit]
- Affects 2.7–6.1 million people in the U.S.
- Increases with age: ~9% prevalence in adults ‚â•65
- More common in males and individuals of European descent
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
External Links[edit]
- American Heart Association – Atrial Fibrillation
- CDC Factsheet on AFib
- NIH – Atrial Fibrillation
| Cardiovascular disease (heart) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|