Epidemic typhus: Difference between revisions
No edit summary Tag: visualeditor-wikitext |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Epidemic typhus | |||
| image = [[File:Epidemic_Typhus._Macular_rash.png|250px]] | |||
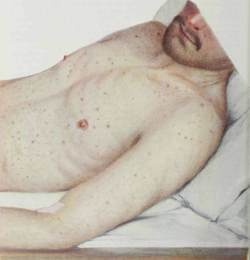
| caption = Macular rash associated with epidemic typhus | |||
| field = [[Infectious disease]] | |||
| synonyms = Louse-borne typhus, camp fever, jail fever | |||
| symptoms = [[Fever]], [[headache]], [[rash]], [[muscle pain]] | |||
| complications = [[Pneumonia]], [[encephalitis]], [[septic shock]] | |||
| onset = 1–2 weeks after exposure | |||
| duration = 2–3 weeks | |||
| causes = [[Rickettsia prowazekii]] | |||
| risks = Overcrowding, poor sanitation | |||
| diagnosis = [[Serology]], [[PCR]] | |||
| differential = [[Murine typhus]], [[Rocky Mountain spotted fever]] | |||
| prevention = Avoidance of lice, improved hygiene | |||
| treatment = [[Doxycycline]], [[chloramphenicol]] | |||
| prognosis = Good with treatment, high mortality without | |||
| frequency = Rare in developed countries, outbreaks in areas of conflict | |||
| deaths = High mortality rate if untreated | |||
}} | |||
* A [[gram-negative]] bacterial infection caused by [[rickettsia prowazekii]]. | * A [[gram-negative]] bacterial infection caused by [[rickettsia prowazekii]]. | ||
* It is spread by lice infected with the bacteria. | * It is spread by lice infected with the bacteria. | ||
* Signs and symptoms include sudden headache, generalized muscle pain, malaise, and macular skin lesions. | * Signs and symptoms include sudden headache, generalized muscle pain, malaise, and macular skin lesions. | ||
* The infection may affect the central nervous system causing [[encephalitis]]. | * The infection may affect the central nervous system causing [[encephalitis]]. | ||
[[File:Epidemic Typhus. Macular rash 1.png|alt=Epidemic Typhus - macular rash|thumb|'''Epidemic Typhus - macular rash''']] | [[File:Epidemic Typhus. Macular rash 1.png|alt=Epidemic Typhus - macular rash|left|thumb|'''Epidemic Typhus - macular rash''']] | ||
<youtube> | <youtube> | ||
title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | ||
| Line 15: | Line 36: | ||
==Other names== | ==Other names== | ||
Epidemic typhus, also called louse-borne typhus, is an uncommon disease caused by a bacteria called Rickettsia prowazekii. | Epidemic typhus, also called louse-borne typhus, is an uncommon disease caused by a bacteria called Rickettsia prowazekii. | ||
==Transmission== | ==Transmission== | ||
Epidemic typhus is spread to people through contact with infected body lice. | Epidemic typhus is spread to people through contact with infected body lice. | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
Though epidemic typhus was responsible for millions of deaths in previous centuries, it is now considered a rare disease. | Though epidemic typhus was responsible for millions of deaths in previous centuries, it is now considered a rare disease. | ||
==Risk factors== | ==Risk factors== | ||
* Occasionally, cases continue to occur, in areas where extreme overcrowding is common and body lice can travel from one person to another. | * Occasionally, cases continue to occur, in areas where extreme overcrowding is common and body lice can travel from one person to another. | ||
* In the United States, rare cases of epidemic typhus, called sylvatic typhus, can occur. | * In the United States, rare cases of epidemic typhus, called sylvatic typhus, can occur. | ||
* These cases occur when people are exposed to flying squirrels and their nests. | * These cases occur when people are exposed to flying squirrels and their nests. | ||
[[File:Epidemic Typhus. Petechial rash in the vicinity of the nipple.png|alt=Epidemic Typhus - Petechial rash|thumb|Epidemic Typhus - Petechial rash ]] | [[File:Epidemic Typhus. Petechial rash in the vicinity of the nipple.png|alt=Epidemic Typhus - Petechial rash|left|thumb|Epidemic Typhus - Petechial rash ]] | ||
==Signs and Symptoms== | ==Signs and Symptoms== | ||
Xenopsylla cheopis, the Oriental rat flea | Xenopsylla cheopis, the Oriental rat flea | ||
Symptoms of epidemic typhus begin within 2 weeks after contact with infected body lice. Signs and symptoms may include: | Symptoms of epidemic typhus begin within 2 weeks after contact with infected body lice. Signs and symptoms may include: | ||
* Fever and chills | * Fever and chills | ||
* Headache | * Headache | ||
| Line 42: | Line 58: | ||
* Confusion | * Confusion | ||
* Brill-Zinsser disease | * Brill-Zinsser disease | ||
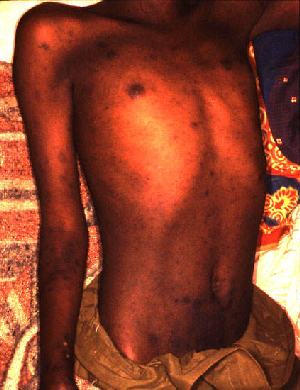
[[File:Epidemic typhus Burundi.jpg|alt= Epidemic typhus Burundi|thumb|Epidemic typhus Burundi]] | [[File:Epidemic typhus Burundi.jpg|alt= Epidemic typhus Burundi|left|thumb|Epidemic typhus Burundi]] | ||
==Clinical course== | ==Clinical course== | ||
* Some people can remain infected, without symptoms, for years after they first get sick. | * Some people can remain infected, without symptoms, for years after they first get sick. | ||
* Rarely, these individuals can have a relapse in disease, called Brill-Zinsser disease, months or years following their first illness. | * Rarely, these individuals can have a relapse in disease, called Brill-Zinsser disease, months or years following their first illness. | ||
* When this happens, it often occurs when the | * When this happens, it often occurs when the body’s immune system is weakened due to certain medications, old age, or illness. | ||
* The symptoms of Brill-Zinsser disease are similar to the original infection, but are usually milder than the initial illness. | * The symptoms of Brill-Zinsser disease are similar to the original infection, but are usually milder than the initial illness. | ||
[[File:Epidemic Typhus. Rash on the volar surface of the hand.png|alt=Epidemic Typhus. Rash on the volar surface of the hand|thumb|Epidemic Typhus. Rash on the volar surface of the hand]] | [[File:Epidemic Typhus. Rash on the volar surface of the hand.png|alt=Epidemic Typhus. Rash on the volar surface of the hand|left|thumb|Epidemic Typhus. Rash on the volar surface of the hand]] | ||
==Diagnosis and Testing== | ==Diagnosis and Testing== | ||
* The symptoms of epidemic typhus are similar to symptoms of many other diseases. See your health care provider if you develop the symptoms listed above following travel or contact with animals. | * The symptoms of epidemic typhus are similar to symptoms of many other diseases. See your health care provider if you develop the symptoms listed above following travel or contact with animals. | ||
| Line 55: | Line 71: | ||
* Laboratory testing and reporting of results can take several weeks. Your health care provider may start treatment before results are available. | * Laboratory testing and reporting of results can take several weeks. Your health care provider may start treatment before results are available. | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
==== Laboratory Confirmation ==== | ==== Laboratory Confirmation ==== | ||
''Rickettsia prowazekii'' can be detected via indirect immunofluorescence antibody (IFA) assay, immunohistochemistry (IHC), polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay of blood, plasma, or tissue samples, or culture isolation. Serologic tests are the most common means of confirmation and can be used to detect either IgG or IgM antibodies. Diagnosis is typically confirmed by documenting a four-fold rise in antibody titer between acute and convalescent samples. Acute specimens are taken during the first week of illness and convalescent samples are taken 2–4 weeks later. Detectable levels of IgG or IgM antibodies generally do not appear until 7–10 days after the onset of illness. | ''Rickettsia prowazekii'' can be detected via indirect immunofluorescence antibody (IFA) assay, immunohistochemistry (IHC), polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay of blood, plasma, or tissue samples, or culture isolation. Serologic tests are the most common means of confirmation and can be used to detect either IgG or IgM antibodies. Diagnosis is typically confirmed by documenting a four-fold rise in antibody titer between acute and convalescent samples. Acute specimens are taken during the first week of illness and convalescent samples are taken 2–4 weeks later. Detectable levels of IgG or IgM antibodies generally do not appear until 7–10 days after the onset of illness. | ||
==Lab tests== | ==Lab tests== | ||
Because IgG antibody titers may persist in some individuals for years after the original exposure, only demonstration of recent changes in titers between paired specimens can be considered reliable serological confirmation of an acute epidemic typhus infection. ''R. prowazekii'' antigens may cross react with those of ''R. typhi,'' and occasionally with ''R. rickettsii''. When possible, species-specific serological assays for ''R.'' ''prowazekii, R. typhi,'' and ''R. rickettsii'' should be run in parallel. Persons with Brill-Zinsser disease generally show a rise in IgG but not IgM antibodies to ''R. prowazekii''. IHC can be used to detect infection with typhus group ''Rickettsia'' (including ''R. prowazekii'' and ''R. typhi'') in formalin-fixed tissue samples. PCR of whole blood or tissue can distinguish between infection with ''R. typhi'' and ''R. prowazekii'' although the sensitivity of these assays vary considerably based on the sample type, timing of sample collection, and the severity of disease. Since epidemic typhus is not common in the United States, testing is not typically available at state and local health departments. IFA, culture, and PCR can all be performed at the CDC, through submission from state health departments. | Because IgG antibody titers may persist in some individuals for years after the original exposure, only demonstration of recent changes in titers between paired specimens can be considered reliable serological confirmation of an acute epidemic typhus infection. ''R. prowazekii'' antigens may cross react with those of ''R. typhi,'' and occasionally with ''R. rickettsii''. When possible, species-specific serological assays for ''R.'' ''prowazekii, R. typhi,'' and ''R. rickettsii'' should be run in parallel. Persons with Brill-Zinsser disease generally show a rise in IgG but not IgM antibodies to ''R. prowazekii''. IHC can be used to detect infection with typhus group ''Rickettsia'' (including ''R. prowazekii'' and ''R. typhi'') in formalin-fixed tissue samples. PCR of whole blood or tissue can distinguish between infection with ''R. typhi'' and ''R. prowazekii'' although the sensitivity of these assays vary considerably based on the sample type, timing of sample collection, and the severity of disease. Since epidemic typhus is not common in the United States, testing is not typically available at state and local health departments. IFA, culture, and PCR can all be performed at the CDC, through submission from state health departments. | ||
==== Treatment ==== | ==== Treatment ==== | ||
Doxycycline is the treatment of choice for suspected cases of acute epidemic typhus and Brill-Zinsser disease in adults and children of all ages. Recommended dosages of doxycycline: | Doxycycline is the treatment of choice for suspected cases of acute epidemic typhus and Brill-Zinsser disease in adults and children of all ages. Recommended dosages of doxycycline: | ||
* Adults: 100 mg twice per day | * Adults: 100 mg twice per day | ||
* Children under 45 kg (100 lbs.): 2.2 mg/kg body weight given twice a day | * Children under 45 kg (100 lbs.): 2.2 mg/kg body weight given twice a day | ||
Patients should be treated for at least 3 days after the fever subsides and until there is evidence of clinical improvement (usually 7–10 days). | Patients should be treated for at least 3 days after the fever subsides and until there is evidence of clinical improvement (usually 7–10 days). | ||
Studies have shown that even a single 200 mg dose of doxycycline for adults has been reported as effective in halting outbreaks of epidemic typhus, although some patients may relapse if not treated for the full 7–10 days. There is no information about the efficacy of antibiotic therapy in the prevention of Brill-Zinsser disease. Patients with body louse infestations should be treated with delousing gels or creams (pediculicide). | Studies have shown that even a single 200 mg dose of doxycycline for adults has been reported as effective in halting outbreaks of epidemic typhus, although some patients may relapse if not treated for the full 7–10 days. There is no information about the efficacy of antibiotic therapy in the prevention of Brill-Zinsser disease. Patients with body louse infestations should be treated with delousing gels or creams (pediculicide). | ||
<youtube> | <youtube> | ||
| Line 80: | Line 90: | ||
height=600 | height=600 | ||
</youtube> | </youtube> | ||
[[File:Epidemic Typhus. Typical temperature curve.png|alt=Epidemic Typhus. Typical temperature curve|thumb|Epidemic Typhus. Typical temperature curve]] | [[File:Epidemic Typhus. Typical temperature curve.png|alt=Epidemic Typhus. Typical temperature curve|left|thumb|Epidemic Typhus. Typical temperature curve]] | ||
==Prevention== | ==Prevention== | ||
* There is no vaccine to prevent epidemic typhus. | * There is no vaccine to prevent epidemic typhus. | ||
* Reduce your risk of getting epidemic typhus by avoiding overcrowded areas. | * Reduce your risk of getting epidemic typhus by avoiding overcrowded areas. | ||
* Body lice thrive in areas that are overcrowded and where people | * Body lice thrive in areas that are overcrowded and where people aren’t able to bathe or change clothes regularly. To avoid body louse infestations: | ||
* Bathe regularly and change into clean clothes at least once a week. | * Bathe regularly and change into clean clothes at least once a week. | ||
* Wash louse-infested clothing at least once a week. Machine wash and dry infested clothing and bedding using hot water (at least | * Wash louse-infested clothing at least once a week. Machine wash and dry infested clothing and bedding using hot water (at least 130°F), and dry on high heat when possible. Clothing and items that are not washable can be dry-cleaned OR sealed in a plastic bag and stored for 2 weeks. | ||
* Do not share clothing, beds, bedding, or towels used by a person who has body lice or is infected with typhus. | * Do not share clothing, beds, bedding, or towels used by a person who has body lice or is infected with typhus. | ||
* Treat bedding, uniforms, and other clothing with permethrin. Permethrin kills lice and may provide long-lasting protection for clothing for many washings. | * Treat bedding, uniforms, and other clothing with permethrin. Permethrin kills lice and may provide long-lasting protection for clothing for many washings. | ||
* Do NOT use permethrin products directly on skin. They are intended to treat clothing. | * Do NOT use permethrin products directly on skin. They are intended to treat clothing. | ||
* People should avoid contact with flying squirrels and their nests. | * People should avoid contact with flying squirrels and their nests. | ||
{{Bacterial diseases}} | {{Bacterial diseases}} | ||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Epidemic Typhus}} | {{DEFAULTSORT:Epidemic Typhus}} | ||
[[Category:Epidemic typhus| ]] | [[Category:Epidemic typhus| ]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:25, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Epidemic typhus | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Louse-borne typhus, camp fever, jail fever |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Fever, headache, rash, muscle pain |
| Complications | Pneumonia, encephalitis, septic shock |
| Onset | 1–2 weeks after exposure |
| Duration | 2–3 weeks |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Rickettsia prowazekii |
| Risks | Overcrowding, poor sanitation |
| Diagnosis | Serology, PCR |
| Differential diagnosis | Murine typhus, Rocky Mountain spotted fever |
| Prevention | Avoidance of lice, improved hygiene |
| Treatment | Doxycycline, chloramphenicol |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Good with treatment, high mortality without |
| Frequency | Rare in developed countries, outbreaks in areas of conflict |
| Deaths | High mortality rate if untreated |
- A gram-negative bacterial infection caused by rickettsia prowazekii.
- It is spread by lice infected with the bacteria.
- Signs and symptoms include sudden headache, generalized muscle pain, malaise, and macular skin lesions.
- The infection may affect the central nervous system causing encephalitis.

Other names[edit]
Epidemic typhus, also called louse-borne typhus, is an uncommon disease caused by a bacteria called Rickettsia prowazekii.
Transmission[edit]
Epidemic typhus is spread to people through contact with infected body lice.
History[edit]
Though epidemic typhus was responsible for millions of deaths in previous centuries, it is now considered a rare disease.
Risk factors[edit]
- Occasionally, cases continue to occur, in areas where extreme overcrowding is common and body lice can travel from one person to another.
- In the United States, rare cases of epidemic typhus, called sylvatic typhus, can occur.
- These cases occur when people are exposed to flying squirrels and their nests.

Signs and Symptoms[edit]
Xenopsylla cheopis, the Oriental rat flea Symptoms of epidemic typhus begin within 2 weeks after contact with infected body lice. Signs and symptoms may include:
- Fever and chills
- Headache
- Rapid breathing
- Body and muscle aches
- Rash
- Cough
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Confusion
- Brill-Zinsser disease
Clinical course[edit]
- Some people can remain infected, without symptoms, for years after they first get sick.
- Rarely, these individuals can have a relapse in disease, called Brill-Zinsser disease, months or years following their first illness.
- When this happens, it often occurs when the body’s immune system is weakened due to certain medications, old age, or illness.
- The symptoms of Brill-Zinsser disease are similar to the original infection, but are usually milder than the initial illness.

Diagnosis and Testing[edit]
- The symptoms of epidemic typhus are similar to symptoms of many other diseases. See your health care provider if you develop the symptoms listed above following travel or contact with animals.
- Tell your health care provider if you have had contact with flying squirrels or their nests.
- Your health care provider will order a blood test to look for epidemic typhus and other diseases.
- Laboratory testing and reporting of results can take several weeks. Your health care provider may start treatment before results are available.
Laboratory Confirmation[edit]
Rickettsia prowazekii can be detected via indirect immunofluorescence antibody (IFA) assay, immunohistochemistry (IHC), polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay of blood, plasma, or tissue samples, or culture isolation. Serologic tests are the most common means of confirmation and can be used to detect either IgG or IgM antibodies. Diagnosis is typically confirmed by documenting a four-fold rise in antibody titer between acute and convalescent samples. Acute specimens are taken during the first week of illness and convalescent samples are taken 2–4 weeks later. Detectable levels of IgG or IgM antibodies generally do not appear until 7–10 days after the onset of illness.
Lab tests[edit]
Because IgG antibody titers may persist in some individuals for years after the original exposure, only demonstration of recent changes in titers between paired specimens can be considered reliable serological confirmation of an acute epidemic typhus infection. R. prowazekii antigens may cross react with those of R. typhi, and occasionally with R. rickettsii. When possible, species-specific serological assays for R. prowazekii, R. typhi, and R. rickettsii should be run in parallel. Persons with Brill-Zinsser disease generally show a rise in IgG but not IgM antibodies to R. prowazekii. IHC can be used to detect infection with typhus group Rickettsia (including R. prowazekii and R. typhi) in formalin-fixed tissue samples. PCR of whole blood or tissue can distinguish between infection with R. typhi and R. prowazekii although the sensitivity of these assays vary considerably based on the sample type, timing of sample collection, and the severity of disease. Since epidemic typhus is not common in the United States, testing is not typically available at state and local health departments. IFA, culture, and PCR can all be performed at the CDC, through submission from state health departments.
Treatment[edit]
Doxycycline is the treatment of choice for suspected cases of acute epidemic typhus and Brill-Zinsser disease in adults and children of all ages. Recommended dosages of doxycycline:
- Adults: 100 mg twice per day
- Children under 45 kg (100 lbs.): 2.2 mg/kg body weight given twice a day
Patients should be treated for at least 3 days after the fever subsides and until there is evidence of clinical improvement (usually 7–10 days). Studies have shown that even a single 200 mg dose of doxycycline for adults has been reported as effective in halting outbreaks of epidemic typhus, although some patients may relapse if not treated for the full 7–10 days. There is no information about the efficacy of antibiotic therapy in the prevention of Brill-Zinsser disease. Patients with body louse infestations should be treated with delousing gels or creams (pediculicide).

Prevention[edit]
- There is no vaccine to prevent epidemic typhus.
- Reduce your risk of getting epidemic typhus by avoiding overcrowded areas.
- Body lice thrive in areas that are overcrowded and where people aren’t able to bathe or change clothes regularly. To avoid body louse infestations:
- Bathe regularly and change into clean clothes at least once a week.
- Wash louse-infested clothing at least once a week. Machine wash and dry infested clothing and bedding using hot water (at least 130°F), and dry on high heat when possible. Clothing and items that are not washable can be dry-cleaned OR sealed in a plastic bag and stored for 2 weeks.
- Do not share clothing, beds, bedding, or towels used by a person who has body lice or is infected with typhus.
- Treat bedding, uniforms, and other clothing with permethrin. Permethrin kills lice and may provide long-lasting protection for clothing for many washings.
- Do NOT use permethrin products directly on skin. They are intended to treat clothing.
- People should avoid contact with flying squirrels and their nests.
| Proteobacteria-associated Gram-negative bacterial infections (primarily A00–A79, 001–041, 080–109) | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|


