Harding ataxia: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
{{Diseases of the nervous system}} | {{Diseases of the nervous system}} | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
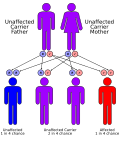
<gallery> | |||
File:Autorecessive.svg|Autorecessive | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 21:43, 20 February 2025
Harding Ataxia is a rare, genetic, neurological disorder characterized by the progressive loss of balance and coordination (ataxia), involuntary eye movements (nystagmus), and abnormal speech (dysarthria).
Symptoms
The symptoms of Harding Ataxia typically begin in early adulthood and may include:
- Ataxia - This is the primary symptom of Harding Ataxia. It is characterized by a lack of muscle control during voluntary movements, resulting in a lack of balance and coordination.
- Nystagmus - This is a condition that causes involuntary eye movements. In people with Harding Ataxia, these movements can be rapid and uncontrollable.
- Dysarthria - This is a condition that affects the muscles that produce speech, resulting in slurred or slow speech that can be difficult to understand.
Causes
Harding Ataxia is caused by mutations in the CACNA1A gene. This gene provides instructions for making a protein that is involved in the transport of calcium ions into cells. The mutations that cause Harding Ataxia result in a reduction of this protein, which disrupts the normal function of nerve cells, leading to the symptoms of the disorder.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of Harding Ataxia is based on the presence of characteristic neurological symptoms, a detailed patient history, a thorough clinical evaluation, and a variety of specialized tests. These tests may include:
- Genetic testing - This can confirm a diagnosis by identifying a mutation in the CACNA1A gene.
- Neurological examination - This may include tests of balance, coordination, and eye movements.
Treatment
There is currently no cure for Harding Ataxia. Treatment is symptomatic and supportive, and may include:
- Physical therapy - This can help improve balance and coordination.
- Speech therapy - This can help manage dysarthria.
- Medication - Certain medications may be used to manage symptoms such as tremors or muscle stiffness.
See also
- Ataxia
- Nystagmus
- Dysarthria
- CACNA1A
- Genetic testing
- Neurological examination
- Physical therapy
- Speech therapy
- Medication
| Diseases of the nervous system, primarily CNS (G04–G47, 323–349) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|