Ethics of eating meat: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
{{Health}} | {{Health}} | ||
{{food-stub}} | {{food-stub}} | ||
== Ethics of eating meat == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:FoodMeat.jpg|Various cuts of meat | |||
File:Slaughterhouse_cattle_bodies.jpg|Cattle bodies in a slaughterhouse | |||
File:Shorthorn_Heifers_DSCN2089b.jpg|Shorthorn heifers in a field | |||
File:Alex_Hershaft.jpg|Alex Hershaft, animal rights activist | |||
File:Tractors_in_Potato_Field.jpg|Tractors working in a potato field | |||
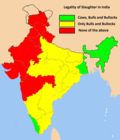
File:Status_of_cow_slaughter_in_India.png|Status of cow slaughter in India | |||
File:Indiapoultry.JPG|Poultry farming in India | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:16, 18 February 2025
Ethics of Eating Meat
The Ethics of Eating Meat is a complex and multifaceted topic that encompasses a range of philosophical, environmental, and health-related issues. It involves the examination of the moral implications of consuming animal products, particularly in the context of modern industrial farming practices.
Philosophical Perspectives[edit]
The philosophical perspectives on the ethics of eating meat often revolve around the concepts of animal rights, animal welfare, and speciesism. Some philosophers argue that animals have inherent rights that should be respected, which includes the right not to be killed for food. Others, however, contend that while animals should be treated humanely, they do not possess the same rights as humans.
Animal Rights[edit]
The Animal Rights perspective asserts that animals have inherent rights, similar to human rights. This view often leads to the conclusion that killing animals for food is morally wrong, regardless of how the animals are treated during their lives.
Animal Welfare[edit]
The Animal Welfare perspective, on the other hand, focuses on the treatment of animals rather than their inherent rights. Advocates of this view argue that it is morally acceptable to use animals for food, provided they are treated humanely and killed painlessly.
Speciesism[edit]
Speciesism is the belief that humans are superior to other species and therefore have the right to use them for their own purposes, including food. Critics of speciesism argue that this belief is a form of discrimination, similar to racism or sexism.
Environmental Considerations[edit]
The environmental impact of meat consumption is another significant aspect of the ethics of eating meat. Industrial farming practices are often associated with a range of environmental problems, including climate change, deforestation, and water pollution.
Health Considerations[edit]
The health implications of meat consumption are also a key part of the debate. Some studies suggest that a diet high in meat can lead to health problems such as heart disease, cancer, and obesity. However, others argue that meat is a vital source of nutrients that are difficult to obtain from plant-based sources.
See Also[edit]
| Human impact on the environment | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Health Topics > A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z |
| View All Health Topics in one page! | Health Encyclopedia | Index of health articles |
Professions:Medicine | Nursing | Pharmacy | Healthcare science | Dentistry | Allied health professions | Healthcare
| Medicine | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ethics of eating meat[edit]
-
Various cuts of meat
-
Cattle bodies in a slaughterhouse
-
Shorthorn heifers in a field
-
Alex Hershaft, animal rights activist
-
Tractors working in a potato field
-
Status of cow slaughter in India
-
Poultry farming in India