Mycotic aneurysm: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
{{Infectious diseases}} | {{Infectious diseases}} | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
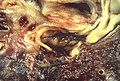
File:Mycotic_pulmonary_artery_aneurysm,_ruptured_(4860663580).jpg|Mycotic pulmonary artery aneurysm, ruptured | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 02:03, 17 February 2025
Mycotic Aneurysm
A Mycotic Aneurysm is a rare but serious medical condition that involves the formation of an aneurysm due to an infection. The term "mycotic" is derived from the Greek word "mykes", meaning fungus, as the condition was first observed in patients with fungal infections. However, it is now known that mycotic aneurysms can be caused by a variety of bacterial infections, including syphilis, tuberculosis, and endocarditis.
Etiology
Mycotic aneurysms are typically caused by a bacterial infection that has spread to the wall of an artery, often via the bloodstream. The most common causative organisms are Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella species. Less commonly, mycotic aneurysms can be caused by fungal infections.
Pathophysiology
The infection causes inflammation and weakening of the arterial wall, leading to the formation of an aneurysm. The aneurysm can then rupture, leading to serious complications such as hemorrhage, ischemia, and death.
Clinical Presentation
Patients with a mycotic aneurysm may present with a variety of symptoms, depending on the location of the aneurysm. Common symptoms include pain, fever, and a pulsatile mass. If the aneurysm ruptures, it can cause severe pain, shock, and potentially life-threatening bleeding.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of a mycotic aneurysm involves a combination of clinical history, physical examination, and imaging studies. Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are commonly used to visualize the aneurysm. Blood cultures may also be performed to identify the causative organism.
Treatment
Treatment of mycotic aneurysms involves both medical and surgical interventions. Antibiotics are used to treat the underlying infection, while surgery may be required to repair or remove the aneurysm.
Prognosis
The prognosis for patients with a mycotic aneurysm depends on a variety of factors, including the size and location of the aneurysm, the patient's overall health, and the success of treatment. Despite advances in diagnosis and treatment, mycotic aneurysms continue to have a high mortality rate.
| Cardiovascular disease (vessels) | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Infectious diseases | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This infectious diseases related article is a stub.
|
-
Mycotic pulmonary artery aneurysm, ruptured