Arrhythmia
| Heart arrhythmia | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Cardiac arrhythmia, cardiac dysrhythmia, irregular heartbeat |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Field | Cardiology |
| Symptoms | Palpitations, lightheadedness, passing out, shortness of breath, chest pain |
| Complications | Stroke, heart failure |
| Onset | Older age |
| Duration | |
| Types | Extra beats, supraventricular tachycardias, ventricular arrhythmias, bradyarrhythmias |
| Causes | Problems with the electrical conduction system of the heart |
| Risks | |
| Diagnosis | Electrocardiogram, Holter monitor |
| Differential diagnosis | |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | Medications, medical procedures (pacemaker), surgery |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | |
| Frequency | Millions |
| Deaths | |

Arrhythmia or Cardiac arrhythmia is a group of conditions in which the muscle contraction of the heart is irregular or is faster or slower than normal. Cardiac dysrhythmia is technically more correct, as arrhythmia would imply that there is "no rhythm," but this term is not used frequently.
Some arrhythmias are life-threatening medical emergencies that can cause cardiac arrest and sudden death. Others cause aggravating symptoms, such as an awareness of a different heart beat, or palpitation, which can be annoying. Some are quite benign and normal. Sinus arrhythmia is the mild acceleration followed by slowing of the normal rhythm that occurs with breathing. In adults the normal heart rate ranges from 60 beats per minute to 100 beats per minute. The normal heart beat is controlled by a small area in the upper chamber of the heart called the sinoatrial node or sinus node. The sinus node contains specialized cells that have spontaneous electrical activity that starts each normal heart beat.
Frequency too high or too low[edit]
A heart rate faster than 100 beats/minute is considered a tachycardia. With exercise the sinus node increases its rate of electrical activity to accelerate the heart rate. The normal fast rate that develops is called sinus tachycardia. Arrhythmias that are due to fast, abnormal electrical activity can cause tachycardias that are dangerous. If the ventricles of the heart experiences one of these tachycardias for a long period of time, there can be deleterious effects. Individuals may sense a tachycardia as a pounding sensation of the heart, known as palpitations. If a tachycardia lowers blood pressure it may cause lightheadedness or dizzinesses, or even fainting (syncope). If the tachycardia is too fast that the pump function of the heart is impeded, which may lead to a sudden death.
Most tachycardias are not dangerous. Anything that increases adrenaline or its effects on the heart will increase the heart rate and potentially cause palpitations or tachycardias. Causes include stress, ingested or injected substances (ie: caffeine, alcohol (see Holiday heart syndrome), and an overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism). Individuals who have a tachycardia are often advised to limit or remove exposure to any causative agent.
A slow rhythm, known as bradycardia (less than 60 beats/min), is usually not life threatening, but may cause symptoms. When it causes symptoms implantation of a permanent pacemaker may be needed.
Either dysrhythmia requires medical attention to evaluate the risks associated with the arrhythmia.
Fibrillation[edit]
A serious variety of arrhythmia is known as fibrillation. Fibrillation occurs when the heart muscle begins a quivering motion instead of a normal, healthy pumping rhythm. Fibrillation can affect the atrium (atrial fibrillation) or the ventricle (ventricular fibrillation); ventricular fibrillation is imminently life-threatening.
Atrial fibrillationAtrial fibrillation is the quivering, chaotic motion in the upper chambers of the heart, known as the atria. Atrial fibrillation is often due to serious underlying medical conditions, and should be evaluated by a physician. It is not typically a medical emergency.
Ventricular fibrillationVentricular fibrillation occurs in the ventricles (lower chambers) of the heart; it is always a medical emergency. If left untreated, ventricular fibrillation (VF, or V-fib) can lead to death within minutes. When a heart goes into V-fib, effective pumping of the blood stops. V-fib is considered a form of cardiac arrest, and an individual suffering from it will not survive unless cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and defibrillation are provided immediately.
CPR can prolong the survival of the brain in the lack of a normal pulse, but defibrillation is the intervention which is most likely to restore a more healthy heart rhythm. It does this by applying an electric shock to the heart, after which sometimes the heart will revert to a rhythm that can once again pump blood.
Almost every person goes into ventricular fibrillation in the last few minutes of life as the heart muscle reacts to diminished oxygen or general blood flow, trauma, irritants, or depression of electrical impulses themselves from the brain.
Origin of impulse[edit]
When an electrical impulse begins in any part of the heart, it will spread throughout the myocardium and cause a contraction; see Electrical conduction system of the heart. Abnormal impulses can begin by one of two mechanisms: automaticity or reentry.
Automaticity[edit]
Automaticity refers to a cardiac muscle cell firing off an impulse on its own. Every cardiac cell has this potential: if it does not receive any impulses from elsewhere, its internal "pacemaker" will fire off an impulse after a certain amount of time. A single specialized location in the atria, the sinoatrial node, has a higher automaticity (a faster pacemaker) than the rest of the heart, and therefore is usually the one to start the heartbeat.
Any part of the heart that initiates an impulse without waiting for the sinoatrial node is called an ectopic focus, and is by definition a pathological phenomenon. This may cause a single premature beat now and then, or, if the ectopic focus fires more often than the sinoatrial node, it can produce a sustained abnormal rhythm. Rhythms produced by an ectopic focus in the atria, or by the atrioventricular node, are the least dangerous dysrhythmias; but they can still produce a decrease in the heart's pumping efficiency, because the signal reaches the various parts of the heart muscle with slightly different timing than usual and causes a poorly coordinated contraction.
Conditions that increase automaticity include sympathetic nervous system stimulation and hypoxia. The resulting heart rhythm depends on where the first signal begins: if it is the sinoatrial node, the rhythm remains normal but rapid; if it is an ectopic focus, many types of dysrhythmia can result.
Reentry[edit]
Reentrant dysrhythmias occur when an electrical impulse travels in a circle within the heart, rather than moving outward and then stopping. Every cardiac cell is able to transmit impulses in every direction, but will only do so once within a short period of time. Normally the impulse spreads through the heart quickly enough that each cell will only respond once, but if conduction is abnormally slow in some areas, part of the impulse will arrive late and will be treated as a new impulse, which can then spread backward. Depending on the timing, this can produce a sustained abnormal rhythm, such as atrial flutter, a self-limiting burst of supraventricular tachycardia, or the dangerous ventricular tachycardia.
By analogy, imagine a room full of people all given these instructions: "If you see anyone starting to stand up, then stand up for three seconds and sit back down." If the people are quick enough to respond, the first person to stand will trigger a single wave which will then die out; but if there are stragglers on one side of the room, people who have already sat down will see them and start a second wave, and so on.
Diagnosis[edit]
Cardiac dysrhythmias are often first detected by simple but nonspecific means: auscultation of the heartbeat with a stethoscope, or feeling for peripheral pulses. These cannot usually diagnose specific dysrhythmias, but can give a general indication of the heart rate and whether it is regular or irregular. Not all the electrical impulses of the heart produce audible or palpable beats; in many cardiac arrhythmias, the premature or abnormal beats do not produce an effective pumping action and are experienced as "skipped" beats.
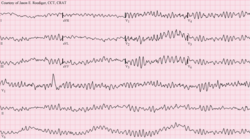
The simplest specific diagnostic test for assessment of heart rhythm is the electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG). A Holter monitor is an ECG recorded over a 24-hour period, to detect dysrhythmias that may happen briefly and unpredictably throughout the day.
SADS[edit]
SADS, or sudden arrhythmia death syndrome, is a term used to describe sudden death due to cardiac arrest brought on by an arrhythmia. The most common cause of sudden death in the US is coronary artery disease. Approximately 300,000 people die suddenly of this cause every year in the US. SADS can also occur from other causes. Tragically there are many inherited conditions and heart diseases that can affect young people that can cause sudden death. Many of these victims have no symptoms before dying suddenly.
The most common causes of SADS in young people are long QT syndrome, Brugada syndrome, and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia.
List of common cardiac dysrhythmias[edit]
- Atrial Arrhythmias
- Atrial Dysrhythmias
- Ventricular Arrhythmias
- Ventricular Dysrhythmias
- Junctional Dysrhythmias
- Heart Blocks
- Second degree heart block
- Type 1 Second degree heart block, also known as Mobitz I or Wenckebach
- Type 2 Second degree heart block, also known as Mobitz II
- Third degree heart block, also known as complete heart block
- Second degree heart block
Antiarrhythmic therapies[edit]
There are many classes of antiarrhythmic medications and many individual drugs within these classes. See the article on antiarrhythmic agents.
Dysrhythmias may also be treated electrically. Cardioversion is the application of electrical current across the chest wall to the heart and it is used for treatment of supraventricular or pulsed ventricular tachycardia. Defibrillation differs in that it is used for ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia, and more electricity is delivered with defibrillation than with cardioversion. In cardioversion, the recipient is either sedated or lightly anesthetized for the procedure. In defibrillation, the recipient has lost consciousness so there is no need for sedation.
Electrical treatment of dysrhythmia includes cardiac pacing. Temporay pacing may be done for very slow heartbeats, or bradycardia, from drug overdose or myocardial infarction. A pacemaker may be placed in situations where the bradycardia is not expected to recover.
Atrial fibrillation can also be treated through a procedure, e.g. pulmonary vein isolation. This is performed by a cardiologist who specializes in electrophysiology and is done percutaneously with catheters. Alternatively, a maze procedure can be performed through cardiothoracic surgery.
See also[edit]
- Antiarrhythmic agents
- Artificial pacemaker
- Electrical conduction system of the heart
- Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator.
External links[edit]
- Arrhythmia information from Seattle Children's Hospital Heart Center
- SADS Foundation
- Cardiac Risk in the Young (UK)
|
|
|
| Cardiovascular disease (heart) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian


