Fibromyalgia: Difference between revisions
Replaced content with "thumb Fibromyalgia tender points|thumb File:Fibromyalgia_symptoms.svg|Fibromyalgia sympt..." Tag: Replaced |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Widespread_Pain_Index_Areas.svg|thumb]] | {{SI}} | ||
[[File:Tender_points_fibromyalgia.svg|Fibromyalgia tender points|thumb]] | {{Infobox medical condition | ||
[[File:Fibromyalgia_symptoms.svg|Fibromyalgia symptoms|thumb]] | | name = Fibromyalgia | ||
| image = [[File:Symptoms_of_fibromyalgia.svg|250px]] | |||
| caption = Common symptoms of fibromyalgia | |||
| field = [[Rheumatology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Chronic pain]], [[fatigue]], [[sleep disturbances]], [[cognitive dysfunction]] | |||
| onset = Middle adulthood | |||
| duration = Long-term | |||
| causes = Unknown | |||
| risks = [[Genetics]], [[stress]], [[trauma]] | |||
| diagnosis = Based on symptoms, [[exclusion of other conditions]] | |||
| differential = [[Chronic fatigue syndrome]], [[rheumatoid arthritis]], [[lupus]] | |||
| treatment = [[Medication]], [[exercise]], [[cognitive behavioral therapy]] | |||
| medication = [[Antidepressants]], [[anticonvulsants]], [[pain relievers]] | |||
| frequency = ~2-8% of the population | |||
| deaths = Not directly fatal | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Widespread_Pain_Index_Areas.svg|left|thumb]] | |||
[[File:Tender_points_fibromyalgia.svg|Fibromyalgia tender points|left|thumb]] | |||
[[File:Fibromyalgia_symptoms.svg|Fibromyalgia symptoms|left|thumb]] | |||
Fibromyalgia is a chronic disorder characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and tenderness in localized areas. The condition is often associated with additional symptoms, such as headaches, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and mood disorders. The exact cause of fibromyalgia is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. There is no cure for fibromyalgia, but various treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve patients' quality of life. | Fibromyalgia is a chronic disorder characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and tenderness in localized areas. The condition is often associated with additional symptoms, such as headaches, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and mood disorders. The exact cause of fibromyalgia is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. There is no cure for fibromyalgia, but various treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve patients' quality of life. | ||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
The primary symptoms of fibromyalgia include: | The primary symptoms of fibromyalgia include: | ||
* '''Widespread pain''': Patients often report a constant dull ache that has lasted for at least three months. The pain must occur on both sides of the body and above and below the waist. | * '''Widespread pain''': Patients often report a constant dull ache that has lasted for at least three months. The pain must occur on both sides of the body and above and below the waist. | ||
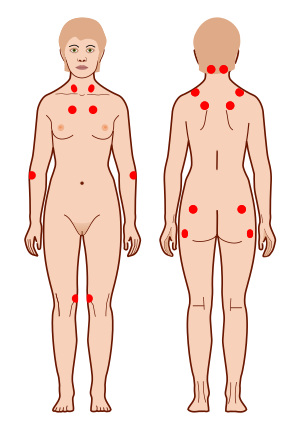
* '''Tenderness''': Tender points are specific areas on the body that are painful when pressure is applied. These points are often located in the neck, shoulders, back, hips, arms, and legs. | * '''Tenderness''': Tender points are specific areas on the body that are painful when pressure is applied. These points are often located in the neck, shoulders, back, hips, arms, and legs. | ||
| Line 13: | Line 28: | ||
* '''Sleep disturbances''': Many patients report difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing non-restorative sleep. | * '''Sleep disturbances''': Many patients report difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing non-restorative sleep. | ||
* '''Cognitive difficulties''': Often referred to as "fibro fog," this symptom involves problems with memory, concentration, and attention. | * '''Cognitive difficulties''': Often referred to as "fibro fog," this symptom involves problems with memory, concentration, and attention. | ||
Additional symptoms may include: | Additional symptoms may include: | ||
* Headaches | * Headaches | ||
* Irritable bowel syndrome | * Irritable bowel syndrome | ||
| Line 22: | Line 35: | ||
* Interstitial cystitis or painful bladder syndrome | * Interstitial cystitis or painful bladder syndrome | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
The exact cause of fibromyalgia remains unknown, but it is likely to involve a combination of factors, such as: | The exact cause of fibromyalgia remains unknown, but it is likely to involve a combination of factors, such as: | ||
* '''Genetics''': Fibromyalgia tends to run in families, suggesting that genetic factors may contribute to the development of the disorder. | * '''Genetics''': Fibromyalgia tends to run in families, suggesting that genetic factors may contribute to the development of the disorder. | ||
* '''Infections''': Some illnesses, such as viral or bacterial infections, may trigger or worsen fibromyalgia symptoms. | * '''Infections''': Some illnesses, such as viral or bacterial infections, may trigger or worsen fibromyalgia symptoms. | ||
| Line 30: | Line 41: | ||
* '''Abnormal pain perception''': Research suggests that people with fibromyalgia have an altered pain perception due to changes in the way the brain processes pain signals. | * '''Abnormal pain perception''': Research suggests that people with fibromyalgia have an altered pain perception due to changes in the way the brain processes pain signals. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Diagnosing fibromyalgia can be challenging, as there is no specific test to confirm the disorder. Instead, doctors rely on a combination of patient history, physical examination, and ruling out other potential causes of the symptoms. The American College of Rheumatology has established diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia, which include: | Diagnosing fibromyalgia can be challenging, as there is no specific test to confirm the disorder. Instead, doctors rely on a combination of patient history, physical examination, and ruling out other potential causes of the symptoms. The American College of Rheumatology has established diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia, which include: | ||
* Widespread pain lasting at least three months | * Widespread pain lasting at least three months | ||
| Line 42: | Line 52: | ||
* '''Counseling''': Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other forms of counseling can help patients develop coping strategies and address mood disorders associated with fibromyalgia. | * '''Counseling''': Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other forms of counseling can help patients develop coping strategies and address mood disorders associated with fibromyalgia. | ||
* '''Lifestyle changes''': Patients are encouraged to adopt healthy lifestyle habits, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and proper sleep hygiene, to help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being. | * '''Lifestyle changes''': Patients are encouraged to adopt healthy lifestyle habits, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and proper sleep hygiene, to help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being. | ||
'''Alternative therapies''': Some patients find relief from symptoms through alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, massage, yoga, and meditation. | '''Alternative therapies''': Some patients find relief from symptoms through alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, massage, yoga, and meditation. | ||
== Prognosis == | == Prognosis == | ||
Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition, and symptoms may persist over time. However, the severity of symptoms can vary from person to person and may even improve with proper treatment and self-management. Patients who receive early and comprehensive treatment often experience better outcomes and an improved quality of life. | Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition, and symptoms may persist over time. However, the severity of symptoms can vary from person to person and may even improve with proper treatment and self-management. Patients who receive early and comprehensive treatment often experience better outcomes and an improved quality of life. | ||
== Research and Future Directions == | == Research and Future Directions == | ||
Current research in fibromyalgia aims to better understand the underlying causes, identify biomarkers for diagnosis, and develop more effective treatments. Ongoing studies are exploring the role of genetic factors, the relationship between fibromyalgia and other chronic pain conditions, and potential therapies targeting the central nervous system. | Current research in fibromyalgia aims to better understand the underlying causes, identify biomarkers for diagnosis, and develop more effective treatments. Ongoing studies are exploring the role of genetic factors, the relationship between fibromyalgia and other chronic pain conditions, and potential therapies targeting the central nervous system. | ||
== Support and Resources == | == Support and Resources == | ||
Several organizations provide support, resources, and advocacy for patients with fibromyalgia and their families, including: | Several organizations provide support, resources, and advocacy for patients with fibromyalgia and their families, including: | ||
Latest revision as of 15:41, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Fibromyalgia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Chronic pain, fatigue, sleep disturbances, cognitive dysfunction |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Middle adulthood |
| Duration | Long-term |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Unknown |
| Risks | Genetics, stress, trauma |
| Diagnosis | Based on symptoms, exclusion of other conditions |
| Differential diagnosis | Chronic fatigue syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Medication, exercise, cognitive behavioral therapy |
| Medication | Antidepressants, anticonvulsants, pain relievers |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | ~2-8% of the population |
| Deaths | Not directly fatal |


Fibromyalgia is a chronic disorder characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and tenderness in localized areas. The condition is often associated with additional symptoms, such as headaches, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and mood disorders. The exact cause of fibromyalgia is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. There is no cure for fibromyalgia, but various treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve patients' quality of life.
Symptoms[edit]
The primary symptoms of fibromyalgia include:
- Widespread pain: Patients often report a constant dull ache that has lasted for at least three months. The pain must occur on both sides of the body and above and below the waist.
- Tenderness: Tender points are specific areas on the body that are painful when pressure is applied. These points are often located in the neck, shoulders, back, hips, arms, and legs.
- Fatigue: People with fibromyalgia frequently experience tiredness and wake up feeling unrefreshed, even after a full night's sleep.
- Sleep disturbances: Many patients report difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing non-restorative sleep.
- Cognitive difficulties: Often referred to as "fibro fog," this symptom involves problems with memory, concentration, and attention.
Additional symptoms may include:
- Headaches
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders
- Anxiety and depression
- Interstitial cystitis or painful bladder syndrome
Causes[edit]
The exact cause of fibromyalgia remains unknown, but it is likely to involve a combination of factors, such as:
- Genetics: Fibromyalgia tends to run in families, suggesting that genetic factors may contribute to the development of the disorder.
- Infections: Some illnesses, such as viral or bacterial infections, may trigger or worsen fibromyalgia symptoms.
- Physical or emotional trauma: Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and other traumatic events have been linked to the onset of fibromyalgia.
- Abnormal pain perception: Research suggests that people with fibromyalgia have an altered pain perception due to changes in the way the brain processes pain signals.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosing fibromyalgia can be challenging, as there is no specific test to confirm the disorder. Instead, doctors rely on a combination of patient history, physical examination, and ruling out other potential causes of the symptoms. The American College of Rheumatology has established diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia, which include:
- Widespread pain lasting at least three months
- Presence of other symptoms, such as fatigue, cognitive difficulties, and sleep disturbances
- Absence of another underlying condition that could explain the symptoms
Treatment[edit]
There is no cure for fibromyalgia, but a variety of treatments can help manage symptoms and improve patients' quality of life. Treatment options may include:
- Medications: Prescription medications, such as pain relievers, antidepressants, and anti-seizure drugs, may help alleviate pain and improve sleep.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapists can develop individualized exercise programs to help improve strength, flexibility, and endurance.
- Occupational therapy: Occupational therapists can provide guidance on managing daily activities and reducing stress on the body.
- Counseling: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other forms of counseling can help patients develop coping strategies and address mood disorders associated with fibromyalgia.
- Lifestyle changes: Patients are encouraged to adopt healthy lifestyle habits, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and proper sleep hygiene, to help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Alternative therapies: Some patients find relief from symptoms through alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, massage, yoga, and meditation.
Prognosis[edit]
Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition, and symptoms may persist over time. However, the severity of symptoms can vary from person to person and may even improve with proper treatment and self-management. Patients who receive early and comprehensive treatment often experience better outcomes and an improved quality of life.
Research and Future Directions[edit]
Current research in fibromyalgia aims to better understand the underlying causes, identify biomarkers for diagnosis, and develop more effective treatments. Ongoing studies are exploring the role of genetic factors, the relationship between fibromyalgia and other chronic pain conditions, and potential therapies targeting the central nervous system.
Support and Resources[edit]
Several organizations provide support, resources, and advocacy for patients with fibromyalgia and their families, including:
- National Fibromyalgia Association (NFA): A nonprofit organization dedicated to improving the quality of life for people with fibromyalgia through education, research, and advocacy.
- Fibromyalgia Care Society of America (FCSA): A nonprofit organization that offers support services, education, and resources for individuals living with fibromyalgia and their families.
- American Chronic Pain Association (ACPA): A nonprofit organization providing education, support, and advocacy for individuals with chronic pain, including those with fibromyalgia.
|
|
|
| Neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia pharmacotherapies | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Arthritis in children | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|


