Dermatomyositis
| Dermatomyositis | |
|---|---|
| File:Dermatomyositis.jpg | |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Field | Rheumatology |
| Symptoms | Rash, muscle weakness, weight loss, fever |
| Complications | Calcinosis, lung inflammation, heart disease |
| Onset | 40s to 50s |
| Duration | Long term |
| Types | |
| Causes | Unknown |
| Risks | |
| Diagnosis | Based on symptoms, blood tests, electromyography, muscle biopsies |
| Differential diagnosis | Polymyositis, inclusion body myositis, scleroderma |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | Medication, physical therapy, exercise, heat therapy, orthotics, assistive devices, rest |
| Medication | Corticosteroids, methotrexate, azathioprine |
| Prognosis | |
| Frequency | ~ 1 per 100,000 people per year |
| Deaths | |
Dermatomyositis (DM) is a chronic inflammatory disorder that primarily affects muscles and skin.
Overview[edit]
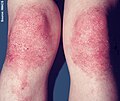
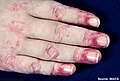
Dermatomyositis is characterized by a distinctive skin rash and progressive muscle weakness, which may occur suddenly or develop gradually over months. Additional symptoms might include weight loss, fever, lung inflammation, or light sensitivity. Complications can involve calcium deposits in muscles or skin.
Etiology[edit]
The exact cause of dermatomyositis remains unknown. It is postulated to be an autoimmune disease or potentially triggered by a viral infection, categorizing it as a type of inflammatory myopathy.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of dermatomyositis typically relies on a combination of symptomatology, blood tests, electromyography, and muscle biopsies.
Treatment[edit]
While there is currently no cure for dermatomyositis, various treatment strategies can alleviate symptoms. These may include medication, physical therapy, exercise, heat therapy, orthotics, assistive devices, and rest. Corticosteroids are commonly used, with additional agents such as methotrexate or azathioprine recommended if steroid therapy is insufficient. Intravenous immunoglobulin may also be beneficial. The condition may improve with treatment, and in some cases, it may resolve completely.
Epidemiology[edit]
Dermatomyositis affects approximately 1 per 100,000 people each year. It commonly presents in individuals in their 40s and 50s, with a higher incidence in women than men. However, it can affect individuals of any age. The condition was first described in the 1800s.
-
Gottron's papules on finger joints.
-
Gottron's papules on the elbows of a person with juvenile DM
-
Gottron's papules
-
Gottron's papules on a person with juvenile DM
-
Gottron's papules in severe case of juvenile dermatomyositis
-
Heliotrope with swelling around the eyes
-
Heliotrope
-
Facial rash
-
Severe rash on the hands, extending up the forearm
-
Forearm rash
See Also[edit]
|
|
|
External links[edit]
Lua error: bad argument #2 to 'title.new' (unrecognized namespace name 'Portal').
|
|
|
| Systemic connective tissue disorders | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Inflammation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Paraneoplastic syndromes | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian