Adiposis dolorosa: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|A rare condition characterized by painful lipomas}} | {{Short description|A rare condition characterized by painful lipomas}} | ||
{{ | {{Infobox medical condition (new) | ||
| name = Adiposis dolorosa | |||
| image = Nervous and mental diseases (1919) (14781727145).jpg | |||
| alt = A historical image of a woman with adiposis dolorosa | |||
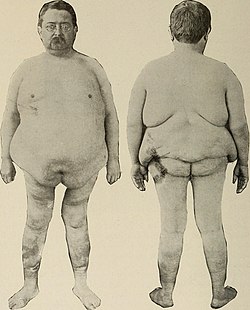
| caption = A patient with adiposis dolorosa showing fatty deposits | |||
| pronounce = | |||
| field = [[Endocrinology]], [[Neurology]], [[Rheumatology]] | |||
| synonyms = Dercum's disease, Anders disease | |||
| symptoms = Painful fatty tumors, chronic pain, fatigue, weight gain, memory issues, depression | |||
| complications = Impaired mobility, mental health challenges, social isolation | |||
| onset = Typically between ages 35 and 50 | |||
| duration = Chronic, lifelong | |||
| types = Generalized, nodular, localized, juxta-articular | |||
| causes = Unknown; possibly related to [[nervous system]], [[autoimmune]] or [[metabolic]] dysfunction | |||
| risks = More common in women, especially those who are overweight or obese | |||
| diagnosis = Based on clinical symptoms and exclusion of other conditions | |||
| differential = [[Lipomas]], [[fibromyalgia]], [[multiple lipomatosis]], [[lipoedema]] | |||
| prevention = None known | |||
| treatment = Pain management, physical therapy, psychological support | |||
| medication = [[Analgesics]], [[antidepressants]], [[anticonvulsants]] (for neuropathic pain) | |||
| prognosis = Variable; chronic pain often persists, but not life-threatening | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
| deaths = Not typically fatal | |||
}} | |||
'''Adiposis dolorosa''', also known as '''Dercum's disease''', is a rare condition characterized by multiple painful [[lipomas]], which are benign tumors composed of [[adipose tissue]]. This condition predominantly affects [[adults]] and is more common in [[women]] than in [[men]]. | '''Adiposis dolorosa''', also known as '''Dercum's disease''', is a rare condition characterized by multiple painful [[lipomas]], which are benign tumors composed of [[adipose tissue]]. This condition predominantly affects [[adults]] and is more common in [[women]] than in [[men]]. | ||
| Line 25: | Line 47: | ||
* [[Rare diseases]] | * [[Rare diseases]] | ||
{{Medical resources | |||
| DiseasesDB = 29660 | |||
| ICD10 = {{ICD10|E|88|2|e|70}} | |||
| ICD9 = {{ICD9|272.8}} | |||
| ICDO = | |||
| OMIM = 103200 | |||
| MedlinePlus = | |||
| eMedicineSubj = derm | |||
| eMedicineTopic = 839 | |||
| MeshID = D000274 | |||
| Orphanet=36397 | |||
}} | |||
{{Soft tissue tumors and sarcomas}} | |||
{{stub}} | |||
[[Category:Rare diseases]] | |||
[[Category:Rare diseases]] | [[Category:Rare diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Adipose tissue disorders]] | [[Category:Adipose tissue disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Chronic pain syndromes]] | [[Category:Chronic pain syndromes]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:13, 23 March 2025
A rare condition characterized by painful lipomas
| Adiposis dolorosa | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Dercum's disease, Anders disease |
| Pronounce | |
| Field | Endocrinology, Neurology, Rheumatology |
| Symptoms | Painful fatty tumors, chronic pain, fatigue, weight gain, memory issues, depression |
| Complications | Impaired mobility, mental health challenges, social isolation |
| Onset | Typically between ages 35 and 50 |
| Duration | Chronic, lifelong |
| Types | Generalized, nodular, localized, juxta-articular |
| Causes | Unknown; possibly related to nervous system, autoimmune or metabolic dysfunction |
| Risks | More common in women, especially those who are overweight or obese |
| Diagnosis | Based on clinical symptoms and exclusion of other conditions |
| Differential diagnosis | Lipomas, fibromyalgia, multiple lipomatosis, lipoedema |
| Prevention | None known |
| Treatment | Pain management, physical therapy, psychological support |
| Medication | Analgesics, antidepressants, anticonvulsants (for neuropathic pain) |
| Prognosis | Variable; chronic pain often persists, but not life-threatening |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | Not typically fatal |
Adiposis dolorosa, also known as Dercum's disease, is a rare condition characterized by multiple painful lipomas, which are benign tumors composed of adipose tissue. This condition predominantly affects adults and is more common in women than in men.
Signs and symptoms[edit]
Individuals with adiposis dolorosa typically present with multiple, painful lipomas located primarily on the trunk, upper arms, and upper legs. The pain associated with these lipomas can be severe and is often described as burning or aching. In addition to the lipomas, patients may experience fatigue, weakness, and emotional disturbances such as depression and anxiety.
Pathophysiology[edit]
The exact cause of adiposis dolorosa is not well understood. It is believed to involve abnormalities in the nervous system and adipose tissue metabolism. Some researchers suggest that the pain may be due to nerve compression by the lipomas or an inflammatory process within the adipose tissue. There is also evidence to suggest a possible genetic component, as the condition can run in families.
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of adiposis dolorosa is primarily clinical, based on the presence of painful lipomas and associated symptoms. Imaging studies such as ultrasound or MRI may be used to assess the lipomas and rule out other conditions. A biopsy of the lipomas can confirm the diagnosis by showing mature adipose tissue without atypical features.
Treatment[edit]
There is no cure for adiposis dolorosa, and treatment is primarily symptomatic. Pain management is a key component and may include analgesics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and in some cases, opioids. Surgical removal of the lipomas may be considered for those causing significant pain or discomfort. Other treatments that have been explored include liposuction, corticosteroid injections, and physical therapy.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for individuals with adiposis dolorosa varies. While the condition is chronic and can significantly impact quality of life, it is not life-threatening. The severity of symptoms can fluctuate, and some patients may experience periods of remission.
Related pages[edit]


