Amygdalofugal pathway: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
File:Amygdala_and_Nucleus_Basalis_connections_to_the_Thalamus2.png|Amygdalofugal pathway | File:Amygdala_and_Nucleus_Basalis_connections_to_the_Thalamus2.png|Amygdalofugal pathway | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
== Amygdalofugal Pathway == | |||
The '''amygdalofugal pathway''' is a neural pathway that connects the [[amygdala]] to various regions of the brain. It plays a crucial role in the processing of emotions, particularly those related to fear and pleasure, and is involved in the regulation of autonomic and endocrine responses. | |||
=== Anatomy === | |||
The amygdalofugal pathway originates in the [[amygdala]], a complex structure located in the medial temporal lobe of the brain. The amygdala is composed of several nuclei, including the basolateral, central, and medial nuclei, each of which contributes to different aspects of emotional processing. | |||
From the amygdala, the amygdalofugal fibers project to several key brain regions: | |||
* The [[hypothalamus]], which is involved in the regulation of autonomic functions and the endocrine system. | |||
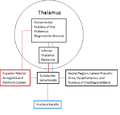
* The [[thalamus]], which acts as a relay station for sensory and motor signals. | |||
* The [[brainstem]], which is involved in controlling basic life functions such as heart rate and respiration. | |||
* The [[prefrontal cortex]], which is associated with higher cognitive functions such as decision-making and social behavior. | |||
The pathway is part of the larger [[limbic system]], which is involved in emotion, behavior, and long-term memory. | |||
=== Function === | |||
The amygdalofugal pathway is primarily involved in the processing and regulation of emotions. It plays a significant role in: | |||
* '''Fear conditioning''': The pathway is crucial for the formation and retrieval of fear-related memories. It helps in associating sensory stimuli with emotional responses. | |||
* '''Emotional regulation''': By connecting the amygdala with the prefrontal cortex, the pathway helps in modulating emotional responses and controlling impulsive behaviors. | |||
* '''Autonomic and endocrine responses''': The pathway influences the hypothalamus, thereby affecting the autonomic nervous system and the release of hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol during stress responses. | |||
=== Clinical Significance === | |||
Dysfunction in the amygdalofugal pathway has been implicated in various psychiatric and neurological disorders, including: | |||
* [[Anxiety disorders]]: Abnormal activity in the pathway can lead to heightened fear responses and anxiety. | |||
* [[Depression]]: Altered connectivity between the amygdala and prefrontal cortex may contribute to mood dysregulation. | |||
* [[Post-traumatic stress disorder]] (PTSD): Impaired processing of fear-related memories can result in persistent and intrusive recollections of traumatic events. | |||
Understanding the amygdalofugal pathway is essential for developing therapeutic strategies for these conditions. | |||
== Related Pages == | |||
* [[Amygdala]] | |||
* [[Limbic system]] | |||
* [[Hypothalamus]] | |||
* [[Prefrontal cortex]] | |||
* [[Fear conditioning]] | |||
{{Neuroscience}} | |||
{{Neuroanatomy}} | |||
[[Category:Neuroanatomy]] | |||
[[Category:Limbic system]] | |||
Latest revision as of 00:42, 19 February 2025
Amygdalofugal_pathway[edit]
-
Amygdalofugal pathway
-
Amygdalofugal pathway
Amygdalofugal Pathway[edit]
The amygdalofugal pathway is a neural pathway that connects the amygdala to various regions of the brain. It plays a crucial role in the processing of emotions, particularly those related to fear and pleasure, and is involved in the regulation of autonomic and endocrine responses.
Anatomy[edit]
The amygdalofugal pathway originates in the amygdala, a complex structure located in the medial temporal lobe of the brain. The amygdala is composed of several nuclei, including the basolateral, central, and medial nuclei, each of which contributes to different aspects of emotional processing.
From the amygdala, the amygdalofugal fibers project to several key brain regions:
- The hypothalamus, which is involved in the regulation of autonomic functions and the endocrine system.
- The thalamus, which acts as a relay station for sensory and motor signals.
- The brainstem, which is involved in controlling basic life functions such as heart rate and respiration.
- The prefrontal cortex, which is associated with higher cognitive functions such as decision-making and social behavior.
The pathway is part of the larger limbic system, which is involved in emotion, behavior, and long-term memory.
Function[edit]
The amygdalofugal pathway is primarily involved in the processing and regulation of emotions. It plays a significant role in:
- Fear conditioning: The pathway is crucial for the formation and retrieval of fear-related memories. It helps in associating sensory stimuli with emotional responses.
- Emotional regulation: By connecting the amygdala with the prefrontal cortex, the pathway helps in modulating emotional responses and controlling impulsive behaviors.
- Autonomic and endocrine responses: The pathway influences the hypothalamus, thereby affecting the autonomic nervous system and the release of hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol during stress responses.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Dysfunction in the amygdalofugal pathway has been implicated in various psychiatric and neurological disorders, including:
- Anxiety disorders: Abnormal activity in the pathway can lead to heightened fear responses and anxiety.
- Depression: Altered connectivity between the amygdala and prefrontal cortex may contribute to mood dysregulation.
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): Impaired processing of fear-related memories can result in persistent and intrusive recollections of traumatic events.
Understanding the amygdalofugal pathway is essential for developing therapeutic strategies for these conditions.
Related Pages[edit]
| Neuroanatomy | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This neuroanatomy-related article is a stub.
|