Sickle cell disease: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Sickle cell disease | |||
| image = [[File:Sickle_cell_01.jpg|250px]] | |||
| caption = Sickle-shaped red blood cells | |||
| field = [[Hematology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Anemia]], [[pain crisis]], [[swelling]] in hands and feet, [[infections]], [[delayed growth]] | |||
| complications = [[Stroke]], [[acute chest syndrome]], [[organ damage]], [[pulmonary hypertension]] | |||
| onset = Usually in [[infancy]] | |||
| duration = [[Chronic]] | |||
| causes = [[Genetic mutation]] in the [[HBB gene]] | |||
| risks = [[Family history]], [[African]], [[Mediterranean]], [[Middle Eastern]], [[Indian]] ancestry | |||
| diagnosis = [[Blood test]], [[genetic testing]] | |||
| treatment = [[Pain management]], [[blood transfusions]], [[hydroxyurea]], [[bone marrow transplant]] | |||
| prognosis = [[Variable]], improved with treatment | |||
| frequency = Common in certain populations | |||
}} | |||
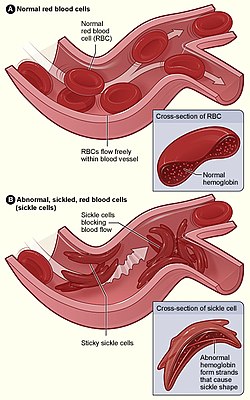
SCD is a hereditary genetic illness in which defective red blood cells transport less oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. These aberrant red blood cells aggregate in the blood arteries, causing discomfort, infections, and organ damage. | SCD is a hereditary genetic illness in which defective red blood cells transport less oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. These aberrant red blood cells aggregate in the blood arteries, causing discomfort, infections, and organ damage. | ||
[[File:Sickle Cell Disease (27249799083).jpg|thumb|Sickle Cell Disease]] | [[File:Sickle Cell Disease (27249799083).jpg|left|thumb|Sickle Cell Disease]] | ||
[[File:Red Blood Cells in Sickle Cell Disease.jpg|thumb|Red Blood Cells in Sickle Cell Disease]] | [[File:Red Blood Cells in Sickle Cell Disease.jpg|left|thumb|Red Blood Cells in Sickle Cell Disease]] | ||
== Cause == | == Cause == | ||
A mutation in the HBB gene, which encodes the beta-globin portion of hemoglobin, causes sickle cell disease. This mutation produces an aberrant form of hemoglobin known as hemoglobin S, which causes red blood cells to become sickle-shaped and less flexible. A person must inherit two copies of the defective gene from each parent in order to develop sickle cell disease. | A mutation in the HBB gene, which encodes the beta-globin portion of hemoglobin, causes sickle cell disease. This mutation produces an aberrant form of hemoglobin known as hemoglobin S, which causes red blood cells to become sickle-shaped and less flexible. A person must inherit two copies of the defective gene from each parent in order to develop sickle cell disease. | ||
[[File:Sickle cell 02.gif|Sickle cell genetics|left|thumb]] | |||
[[File:Sickle cell 02.gif|Sickle cell genetics|thumb]] | |||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
Primary sickle cell disease symptoms include: | Primary sickle cell disease symptoms include: | ||
* Anemia is a deficiency in red blood cells that can result in fatigue and shortness of breath. | * Anemia is a deficiency in red blood cells that can result in fatigue and shortness of breath. | ||
* Pain crises: Episodes of extreme agony lasting from hours to days caused by sickle-shaped cells obstructing blood flow in small capillaries. | * Pain crises: Episodes of extreme agony lasting from hours to days caused by sickle-shaped cells obstructing blood flow in small capillaries. | ||
* High vulnerability to infections as a result of spleen dysfunction. | * High vulnerability to infections as a result of spleen dysfunction. | ||
* Decreased blood supply to organs can result in long-term organ damage, affecting the kidneys, liver, and lungs. | * Decreased blood supply to organs can result in long-term organ damage, affecting the kidneys, liver, and lungs. | ||
== Complications == | == Complications == | ||
Many consequences can result from sickle cell disease, including: | Many consequences can result from sickle cell disease, including: | ||
* Acute chest syndrome is a potentially fatal illness marked by chest discomfort, fever, and breathing trouble. | * Acute chest syndrome is a potentially fatal illness marked by chest discomfort, fever, and breathing trouble. | ||
* Stroke is the interruption of blood flow to the brain, which can result in permanent neurological damage. | * Stroke is the interruption of blood flow to the brain, which can result in permanent neurological damage. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 35: | ||
* Visual impairment caused by damage to the blood vessels in the eye, resulting in retinal detachment or other eye issues. | * Visual impairment caused by damage to the blood vessels in the eye, resulting in retinal detachment or other eye issues. | ||
* Gallstones are stones that form in the gallbladder as a result of increased bilirubin production. | * Gallstones are stones that form in the gallbladder as a result of increased bilirubin production. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Blood tests, such as a complete blood count (CBC) and hemoglobin electrophoresis, can detect the presence of aberrant hemoglobin during sickle cell disease diagnosis. In addition to confirming the diagnosis, genetic testing can help identify disease carriers. | Blood tests, such as a complete blood count (CBC) and hemoglobin electrophoresis, can detect the presence of aberrant hemoglobin during sickle cell disease diagnosis. In addition to confirming the diagnosis, genetic testing can help identify disease carriers. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Currently, there is no cure for sickle cell disease, although therapies are available to help control symptoms and prevent complications. They consist of: | Currently, there is no cure for sickle cell disease, although therapies are available to help control symptoms and prevent complications. They consist of: | ||
| Line 32: | Line 43: | ||
* A drug that can minimize the frequency of pain crises and acute chest syndrome is hydroxyurea. | * A drug that can minimize the frequency of pain crises and acute chest syndrome is hydroxyurea. | ||
* A potentially curative treatment involving the replacement of the patient's bone marrow with healthy donor bone marrow. Yet, this operation has substantial risks and is not appropriate for many individuals. | * A potentially curative treatment involving the replacement of the patient's bone marrow with healthy donor bone marrow. Yet, this operation has substantial risks and is not appropriate for many individuals. | ||
== Summary == | == Summary == | ||
'''Sickle cell disease''' is an inherited disease in which the body makes abnormal red blood cells that carry less oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. These abnormal red blood cells form clumps that get stuck in the blood vessels, causing pain, infections, and organ damage. | '''Sickle cell disease''' is an inherited disease in which the body makes abnormal red blood cells that carry less oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. These abnormal red blood cells form clumps that get stuck in the blood vessels, causing pain, infections, and organ damage. | ||
Latest revision as of 21:16, 8 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Sickle cell disease | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Anemia, pain crisis, swelling in hands and feet, infections, delayed growth |
| Complications | Stroke, acute chest syndrome, organ damage, pulmonary hypertension |
| Onset | Usually in infancy |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic mutation in the HBB gene |
| Risks | Family history, African, Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, Indian ancestry |
| Diagnosis | Blood test, genetic testing |
| Differential diagnosis | N/A |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Pain management, blood transfusions, hydroxyurea, bone marrow transplant |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, improved with treatment |
| Frequency | Common in certain populations |
| Deaths | N/A |
SCD is a hereditary genetic illness in which defective red blood cells transport less oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. These aberrant red blood cells aggregate in the blood arteries, causing discomfort, infections, and organ damage.


Cause[edit]
A mutation in the HBB gene, which encodes the beta-globin portion of hemoglobin, causes sickle cell disease. This mutation produces an aberrant form of hemoglobin known as hemoglobin S, which causes red blood cells to become sickle-shaped and less flexible. A person must inherit two copies of the defective gene from each parent in order to develop sickle cell disease.

Symptoms[edit]
Primary sickle cell disease symptoms include:
- Anemia is a deficiency in red blood cells that can result in fatigue and shortness of breath.
- Pain crises: Episodes of extreme agony lasting from hours to days caused by sickle-shaped cells obstructing blood flow in small capillaries.
- High vulnerability to infections as a result of spleen dysfunction.
- Decreased blood supply to organs can result in long-term organ damage, affecting the kidneys, liver, and lungs.
Complications[edit]
Many consequences can result from sickle cell disease, including:
- Acute chest syndrome is a potentially fatal illness marked by chest discomfort, fever, and breathing trouble.
- Stroke is the interruption of blood flow to the brain, which can result in permanent neurological damage.
- Leg ulcers are painful, sluggishly-healing wounds on the legs.
- Visual impairment caused by damage to the blood vessels in the eye, resulting in retinal detachment or other eye issues.
- Gallstones are stones that form in the gallbladder as a result of increased bilirubin production.
Diagnosis[edit]
Blood tests, such as a complete blood count (CBC) and hemoglobin electrophoresis, can detect the presence of aberrant hemoglobin during sickle cell disease diagnosis. In addition to confirming the diagnosis, genetic testing can help identify disease carriers.
Treatment[edit]
Currently, there is no cure for sickle cell disease, although therapies are available to help control symptoms and prevent complications. They consist of:
- Pain treatment medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and opioids, can assist in the management of pain crises.
- Frequent transfusions of blood can minimize anemia and the risk of complications.
- A drug that can minimize the frequency of pain crises and acute chest syndrome is hydroxyurea.
- A potentially curative treatment involving the replacement of the patient's bone marrow with healthy donor bone marrow. Yet, this operation has substantial risks and is not appropriate for many individuals.
Summary[edit]
Sickle cell disease is an inherited disease in which the body makes abnormal red blood cells that carry less oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. These abnormal red blood cells form clumps that get stuck in the blood vessels, causing pain, infections, and organ damage.
|
|
|
| Diseases of red blood cells | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|


