Muscle: Difference between revisions
From WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia
No edit summary Tag: visualeditor-wikitext |
CSV import |
||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
[[Category:Soft tissue]] | [[Category:Soft tissue]] | ||
[[Category:Tissues (biology)]] | [[Category:Tissues (biology)]] | ||
== Muscle == | |||
<gallery> | |||
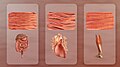
File:Types Of Muscle.jpg|Types Of Muscle | |||
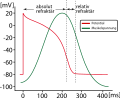
File:Muskelreiz-glatt.svg|Smooth Muscle Stimulation | |||
File:Muskelreiz-herz.svg|Heart Muscle Stimulation | |||
File:Muskelreiz-skelett.svg|Skeletal Muscle Stimulation | |||
File:Skeletal Muscle Tissue.jpg|Skeletal Muscle Tissue | |||
File:Gray18.png|Muscle Anatomy | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:41, 20 February 2025
Muscle is part of the muscular system or musculoskeletal system that is composed of specialized cells called muscle fibers.

Function[edit]
Their predominant function is contractibility. Muscles, attached to bones or internal organs and blood vessels, are responsible for movement.
Movement and muscle action[edit]
- Nearly all movement in the body is the result of muscle contraction.
- Exceptions to this are the action of cilia, the flagellum on sperm cells, and amoeboid movement of some white blood cells.
- The integrated action of joints, bones, and skeletal muscles produces obvious movements such as walking and running.

Facial expressions[edit]
Skeletal muscles also produce more subtle movements that result in various facial expressions, eye movements, and respiration.
Posture and stability[edit]
- In addition to movement, muscle contraction also fulfills some other important functions in the body, such as posture, joint stability, and heat production.
- Posture, such as sitting and standing, is maintained as a result of muscle contraction.
- The skeletal muscles are continually making fine adjustments that hold the body in stationary positions.
- The tendons of many muscles extend over joints and in this way contribute to joint stability.
- This is particularly evident in the knee and shoulder joints, where muscle tendons are a major factor in stabilizing the joint.

Thermal actions of muscles[edit]
- Heat production, to maintain body temperature, is an important by-product of muscle metabolism.
- Nearly 85 percent of the heat produced in the body is the result of muscle contraction.
- The brown adipose tissue in the skin helps regulate body heat at times of cold climate.
Structure of skeletal muscles[edit]
- A whole skeletal muscle is considered an organ of the muscular system.
- Each organ or muscle consists of skeletal muscle tissue, connective tissue, nerve tissue, and blood or vascular tissue.
- Skeletal muscles vary considerably in size, shape, and arrangement of fibers.
- They range from extremely tiny strands such as the stapedium muscle of the middle ear to large masses such as the muscles of the thigh.
- Some skeletal muscles are broad in shape and some narrow.
- In some muscles the fibers are parallel to the long axis of the muscle; in some they converge to a narrow attachment; and in some they are oblique.
Types of muscles[edit]
There are three types of muscle: skeletal (striated), smooth, and cardiac.
Skeletal Muscle[edit]

- Skeletal muscle, attached to bones, is responsible for skeletal movements.
- The peripheral portion of the central nervous system (CNS) controls the skeletal muscles.
- Thus, these muscles are under conscious, or voluntary, control.
- The basic unit is the muscle fiber with many nuclei. These muscle fibers are striated (having transverse streaks) and each acts independently of neighboring muscle fibers.
Smooth Muscle[edit]
- Smooth muscle, found in the walls of the hollow internal organs such as blood vessels, the gastrointestinal tract, bladder, and uterus, is under control of the autonomic nervous system.
- Smooth muscle cannot be controlled consciously and thus acts involuntarily.
- The non-striated (smooth) muscle cell is spindle-shaped and has one central nucleus. Smooth muscle contracts slowly and rhythmically.
Cardiac Muscle[edit]
- Cardiac muscle, found in the walls of the heart, is also under control of the autonomic nervous system.
- The cardiac muscle cell has one central nucleus, like smooth muscle, but it also is striated, like skeletal muscle.
- The cardiac muscle cell is rectangular in shape. The contraction of cardiac muscle is involuntary, strong, and rhythmical.
Muscle groups[edit]
- There are more than 600 muscles in the body, which together account for about 40 percent of a person's weight.
External links[edit]
Look up muscle in Wiktionary, the free dictionary.
- University of Dundee article on performing neurological examinations (Quadriceps "strongest")
- Muscle efficiency in rowing
- Muscle Physiology and Modeling Scholarpedia Tsianos and Loeb (2013)
- Human Muscle Tutorial (clear pictures of main human muscles and their Latin names, good for orientation)
- Microscopic stains of skeletal and cardiac muscular fibers to show striations. Note the differences in myofibrilar arrangements.
| Muscular system | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Muscle tissue | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Muscles of the head | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Muscles of the neck | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Muscles of the thorax and back | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Muscles and ligaments of abdomen and pelvis | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Muscles of the arm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Muscles of the hip and human leg | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| This article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by registering to expand it. |
Muscle[edit]
-
Types Of Muscle
-
Smooth Muscle Stimulation
-
Heart Muscle Stimulation
-
Skeletal Muscle Stimulation
-
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
-
Muscle Anatomy