Itraconazole: Difference between revisions
m 1 revision imported |
CSV import |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
{{antifungals}} | {{antifungals}} | ||
{{coststubd}} | {{coststubd}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
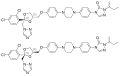
File:Itraconazole.svg|Chemical structure of Itraconazole | |||
File:Itraconazole_chiral_carbons.svg|Chiral carbons in Itraconazole | |||
File:Itraconazole_enantiomers.svg|Enantiomers of Itraconazole | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:48, 18 February 2025
itraconazole (IH-truh-KAH-nuh-zole) is a drug used to prevent or treat fungal infections. It belongs to the family of drugs called antifungal agents.
Information about Itraconazole[edit]
Itraconazole is a orally administered, triazole antifungal agent used in the treatment of systemic and superficial fungal infections.
Liver safety of Itraconazole[edit]
Itraconazole therapy is associated with transient, mild-to-moderate serum elevations and can lead to clinically apparent acute drug induced liver injury.
Mechanism of action of Itraconazole[edit]
Itraconazole (it" ra kon' a zole) is a synthetic triazole fungicidal agent which acts by inhibition of fungal C14-a- ergosterol demethylase, which leads to a decrease in ergosterol synthesis, a necessary component of fungal cell membranes.
Itraconazole is used in the therapy of a broad spectrum of fungal infections including blastomycosis, aspergillosis, histoplasmosis, candidiasis and various superficial mycoses.
FDA approval information for Itraconazole[edit]
Itraconazole was approved for use in the United States in 1992 and continues to be widely used as an antifungal agent.
Dosage and administration for Itraconazole[edit]
Current indications include blastomycosis, histoplasmosis, aspergillosis and onychomycosis. Itraconazole is available in capsules of 100 mg, tablets of 200 mg and oral suspensions of 10 mg/mL in generic forms and under the brand name Sporanox. The typical dose is 100 to 400 mg daily based upon the type and severity of the fungal infection.
Side effects of Itraconazole[edit]
Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, rash and hypokalemia.
-
Chemical structure of Itraconazole
-
Chiral carbons in Itraconazole
-
Enantiomers of Itraconazole