Cardiac arrest: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox medical condition (new) | |||
| name = Cardiac arrest | |||
| image = US Navy 040421-N-8090G-001 Hospital Corpsman 3rd Class Flowers administers chest compressions to a simulated cardiac arrest victim.jpg | |||
| caption = [[Cardiopulmonary resuscitation|CPR]] being administered during a simulation of cardiac arrest | |||
| synonyms = Sudden cardiac death (SCD), cardiopulmonary arrest, circulatory arrest, sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) | |||
| field = [[Cardiology]], [[emergency medicine]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Altered level of consciousness|Decreased level]] or [[unconsciousness|total loss of consciousness]], [[respiratory arrest|abnormal or no breathing]], no pulse | |||
| complications = If reversed, [[coma]], [[persistent vegetative state]], [[post-cardiac arrest syndrome]]; if not reversed, [[death]] | |||
| onset = The risk of onset increases with age | |||
| duration = | |||
| causes = [[Coronary artery disease]], [[congenital heart defect]], major [[bleeding|blood loss]], lack of oxygen, [[electrical injury]], [[hypokalemia|very low potassium]], [[heart failure]], [[myocardial infarction]] | |||
| risks = | |||
| diagnosis = Finding no pulse | |||
| differential = | |||
| prevention = Not smoking, physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, healthy eating | |||
| treatment = [[Cardiopulmonary resuscitation]] (CPR), [[defibrillation]] | |||
| medication = | |||
| prognosis = Overall survival rate ≈10% (outside of hospital) 25% (in hospital); depends strongly on type and cause | |||
| frequency = 13 per 10,000 people per year (outside hospital in the US) | |||
| deaths = > 425,000 per year (US) | |||
}} | |||
'''Cardiac arrest''' is a sudden and unexpected loss of heart function, breathing, and consciousness. It occurs when the heart's electrical system, responsible for coordinating the heartbeat, malfunctions, leading to irregular or rapid heartbeats (arrhythmias). The most common cause of cardiac arrest is a specific type of arrhythmia called ventricular fibrillation (VF), in which the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles) quiver instead of pumping blood effectively. | '''Cardiac arrest''' is a sudden and unexpected loss of heart function, breathing, and consciousness. It occurs when the heart's electrical system, responsible for coordinating the heartbeat, malfunctions, leading to irregular or rapid heartbeats (arrhythmias). The most common cause of cardiac arrest is a specific type of arrhythmia called ventricular fibrillation (VF), in which the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles) quiver instead of pumping blood effectively. | ||
[[File:US Navy 040421-N-8090G-001 Hospital Corpsman 3rd Class Flowers administers chest compressions to a simulated cardiac arrest victim.jpg|thumb]] | [[File:US Navy 040421-N-8090G-001 Hospital Corpsman 3rd Class Flowers administers chest compressions to a simulated cardiac arrest victim.jpg|thumb]] | ||
[[File:Basic representation of cardiac conduction.gif|[[Cardiac conduction system|Conduction of the heart]]. Changes in this pattern can result from injury to the cardiac muscle and lead to non-conducted beats and ultimately cardiac arrest.|thumb|left]] | |||
[[File:Blausen 0543 ImplantableCardioverterDefibrillator.svg|Illustration of an [[implantable cardioverter-defibrillator]] (ICD)|thumb]] | |||
[[File:CPR training-04.jpg|CPR training on a mannequin|thumb]] | |||
[[File:Carotidian pulse and recovery position.jpg|Medical personnel checking the carotid pulse of a simulated patient|thumb]] | |||
== Medical emergency == | == Medical emergency == | ||
Cardiac arrest is a medical emergency and, if not treated immediately, can lead to death within minutes. It is important to differentiate cardiac arrest from a heart attack, although the two conditions can be related. A heart attack occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart muscle is blocked, while cardiac arrest is the result of an electrical problem causing the heart to stop pumping blood. | Cardiac arrest is a medical emergency and, if not treated immediately, can lead to death within minutes. It is important to differentiate cardiac arrest from a heart attack, although the two conditions can be related. A heart attack occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart muscle is blocked, while cardiac arrest is the result of an electrical problem causing the heart to stop pumping blood. | ||
| Line 47: | Line 72: | ||
In some cases, people with known heart problems or a high risk of sudden cardiac arrest may be advised to have an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) placed. This device can detect dangerous heart rhythms and deliver an electric shock to restore a normal heartbeat. | In some cases, people with known heart problems or a high risk of sudden cardiac arrest may be advised to have an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) placed. This device can detect dangerous heart rhythms and deliver an electric shock to restore a normal heartbeat. | ||
== Gallery == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Coronary Artery Disease.png|Normal vs blocked coronary artery | |||
File:Defibrillation Electrode Position.jpg|Demonstration of electrode pad placement for defibrillation | |||
File:Defibrillator-809447 1920.jpg|An automated external defibrillator stored in a visible orange mural support | |||
File:Heart left ventricular hypertrophy sa.jpg|Short axis view of the heart demonstrating wall thickening in left ventricular hypertrophy | |||
File:Left Ventricular Hypertrophy Unlabeled.jpg|EKG depiction of left ventricular hypertrophy | |||
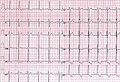
File:Ventricular fibrillation.png|EKG depiction of ventricular fibrillation (no organized rhythm) | |||
File:Ventricular fibrillation.png|Ventricular fibrillation | |||
</gallery> | |||
== Summary == | == Summary == | ||
Cardiac arrest is the sudden cessation of the heart's pumping action, possibly due to a heart attack, respiratory arrest, electrical shock, extreme cold, blood loss, drug overdose, or a severe allergic reaction. | Cardiac arrest is the sudden cessation of the heart's pumping action, possibly due to a heart attack, respiratory arrest, electrical shock, extreme cold, blood loss, drug overdose, or a severe allergic reaction. | ||
{{Medical condition classification and resources | |||
| DiseasesDB = 2095 | |||
| ICD11 = {{ICD11|MC82}} | |||
| ICD10 = {{ICD10|I46}} | |||
| ICD9 = {{ICD9|427.5}} | |||
| ICDO = | |||
| OMIM = | |||
| MedlinePlus = | |||
| eMedicineSubj = | |||
| eMedicineTopic = | |||
| MeshID = D006323 | |||
| SNOMED CT = 410429000 | |||
}} | |||
{{Circulatory system pathology}} | |||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cardiac Arrest}} | {{DEFAULTSORT:Cardiac Arrest}} | ||
[[Category:Cardiac arrhythmia]] | [[Category:Cardiac arrhythmia]] | ||
[[Category:Medical emergencies]] | [[Category:Medical emergencies]] | ||
[[Category:Causes of death]] | [[Category:Causes of death]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:40, 16 January 2025
| Cardiac arrest | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | Sudden cardiac death (SCD), cardiopulmonary arrest, circulatory arrest, sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Field | Cardiology, emergency medicine |
| Symptoms | Decreased level or total loss of consciousness, abnormal or no breathing, no pulse |
| Complications | If reversed, coma, persistent vegetative state, post-cardiac arrest syndrome; if not reversed, death |
| Onset | The risk of onset increases with age |
| Duration | |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Coronary artery disease, congenital heart defect, major blood loss, lack of oxygen, electrical injury, very low potassium, heart failure, myocardial infarction |
| Risks | |
| Diagnosis | Finding no pulse |
| Differential diagnosis | |
| Prevention | Not smoking, physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, healthy eating |
| Treatment | Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), defibrillation |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | Overall survival rate ≈10% (outside of hospital) 25% (in hospital); depends strongly on type and cause |
| Frequency | 13 per 10,000 people per year (outside hospital in the US) |
| Deaths | > 425,000 per year (US) |
Cardiac arrest is a sudden and unexpected loss of heart function, breathing, and consciousness. It occurs when the heart's electrical system, responsible for coordinating the heartbeat, malfunctions, leading to irregular or rapid heartbeats (arrhythmias). The most common cause of cardiac arrest is a specific type of arrhythmia called ventricular fibrillation (VF), in which the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles) quiver instead of pumping blood effectively.




Medical emergency[edit]
Cardiac arrest is a medical emergency and, if not treated immediately, can lead to death within minutes. It is important to differentiate cardiac arrest from a heart attack, although the two conditions can be related. A heart attack occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart muscle is blocked, while cardiac arrest is the result of an electrical problem causing the heart to stop pumping blood.
Causes[edit]
Cardiac arrest can be caused by various factors, including:
- Heart-related causes: coronary artery disease, enlarged heart (cardiomegaly), valvular heart disease, and congenital heart disease.
- Electrical problems: abnormalities in the heart's electrical system (such as long QT syndrome or Brugada syndrome) can lead to life-threatening arrhythmias.
- Trauma: accidents, injuries, or blunt force to the chest can cause cardiac arrest.
- Drug overdose: certain medications or drugs, especially when taken in excessive amounts, can lead to cardiac arrest. These include certain prescription medications, illegal drugs (such as cocaine), and even some over-the-counter medications.
- Drowning, choking, or asphyxiation: lack of oxygen due to these events can cause the heart to stop.
- Severe electrolyte imbalances: imbalances in minerals like potassium, magnesium, and calcium can affect the heart's electrical system and lead to cardiac arrest.
- Hypothermia: extremely low body temperature can cause the heart to stop.
Symptoms[edit]
Symptoms of cardiac arrest usually occur suddenly and without warning. They may include:
- Sudden loss of responsiveness (no response to tapping on shoulders)
- No normal breathing (gasping for air or not breathing at all)
- No pulse or heartbeat
Some individuals may experience dizziness, shortness of breath, chest pain, or palpitations before the onset of cardiac arrest. However, these symptoms are not always present.
Treatment[edit]
Immediate treatment for cardiac arrest is crucial for survival called basic life support or BLS. The primary steps are:
- Call for emergency medical help (such as 911 in the United States)
- Begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) to maintain blood flow and oxygen supply to the brain and other vital organs
- Use an automated external defibrillator (AED) if available to deliver an electric shock to the heart and attempt to restore a normal heart rhythm
Advanced life support[edit]
Emergency medical personnel may also provide advanced life support measures, including advanced airway management, intravenous medications, and manual defibrillation.
Prevention[edit]
Preventing cardiac arrest involves addressing and managing known risk factors, such as:
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help lower the risk of heart disease and cardiac arrest.
- Managing existing health conditions: monitoring and treating conditions such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes can reduce the risk of cardiac arrest.
- Regular check-ups: routine medical check-ups can help identify potential risk factors or conditions that could lead to cardiac arrest.
- Avoiding drug abuse: using drugs, especially stimulants like cocaine, can significantly increase the risk of cardiac arrest.
- Knowing your family history: if you have a family history of heart disease, sudden cardiac arrest, or other heart-related conditions, inform your doctor so they can assess your risk and recommend appropriate preventive measures.
In some cases, people with known heart problems or a high risk of sudden cardiac arrest may be advised to have an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) placed. This device can detect dangerous heart rhythms and deliver an electric shock to restore a normal heartbeat.
Gallery[edit]
-
Normal vs blocked coronary artery
-
Demonstration of electrode pad placement for defibrillation
-
An automated external defibrillator stored in a visible orange mural support
-
Short axis view of the heart demonstrating wall thickening in left ventricular hypertrophy
-
EKG depiction of left ventricular hypertrophy
-
EKG depiction of ventricular fibrillation (no organized rhythm)
-
Ventricular fibrillation
Summary[edit]
Cardiac arrest is the sudden cessation of the heart's pumping action, possibly due to a heart attack, respiratory arrest, electrical shock, extreme cold, blood loss, drug overdose, or a severe allergic reaction.
| Cardiovascular disease (heart) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|