Atrial flutter: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|A type of abnormal heart rhythm}} | {{Short description|A type of abnormal heart rhythm}} | ||
{{Use dmy dates|date=October 2023}} | {{Use dmy dates|date=October 2023}} | ||
{{Infobox medical condition (new) | |||
| name = Atrial flutter | |||
| synonyms = AFL | |||
| field = [[Cardiology]] | |||
| image = Atrial_flutter34.svg | |||
| caption = Atrial flutter with varying A-V conduction (5:1 and 4:1) | |||
| pronounce = | |||
| symptoms = [[Palpitations]], [[shortness of breath]], [[dizziness]], [[fatigue]], [[chest pain]] | |||
| complications = [[Stroke]], [[heart failure]], [[cardiomyopathy]] | |||
| onset = Sudden | |||
| duration = May be intermittent or persistent | |||
| types = Typical (counterclockwise or clockwise), Atypical (non-cavotricuspid isthmus dependent) | |||
| causes = [[Heart disease]], [[hypertension]], [[valvular heart disease]], [[pulmonary embolism]], [[hyperthyroidism]], post-cardiac surgery | |||
| risks = [[Advancing age]], [[hypertension]], [[diabetes]], [[coronary artery disease]], [[heart failure]], previous [[atrial fibrillation]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Electrocardiogram|ECG]], [[Holter monitor]], [[electrophysiology study]] | |||
| differential = [[Atrial fibrillation]], [[supraventricular tachycardia]], [[sinus tachycardia]] | |||
| prevention = Control of underlying conditions, [[anticoagulation]] to reduce stroke risk | |||
| treatment = [[Electrical cardioversion]], [[catheter ablation]], [[rate control]] | |||
| medication = [[Beta blockers]], [[calcium channel blockers]], [[amiodarone]], [[anticoagulants]] | |||
| prognosis = Good with treatment; risk of recurrence without ablation | |||
| frequency = Common; more prevalent in older adults and individuals with heart disease | |||
| deaths = Rare with appropriate management; stroke can be fatal | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Aflut.jpg|thumb|left|Atrial flutter with a two to one block. Note the P waves hiding in the T waves in leads V1 and V2]] | |||
[[Image:AtrialFlutter12.JPG|thumb|300px|right|Type I atrial flutter, counterclockwise rotation with 3:1 and 4:1 [[AV node|AV nodal]] block.]] | |||
'''Atrial flutter''' is a type of [[abnormal heart rhythm]] or [[arrhythmia]] that originates in the [[atria]] of the [[heart]]. It is characterized by a rapid, regular heartbeat and is often associated with [[atrial fibrillation]], another common type of arrhythmia. Atrial flutter can lead to significant symptoms and complications if not properly managed. | '''Atrial flutter''' is a type of [[abnormal heart rhythm]] or [[arrhythmia]] that originates in the [[atria]] of the [[heart]]. It is characterized by a rapid, regular heartbeat and is often associated with [[atrial fibrillation]], another common type of arrhythmia. Atrial flutter can lead to significant symptoms and complications if not properly managed. | ||
| Line 40: | Line 64: | ||
* [[Catheter ablation]] | * [[Catheter ablation]] | ||
== External links == | |||
{{Medical resources | |||
| ICD10 = {{ICD10|I48.3}}, {{ICD10|I48.4}}, {{ICD10|I48.9}} | |||
| ICD9 = {{ICD9|427.32}} | |||
| OMIM = | |||
| OMIM_mult = | |||
| MedlinePlus = 000184 | |||
| eMedicineSubj = med | |||
| eMedicineTopic = 185 | |||
| DiseasesDB = 1072 | |||
| MeshID = D001282 | |||
}} | |||
{{Circulatory system pathology}} | |||
{{stub}} | |||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Atrial Flutter}} | |||
[[Category:Cardiology]] | |||
[[Category:Cardiac arrhythmia]] | |||
[[Category:Heart diseases]] | |||
[[Category:Cardiac arrhythmia]] | [[Category:Cardiac arrhythmia]] | ||
Latest revision as of 03:39, 23 March 2025
A type of abnormal heart rhythm
| Atrial flutter | |
|---|---|
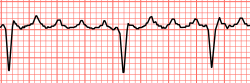
| |
| Synonyms | AFL |
| Pronounce | |
| Field | Cardiology |
| Symptoms | Palpitations, shortness of breath, dizziness, fatigue, chest pain |
| Complications | Stroke, heart failure, cardiomyopathy |
| Onset | Sudden |
| Duration | May be intermittent or persistent |
| Types | Typical (counterclockwise or clockwise), Atypical (non-cavotricuspid isthmus dependent) |
| Causes | Heart disease, hypertension, valvular heart disease, pulmonary embolism, hyperthyroidism, post-cardiac surgery |
| Risks | Advancing age, hypertension, diabetes, coronary artery disease, heart failure, previous atrial fibrillation |
| Diagnosis | ECG, Holter monitor, electrophysiology study |
| Differential diagnosis | Atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia, sinus tachycardia |
| Prevention | Control of underlying conditions, anticoagulation to reduce stroke risk |
| Treatment | Electrical cardioversion, catheter ablation, rate control |
| Medication | Beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, amiodarone, anticoagulants |
| Prognosis | Good with treatment; risk of recurrence without ablation |
| Frequency | Common; more prevalent in older adults and individuals with heart disease |
| Deaths | Rare with appropriate management; stroke can be fatal |


Atrial flutter is a type of abnormal heart rhythm or arrhythmia that originates in the atria of the heart. It is characterized by a rapid, regular heartbeat and is often associated with atrial fibrillation, another common type of arrhythmia. Atrial flutter can lead to significant symptoms and complications if not properly managed.
Pathophysiology[edit]
Atrial flutter occurs when there is a reentrant circuit within the right atrium. This circuit causes the atria to contract at a rapid rate, typically around 240 to 340 beats per minute. However, due to the refractory period of the atrioventricular node, not all of these impulses are conducted to the ventricles, resulting in a ventricular rate that is often slower, commonly around 150 beats per minute.
The reentrant circuit in atrial flutter is usually a macro-reentrant circuit, which means it involves a large loop of electrical activity. This is in contrast to atrial fibrillation, where the electrical activity is more chaotic and disorganized.
Symptoms[edit]
Patients with atrial flutter may experience a variety of symptoms, including:
In some cases, atrial flutter may be asymptomatic and only discovered during a routine electrocardiogram (ECG).
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of atrial flutter is typically made using an electrocardiogram (ECG). The ECG will show a characteristic "sawtooth" pattern of atrial activity, known as "F-waves," particularly in the inferior leads (II, III, and aVF). The ventricular rate is often regular and can be a multiple of the atrial rate, commonly 2:1 conduction.
Treatment[edit]
The treatment of atrial flutter aims to control the heart rate, restore normal rhythm, and prevent complications such as stroke. Treatment options include:
- Rate control: Medications such as beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers can be used to slow the ventricular rate.
- Rhythm control: Cardioversion can be performed to restore normal sinus rhythm. This can be done electrically or with medications such as ibutilide.
- Catheter ablation: This procedure involves destroying the reentrant circuit in the right atrium using radiofrequency energy, which can provide a long-term solution to atrial flutter.
- Anticoagulation: Patients with atrial flutter are at increased risk of thromboembolism, and anticoagulation therapy may be necessary to reduce the risk of stroke.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for patients with atrial flutter varies depending on the underlying cause and the presence of other medical conditions. With appropriate treatment, many patients can achieve good control of their symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.
Related pages[edit]
External links[edit]
| Cardiovascular disease (heart) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|


