COVID-19 pandemic in Asia: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
[[Category:COVID-19 pandemic by continent]] | [[Category:COVID-19 pandemic by continent]] | ||
[[Category:COVID-19 pandemic in Asia]] | [[Category:COVID-19 pandemic in Asia]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Cambodia COVID-19 by number of cases.svg|COVID-19 pandemic in Asia | |||
File:Empty hand sanitizer shelf in Cambodia.jpg|COVID-19 pandemic in Asia | |||
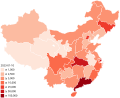
File:COVID-19 Outbreak Cases in Mainland China.svg|COVID-19 pandemic in Asia | |||
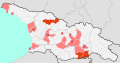
File:COVID-19 Outbreak Cases in Georgia per regional unit (municipality).svg|COVID-19 pandemic in Asia | |||
File:India COVID-19 cases density map.svg|COVID-19 pandemic in Asia | |||
File:COVID-19 pandemic cases in Indonesia map (Density).svg|COVID-19 pandemic in Asia | |||
File:2020 coronavirus cases in South Korea.svg|COVID-19 pandemic in Asia | |||
File:Sri Lanka COVID-19 map of confirmed cases.svg|COVID-19 pandemic in Asia | |||
File:COVID-19 outbreak Taiwan per capita cases map.svg|COVID-19 pandemic in Asia | |||
File:COVID-19 Pandemic Cases in Vietnam.svg|COVID-19 pandemic in Asia | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 00:52, 20 February 2025
COVID-19 Pandemic in Asia[edit]
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the Asian continent. This article provides a detailed overview of the pandemic's effects in various Asian countries.
China[edit]
China, where the outbreak originated, was the first country in Asia to be heavily affected by the pandemic. The Chinese government implemented strict measures to control the spread of the virus, including lockdowns, travel restrictions, and mass testing. The city of Wuhan, where the outbreak began, was placed under a strict quarantine for several months.
Mainland China has made significant progress in containing the virus, with a decline in new cases reported in recent months. However, the country continues to face challenges in preventing imported cases and managing asymptomatic carriers.
South Korea[edit]
South Korea quickly became one of the most affected countries in Asia after China. The government implemented an aggressive testing and contact tracing strategy, which helped to identify and isolate infected individuals. This approach, along with widespread public cooperation, played a crucial role in controlling the spread of the virus.
South Korea has been praised for its effective response to the pandemic, which has resulted in a relatively low number of cases and deaths compared to other countries. The country's experience in dealing with previous outbreaks, such as the MERS epidemic in 2015, also contributed to its preparedness and response.
Japan[edit]
Japan faced unique challenges in managing the pandemic due to its densely populated cities and cultural practices that involve close contact, such as bowing and crowded public transportation. The government declared a state of emergency in several prefectures, leading to the closure of schools, businesses, and public facilities.
Japan has experienced multiple waves of infections, with the number of cases fluctuating over time. The country has implemented various measures, including testing, contact tracing, and promoting hygiene practices, to mitigate the spread of the virus. However, concerns remain about the potential impact of the upcoming Tokyo Olympics on the pandemic situation.
India[edit]
India has been severely impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic, with a high number of cases and deaths reported. The country implemented a nationwide lockdown, which had significant economic and social consequences. The healthcare system faced immense pressure, with shortages of hospital beds, medical supplies, and healthcare workers.
India has been working to ramp up testing and vaccination efforts to control the spread of the virus. The government has also implemented various relief measures to support affected individuals and businesses. However, challenges such as vaccine distribution to remote areas and vaccine hesitancy among certain populations persist.
Other Asian Countries[edit]
Other Asian countries, such as Singapore, Malaysia, and Thailand, have also been affected by the pandemic. Each country has implemented its own set of measures to control the spread of the virus, including testing, contact tracing, and quarantine protocols.
Conclusion[edit]
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on Asia, affecting various aspects of life, including public health, economies, and social interactions. While some countries have made significant progress in controlling the spread of the virus, challenges remain in ensuring widespread vaccination, managing new variants, and addressing the long-term consequences of the pandemic.
-
COVID-19 pandemic in Asia
-
COVID-19 pandemic in Asia
-
COVID-19 pandemic in Asia
-
COVID-19 pandemic in Asia
-
COVID-19 pandemic in Asia
-
COVID-19 pandemic in Asia
-
COVID-19 pandemic in Asia
-
COVID-19 pandemic in Asia
-
COVID-19 pandemic in Asia
-
COVID-19 pandemic in Asia