Myoma: Difference between revisions
From WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | {{SI}} | ||
{{Infobox medical condition | {{Infobox medical condition | ||
| name | | name = Myoma | ||
| image | | image = [[File:Uterine_fibroids.jpg|250px]] | ||
| caption | | caption = Uterine fibroids (myomas) shown in an ultrasound image | ||
| field | | field = [[Gynecology]] | ||
| synonyms | | synonyms = [[Uterine fibroid]], [[leiomyoma]], [[fibromyoma]] | ||
| symptoms | | symptoms = [[Abnormal uterine bleeding]], [[pelvic pain]], [[frequent urination]], [[constipation]], [[infertility]] | ||
| complications | | complications = [[Anemia]], [[urinary tract infections]], [[pregnancy complications]] | ||
| onset | | onset = [[Reproductive age]] | ||
| duration | | duration = [[Chronic]] | ||
| causes | | causes = [[Genetic factors]], [[hormonal factors]] | ||
| risks | | risks = [[Obesity]], [[family history]], [[nulliparity]], [[early menarche]] | ||
| diagnosis | | diagnosis = [[Pelvic examination]], [[ultrasound]], [[MRI]] | ||
| differential | | differential = [[Adenomyosis]], [[endometrial cancer]], [[ovarian cysts]] | ||
| treatment | | treatment = [[Medication]], [[surgery]], [[uterine artery embolization]], [[MRI-guided focused ultrasound]] | ||
| medication | | medication = [[GnRH agonists]], [[oral contraceptives]], [[NSAIDs]] | ||
| frequency | | frequency = Common in women of reproductive age | ||
}} | }} | ||
[[File:Atlas and epitome of gynecology (1900) (14577565757).jpg|An illustrated plate from the "Atlas and Epitome of Gynecology" (1900), showcasing uterine anatomy|left|thumb]] | [[File:Uterine Fibroids.png|thumb|Uterine fibroids|left|thumb]] | ||
[[File:Uterine fibroid Wellcome L0061318.jpg|Fibroids|left|thumb]] | [[File:Atlas and epitome of gynecology (1900) (14577565757).jpg|left|thumb|An illustrated plate from the "Atlas and Epitome of Gynecology" (1900), showcasing uterine anatomy|left|thumb]] | ||
[[File:Uterine fibroid Wellcome L0062136.jpg|Myoma|left|thumb]] | [[File:Uterine fibroid Wellcome L0061318.jpg|left|thumb|Fibroids|left|thumb]] | ||
'''Myoma''' is a type of [[benign tumor]] that develops from [[muscle tissue]]. The most common type of myoma is the [[uterine fibroid]], which grows in the [[muscle tissue]] of the [[uterus]]. Other types of myomas can grow in other muscle tissues, such as the [[heart]] or [[esophagus]]. | [[File:Uterine fibroid Wellcome L0062136.jpg|left|thumb|Myoma|left|thumb]] | ||
'''Myoma''' is a type of [[benign tumor]] that develops from [[muscle tissue]]. The most common type of myoma is the [[uterine fibroid]], which grows in the [[muscle tissue]] of the [[uterus]]. Other types of myomas can grow in other muscle tissues, such as the [[heart]] or [[esophagus]]. | |||
==Types of Myoma== | ==Types of Myoma== | ||
There are several types of myomas, including: | There are several types of myomas, including: | ||
| Line 40: | Line 41: | ||
* '''[[Uterine artery embolization]]''': This is a minimally invasive procedure that can be used to shrink myomas by cutting off their blood supply. | * '''[[Uterine artery embolization]]''': This is a minimally invasive procedure that can be used to shrink myomas by cutting off their blood supply. | ||
== Gallery of Gynecological Illustrations == | == Gallery of Gynecological Illustrations == | ||
<gallery widths="300px" heights=" | <gallery widths="300px" heights="200px" mode="packed" caption="A curated collection of gynecological images from historical and medical sources."> | ||
File:Depiction of a lady who has Uterine Fibroids.png|Illustration of a woman with uterine fibroids. | File:Depiction of a lady who has Uterine Fibroids.png|Illustration of a woman with uterine fibroids. | ||
File:Fibroid locations.jpg|Medical illustration showing the locations of fibroids within the uterus. | File:Fibroid locations.jpg|Medical illustration showing the locations of fibroids within the uterus. | ||
| Line 58: | Line 59: | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
{{Medical resources | {{Medical resources | ||
| | | DiseasesDB = | ||
| | | ICD10 = {{ICD10|D|21|||}} | ||
| | | ICD9 = {{ICD9|}} | ||
| | | ICDO = M8895/3 | ||
| | | OMIM = | ||
| | | MedlinePlus = | ||
| | | eMedicineSubj = | ||
| | | eMedicineTopic = | ||
| | | MeshID = D009214 | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Soft tissue tumors and sarcomas}} | {{Soft tissue tumors and sarcomas}} | ||
Latest revision as of 16:02, 14 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Myoma | |
|---|---|
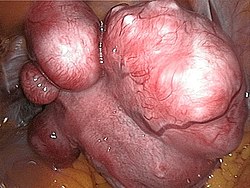
| |
| Synonyms | Uterine fibroid, leiomyoma, fibromyoma |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Abnormal uterine bleeding, pelvic pain, frequent urination, constipation, infertility |
| Complications | Anemia, urinary tract infections, pregnancy complications |
| Onset | Reproductive age |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic factors, hormonal factors |
| Risks | Obesity, family history, nulliparity, early menarche |
| Diagnosis | Pelvic examination, ultrasound, MRI |
| Differential diagnosis | Adenomyosis, endometrial cancer, ovarian cysts |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Medication, surgery, uterine artery embolization, MRI-guided focused ultrasound |
| Medication | GnRH agonists, oral contraceptives, NSAIDs |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | Common in women of reproductive age |
| Deaths | N/A |




Myoma is a type of benign tumor that develops from muscle tissue. The most common type of myoma is the uterine fibroid, which grows in the muscle tissue of the uterus. Other types of myomas can grow in other muscle tissues, such as the heart or esophagus.
Types of Myoma[edit]
There are several types of myomas, including:
- Uterine fibroids: These are the most common type of myoma. They grow in the muscle tissue of the uterus and can cause symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and infertility.
- Leiomyoma: This is a type of myoma that can grow in any smooth muscle tissue, including the uterus, stomach, and esophagus.
- Rhabdomyoma: This is a rare type of myoma that grows in skeletal muscle tissue. It is most commonly found in the heart.
Symptoms[edit]
The symptoms of a myoma can vary depending on its size and location. Some people with myomas have no symptoms, while others may experience:
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for myomas depends on the size and location of the myoma, as well as the patient's symptoms and overall health. Options may include:
- Medication: Certain medications can help to shrink myomas or relieve symptoms.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be needed to remove the myoma.
- Uterine artery embolization: This is a minimally invasive procedure that can be used to shrink myomas by cutting off their blood supply.
Gallery of Gynecological Illustrations[edit]
- A curated collection of gynecological images from historical and medical sources.
-
Illustration of a woman with uterine fibroids.
-
Medical illustration showing the locations of fibroids within the uterus.
-
Photograph of a giant uterine fibroid removed during surgery.
-
A large uterine fibroid, documented in the Wellcome Collection.
-
Histological image of leiomyomata in the uterus.
-
Surgical procedure of myomectomy for removing uterine fibroids.
-
Illustration from the "Pathology and Treatment of Diseases of Women" (1912), detailing fibroid pathology.
-
Illustration comparing the uterus before and after a myomectomy procedure.
See Also[edit]
External links[edit]








