Leukemia: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
[[Category:Blood disorders]] | [[Category:Blood disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Blood cells]] | [[Category:Blood cells]] | ||
==Leukemia== | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:ALL-AML.jpg|ALL-AML | |||
File:Acute leukemia 1.webm|Acute leukemia | |||
File:Symptoms of leukemia.png|Symptoms of leukemia | |||
File:Symptoms of leukemia.png#List|Symptoms of leukemia list | |||
File:Leukemia- SAG.jpg|Leukemia SAG | |||
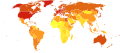
File:Leukaemia world map-Deaths per million persons-WHO2012.svg|Leukemia world map | |||
File:Rudolf Virchow.jpg|Rudolf Virchow | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 00:41, 20 February 2025
| Leukemia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | Leukaemia |
| Pronounce | |
| Field | Hematology and oncology |
| Symptoms | Bleeding, bruising, fatigue, fever, increased risk of infections |
| Complications | |
| Onset | All ages, most common in 60s and 70s. It is the most common malignant cancer in children, but the cure rates are also higher for them. |
| Duration | |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Inherited and environmental factors |
| Risks | Smoking, family history, ionizing radiation, some chemicals such as trichloroethylene, prior chemotherapy, Down syndrome. |
| Diagnosis | Blood tests, bone marrow biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, bone marrow transplant, supportive care |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | Five-year survival rate 67% (U.S.) |
| Frequency | 2.3 million (2015) |
| Deaths | 353,500 (2015) |





Leukemia or leukaemia is a cancer of white blood cells and bone marrow. When a person has leukemia, the body creates too many white blood cells (leukocytes).
There are many kinds of leukemia. Leukemia is part of a bigger group of diseases, the blood cancers (hematological neoplasms). Without treatment, leukemia may lead to death within weeks, months, or years. The life of the person depends upon the type of leukemia.
In 2000, about 256,000 children and adults around the world developed some form of leukemia, and 209,000 died from it.<ref>
WHO Disease and injury country estimates(link). {{{website}}}.
</ref> About 90% of all leukemias are seen in adults.<ref>
SEER Stat Fact Sheets: Leukemia(link). {{{website}}}. National Cancer Institute.
</ref>
Four major types of leukemia
Leukemia can be either acute or chronic. Acute leukemia usually grows quickly. Chronic leukemia grows slowly.
Leukemia can also affect two different types of white blood cells. These are lymphoid cells and young granulocyte cells (which are called myelocytes).
For this reason, all of the different forms of leukemia are divided into four main types:
- Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) is the most common type of leukemia. It is common in young children but can also be seen in old people.
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is usually seen in people over the age of 55. Children almost never have this.
- Acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) is seen more commonly in adults than in children.
- Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) happens mostly in adults.
Causes and risk factors
The causes of most types of leukemia are not known. In general, all cancers have a breakdown in the normal way cell division is controlled. Most likely, the different kinds of leukemias have different causes. The known causes account for relatively few cases.<ref name="pmid12163333">Ross J.A. et al,
Diet and risk of leukemia in the Iowa Women's Health Study, Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev., 2002, Vol. 11(Issue: 8), pp. 777–81, PMID: 12163333, Full text,</ref> Most of the causes are outside our control.
Researchers believe that some things may influence whether a person develops leukemia:
- Exposure to Ionizing radiation
- Exposure to certain chemicals, for example benzene.
- Certain viruses
- Treatment with certain drugs that influence how cells develop; e.g. treatment of a tumor; Chemotherapy
- Certain genetic factors.
Viruses that are believed to cause leukemia include:
Fanconi anemia is also a risk factor for developing acute myelogenous leukemia.
Treatment
Most cases of leukemia are treated with many drugs, which are usually combined into a chemotherapy program. In some cases, radiation therapies or bone marrow transplants are done.
References
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
|
|
|
| Leukaemias, lymphomas and related disease | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Myeloid-related hematological malignancy | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Leukemia
-
ALL-AML
-
Acute leukemia
-
Symptoms of leukemia
-
Symptoms of leukemia list
-
Leukemia SAG
-
Leukemia world map
-
Rudolf Virchow