Nephrocalcinosis: Difference between revisions
No edit summary Tag: visualeditor-wikitext |
CSV import |
||
| Line 79: | Line 79: | ||
{{rarediseases}} | {{rarediseases}} | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
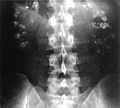
File:Nephrocalcinosis.jpg|Nephrocalcinosis | |||
File:Calcinosis_kidney.jpg|Calcinosis in the kidney | |||
File:Medullary_nephrocalcinoses.jpg|Medullary nephrocalcinosis | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 02:09, 18 February 2025
Other Names
Hypercalcemic nephropathy
Nephrocalcinosis is a disorder that occurs when too much calcium is deposited in the kidneys. It commonly occurs in premature infants. Deposition of calcium in the renal parenchyma, resulting from high levels of calcium in the blood and/or urine.
Cause
Nephrocalcinosis may be caused by a variety of things, including underlying disorders or conditions, medications or supplements, and infections. Causes may include:
- Primary hyperparathyroidism
- Distal renal tubular acidosis (RTA)
- hypervitaminosis-D states (very levels of vitamin D)
- Other cause of hypercalcemia (increased calcium in the blood)
- Sarcoidosis
- Phosphate supplementation
- Medullary sponge kidney
- Osteoporosis due to immobilization, menopause, aging, or steroids
- Primary (familial) hyperoxaluria, or secondary hyperoxaluria
- Chronic disorders such as Bartter syndrome, primary hyperaldosteronism, Liddle syndrome, and 11-beta hydroxylase deficiency
- Autosomal dominant hypophosphatemic rickets and X-linked hypophosphatemic conditions
- Premature birth
- Other causes may include the use of certain medications such as acetazolamide; tuberculosis of the kidney; and infections related to AIDS.
Inheritance
Nephrocalcinosis may have a variety of causes, including underlying disorders, certain medications and supplements, and infections. Nephrocalcinosis itself is not inherited. However, the condition causing nephrocalcinosis in an individual may be inherited. Some inherited conditions that may be associated with nephrocalcinosis include:
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1)
- Familial distal renal tubular acidosis
- Chronic granulomatous disease
- Primary hyperoxaluria
- Bartter syndrome
- Alport syndrome
- Primary hyperaldosteronism
- Liddle syndrome
- 11-beta hydroxylase deficiency
- Autosomal dominant hypophosphatemic rickets and X-linked hypophosphatemic conditions
- Williams syndrome
- Beta thalassemia
Signs and symptoms
Most of the time, there are no early symptoms of nephrocalcinosis beyond those of the condition causing the problem. People who also have kidney stones may have:
- Blood in the urine
- Fever and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
- Severe pain in the belly area, sides of the back (flank), groin, or testicles
- Later symptoms related to nephrocalcinosis may be associated with long-term (chronic) kidney failure.
Diagnosis
Nephrocalcinosis may be discovered when symptoms of renal insufficiency, kidney failure, obstructive uropathy, or urinary tract stones develop. Imaging tests can help diagnose this condition. Tests that may be done include:
- Abdominal CT scan
- Ultrasound of the kidney
Other tests that may be done to diagnose and determine the severity of associated disorders include:
- Blood tests to check levels of calcium, phosphate, uric acid, and parathyroid hormone
- Urinalysis to see crystals and check for red blood cells
- 24-hour urine collection to measure acidity and levels of calcium, sodium, uric acid, oxalate, and citrate
Treatment
Treatment of nephrocalcinosis includes treating the underlying condition causing nephrocalcinosis, if it is known. The goal of treatment is to reduce symptoms and prevent more calcium from being deposited in the kidneys. Measures are usually taken to reduce abnormal levels of calcium, phosphate, and oxalate in the blood. Medications that cause calcium loss are typically stopped.
Treatment of hypercalcemia (increased calcium levels in the blood) and hypercalcemic nephropathy typically includes adequate hydration by isotonic sodium chloride (normal saline) solution to reverse hypercalcemia and protect the kidneys. Treatment of macroscopic nephrocalcinosis (calcium deposition that is visible without magnification) may include thiazide diuretics and dietary salt restriction, potassium and magnesium supplementation, and citrate supplementation in idiopathic hypercalciuria (of unknown cause) and in distal renal tubular acidosis. Lessening of nephrocalcinosis may occur over time, but in many cases, such as when it results from primary hyperoxaluria or distal renal tubular acidosis, nephrocalcinosis is largely irreversible. Therefore, early detection and treatment are important.
Individuals interested in learning about treatment options for themselves should speak with their health care provider or a nephrologist.
Prognosis
What to expect depends on the complications and cause of the disorder. Proper treatment may help prevent further deposits in the kidneys. In most cases, there is no way to remove deposits that have already formed. Many deposits of calcium in the kidneys do NOT always mean severe damage to the kidneys.
Possible Complications Complications may include:
- Acute kidney failure
- Long-term (chronic) kidney failure
- Kidney stones
- Obstructive uropathy (acute or chronic, unilateral or bilateral)
NIH genetic and rare disease info
Nephrocalcinosis is a rare disease.
| Rare and genetic diseases | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Rare diseases - Nephrocalcinosis
|